In this section, use the Square, Skin, and Align tools to create the basic shape of the shower gel bottle.
Build the front half of the bottle, which you later mirror to complete the design. Create a smooth connection between both halves by controlling the implied tangent continuity across the center line.
When you create the shoulder surface, blend it smoothly to the main bottle surface using tangent continuity.
Open the tutorial file
The tutorial file has curves for building the shower gel bottle.
- Choose File > Open
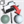 to open the file browser.
to open the file browser. - In the file browser, locate the CourseWare folder and set it as the Current Project.
- Open the file called showergel.wire, located in the wire folder in the CourseWare project.
For information on how to open a file, see Open the tutorial file.
- A dialog box appears, asking if you want to delete all objects, shaders, views, and actions. Click Yes.
- If your values for construction tolerances differ from the values in the showergel.wire file, you are presented with a dialog box.
- Click Accept New Settings to use the construction tolerances in showergel.wire.
The file opens.
The main bottle curves are visible and placed on a layer named Curves.
Other curves are on layers that are not currently visible; you use these curves later in the tutorial.
Set the construction tolerances
Before you start to create your model, choose the construction tolerances you want to work to.
- Choose Preferences > Construction Options
 .
. 
The Construction Preset is set to User Defined. While this setting is suitable for rapid concept development, a more accurate setting is needed for data transfer to a CAD or Rapid Prototyping system.
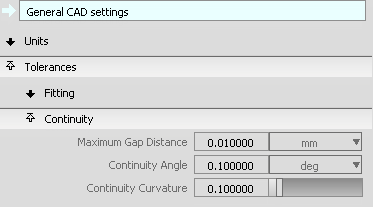
- In the option window, choose General CAD Settings.
To see what tolerances you are working to, open the tolerances section of the Construction Options window.
 Tip:
Tip:For future projects, you can choose settings that match the CAD system you are exporting data to.
- Close the Construction Options window.
Create the main bottle surface
Start by creating the main bottle shape using a Square surface.
- Maximize the Perspective view.
- Check that the Bottle layer tab displays as yellow, indicating the new surfaces you create are assigned to it. If not, click the layer tab to make it active.

- Choose Surfaces > Boundary Surfaces > Square

 to open the option window.
to open the option window. 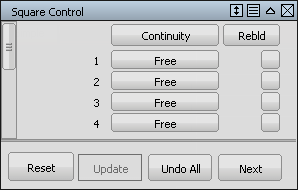
-
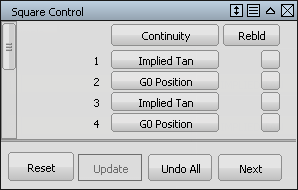
In the Square option window, the four boundaries of the square are listed.
For boundaries, 2 and 4 change the continuity option to G0 Position. This continuity ensures that the square surface accurately matches the curves.
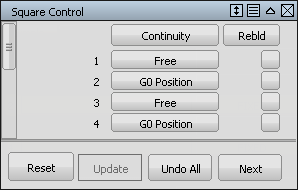
For boundaries 1 and 3, change the Continuity option to Implied Tangent. The Implied Tangent option ensures that the surfaces align smoothly across the center line.
-
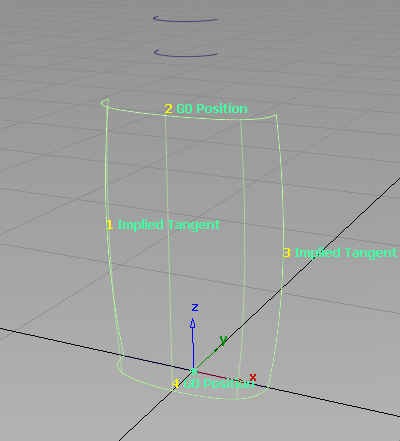
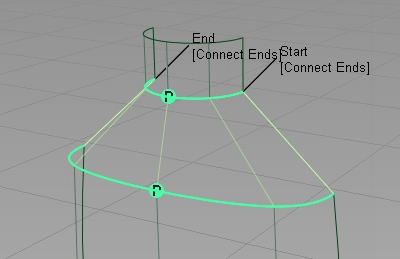
You are prompted to select the four boundary curves. Click the curves in the order shown.

When you select the fourth curve, the square surface is created.
Create the neck surface
- Adjust the view to see the curves for the neck of the bottle.

