Air temperature result
The Air Temperature result shows the temperature of the air surrounding all the components in the model enclosure.
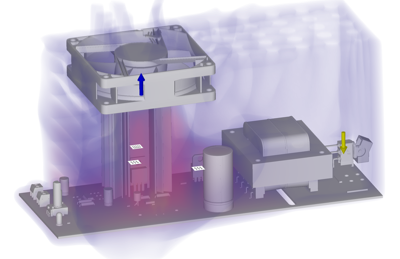
Figure 1 showing the air temperature distribution in a power supply enclosure with three active voltage regulators, cooled by two heat sinks and a fan.
Things to look for
When viewing the Air temperature result, watch for the following:
- Hot spots, showing where heat needs to be removed
- Areas where hot air is accumulating indicating that thermal management needs optimizing
- The air temperature distribution along the fluid flow path to ensure that hot air is not flowing over temperature sensitive components.
Using this result
The Air temperature result uses a range of colors to indicate the region of lowest temperature in blue, to the region of highest temperature in yellow. The maximum temperature that the air reaches is indicated on the legend.
Strive to reduce the air temperature around heat sensitive components below their maximum temperature thresholds
Consider the fluid flow path and the position of thermal management components so air is drawn away from heat sensitive components
Move the Range of interest sliders on the left of the legend bar, and the Threshold sliders on the right to narrow your focus, and make the color contrast more visible.
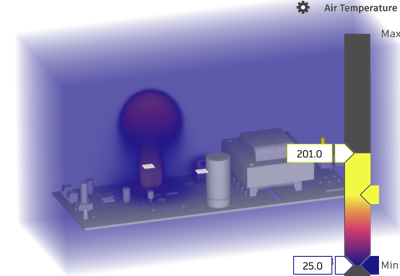
*Image showing hot air accumulating around a 50 W voltage regulator with no heat sink or fan.
Hide a component on the board, for example if it's masking a component of greater interest, by toggling its
 visiblity in the Model components folder.
visiblity in the Model components folder.
Image showing the air temperature around the heat sinks, with the actual heat sinks hidden so the regulators are visible.
Use Surface probes, Point probes, and Cutting planes to inspect the result carefully.
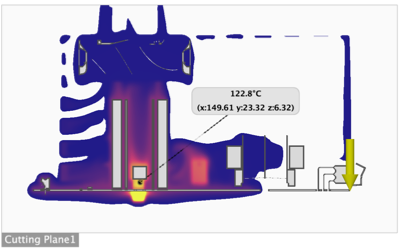
Image with a cutting plane showing the air temperature at the regulators, and a point probe showing the temperature at a given location.
Next Steps
To address the potential issues highlighted by the Air Temperature result, you could:
- Switch board components for different ones that can tolerate higher temperatures
- Select a component that meets the performance requirements but requires a lower internal heat load
- Change the dimensions or material used in the heat sink
- Add a fan, if there isn't one
- Change the location of the fan to move the fluid flow path away from heat sensitive components
- Reverse the blowing direction of the fan.