- Choose Surfaces > Skin Surfaces > Skin
 and when prompted, select the two neck curves to create the neck surface.
and when prompted, select the two neck curves to create the neck surface. 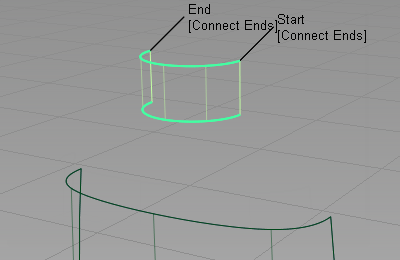
- Now that you have built the main surfaces, turn off the Curves layer, leaving only the surfaces visible on the screen.
- Choose Pick Nothing to deselect all surfaces.
Create the shoulder surface
Blend the shoulder surface smoothly from the main body surface.
First create the shoulder as a simple skin surface from the body to the neck. Then create continuity between the shoulder and body, using the Align tool.
It is useful to understand how the Align tool creates the desired continuity. Observe how the CVs and Hulls change as you apply the Align tool.
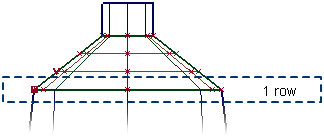
- Positional Continuity
-
One row of CVs is aligned to the other surface. Positional is the default continuity when you create the skin surface.
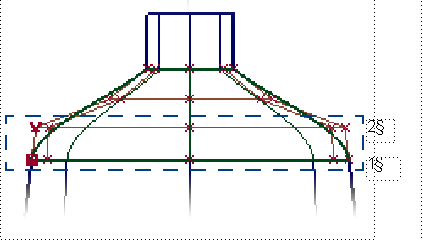
- Tangent Continuity
-
Two rows of CVs are aligned to the other surface.
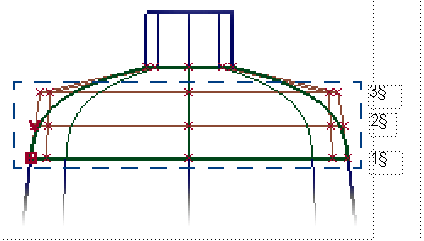
- Curvature Continuity
-
Three rows of CVs are aligned to the other surface.
Create the shoulder surface
First, create the shoulder surface with positional continuity.
- Choose the Surfaces > Skin
 tool.
tool. - When prompted, select the edges of the body and neck surfaces to create the shoulder skin surface.
Align the shoulder surface
Now use the Align tool to modify the shoulder surface, making it Tangent to the body surface.
First, delete the Construction History of the shoulder skin, to allow it to be modified.
- With the shoulder surface still selected, choose Delete > Delete Construction History
 and answer Yes when prompted.
and answer Yes when prompted. - Select the surface and then turn on the display of CVs by clicking the Cv/Hull check box on the Control Panel. Displaying CVs makes it easier to see the results of the Align tool.
- In the Control Panel, change the V degree to 3 and click Accept.
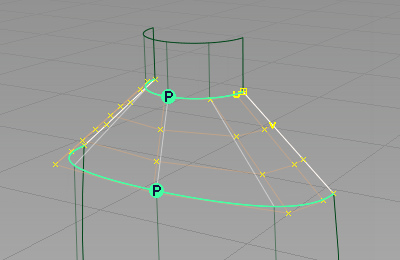
- Choose Object Edit > Align > Align

 to open the option window.
to open the option window. - Set Continuity to G1 Tangent.
You are prompted to select the boundary of the surface to be aligned (the input). This surface is the skin surface you created for the shoulder.
- Move the cursor to the junction of the bottle and shoulder surfaces. Click the edge of the surface and select the skin surface from the pick chooser.
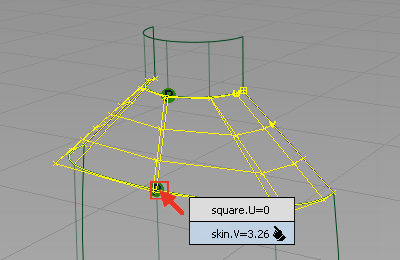
The selected edge is highlighted and labeled as “Input”.
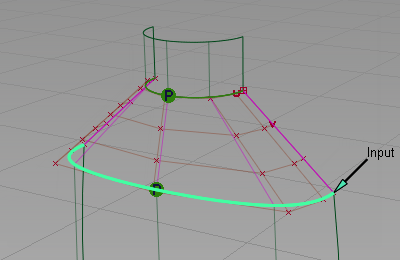
You are prompted to select the object to align to (the master).
- Click on the boundary between the two surfaces again to select the edge of the body.
The top edge of the body surface is selected automatically.
The CVs of the shoulder surface are modified to align the shoulder to the bottle surface with tangent continuity, as indicated by the T on the green indicator.
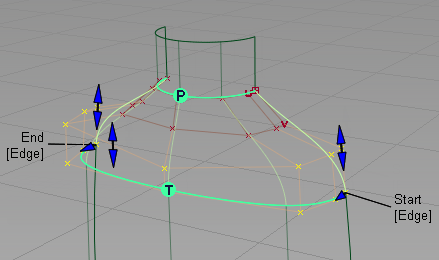
- Turn on Tangent Balance. Tangent Balance adjusts the hull shape of the input surface to match that of the master.
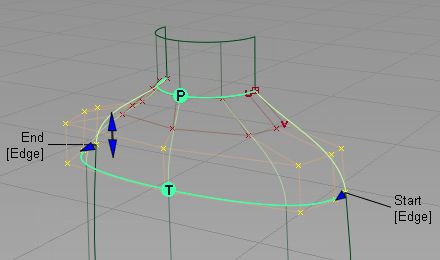
- Scroll to the bottom of the option window and turn off Continuity Check to remove the continuity indicator.
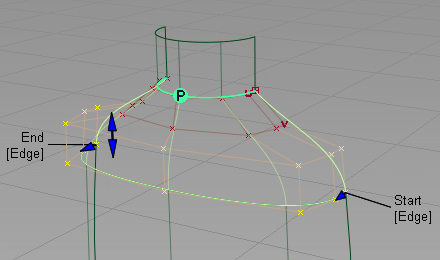
Now modify the character of the shoulder blend by moving and scaling the CVs and Hulls.
- Use the F9 hotkey to show the four modeling windows.
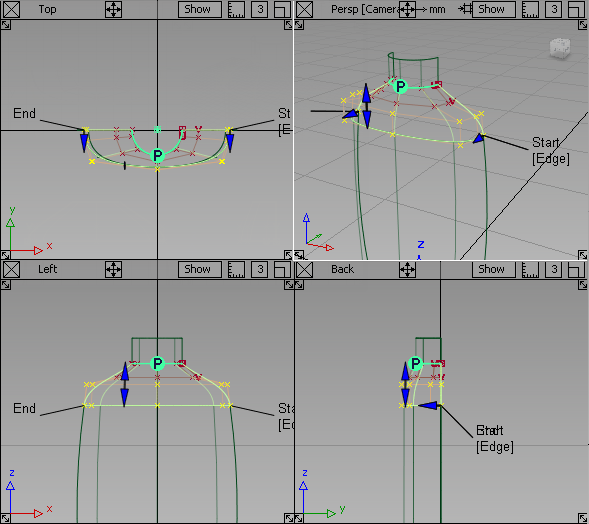
- Choose Pick > Nothing
 to deselect the surface.
to deselect the surface. - Choose Pick > Point Types > Hull
 .
. -
In the Back window, select the hull of the second row of CVs from the top by clicking the red hull line.
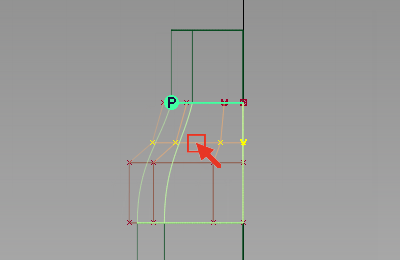
- Choose Transform > Non-p Scale
 and drag with the
and drag with the  to create a smooth shoulder shape. Note:
to create a smooth shoulder shape. Note:The pivot point for the CVs defaults to the origin, so the CVs scale correctly.
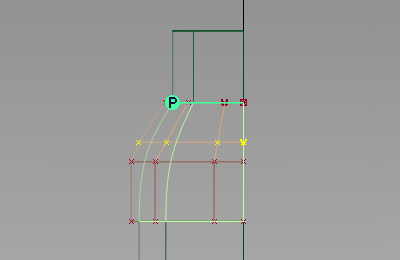
- In the Left window, drag with the
 to refine the shoulder shape.
to refine the shoulder shape. 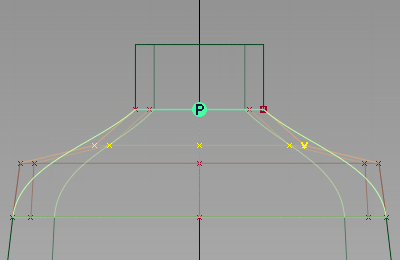

- Turn off the CVs and hulls, in the Control Panel.
- Choose Pick > Nothing
 to deselect the CVs.
to deselect the CVs. - Use diagnostic shading to evaluate the result.
 Tip:
Tip:Set the Continuity option to Curvature in the Align tool to adjust the third row of CVs and get an even smoother transition.
Save your work
Now you save the scene as a new file.
- Save your work in the wire folder of the Lessons project.
- Name your file myshowergel.wire.
For information on creating the Lessons project, or saving your work, see Save your work.