통합 단계 5: 경로를 계산하고 따르도록 캐릭터 설정
경로를 따르는 것은 경로를 찾기 위해 단순히 A* 계산을 실행하는 것보다 훨씬 더 복잡한 문제입니다. 경로 따르기는 동적이고 때로는 제한된 움직임 및 스티어링 시스템과의 상호 작용을 암시합니다. 동적 이벤트는 경로를 변경해야 할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 캐릭터 주변에 있는 NavData가 변경되는 경우입니다. 움직이는 장애물 및 다른 캐릭터 등과의 충돌을 피하려면 동적 회피 시스템이 필요합니다.
이 통합 단계에서는 Gameware Navigation의 경로 따르기 레이어에서 제공하는 도구를 사용하여 캐릭터가 경로를 찾고 따르도록 합니다.
봇의 주기(lifecycle)
경로 따르기 레이어의 주요 컴포넌트는 Bot 클래스입니다. 일반적으로 Gameware Navigation 경로 찾기 및 경로 따르기 시스템을 사용하려는 각 게임 캐릭터를 나타내는 클래스에 Bot 클래스의 인스턴스를 할당합니다. (플레이어 캐릭터와 같은 다른 종류의 캐릭터는 일반적으로 CylinderObstacles로 나타납니다. 동적 장애물 및 TagVolume 사용을(를) 참조하십시오.) Bot은 경로 찾기 쿼리를 사용하여 지정한 대상에 대한 경로를 계산하고 각 프레임에서 원하는 속도를 계산하여 해당 경로를 "따릅니다".
Bot 주기는 적어도 3번, 즉 초기화, 각 프레임에서 업데이트 및 파괴 시 해당 게임 엔티티에서 직접 상호 작용을 암시합니다.
계속 통합하다보면 이러한 동일한 철학이 다른 클래스(예: 동적 장애물, TagVolumes 및 관심 지점)에 사용되는 것을 알게 됩니다.
초기화
- BotInitConfig 오브젝트의 인스턴스를 만들고 원하는 대로 해당 클래스 구성원을 설정하며 Bot::Init()를 호출할 때 전달합니다. 최소한 캐릭터가 경로 계획 및 경로 따르기에 사용하는 NavData를 포함하는 Database에 대한 점으로 BotInitConfig::m_database 구성원을 설정해야 합니다.
- 봇이 경로를 계산할 수 있도록 Bot::ComputeNewPathToDestination() 메서드를 사용하여 경로 찾기 쿼리의 인스턴스를 만듭니다. 이것은 다음 예에 나와 있습니다. ProfileID로 AStarQuery를 인스턴스화하기 위해 Bot::ComputeNewPathToDestination() 메서드가 이전에 실행 중인 쿼리를 모두 취소한 다음 현재 봇의 NavigationProfile을 호출합니다. 그런 다음 Bot::InitAStarQueryForBot() 메서드가 BotConfig로 쿼리를 설정하기 위해 호출됩니다. 마지막으로 Bot::ComputeNewPathAsync() 메서드가 비동기적으로 쿼리를 계산하고 봇의 경로를 제대로 변경하기 위해 호출됩니다.
주:자체적으로 AStarQuery를 초기화한 다음 Bot::ComputeNewPathAsync() 메서드를 호출할 수 있습니다. 그러나 Bot::ComputeNewPathAsync() 메서드를 호출하기 전에 Bot::IsComputingNewPath() 메서드를 사용하여 계산 상태를 확인해야 합니다.
- 경로를 계획하고 다른 봇과의 충돌을 피할 수 있도록 Bot::AddToDatabase()를 호출하여 Database에서 Bot을 활성화합니다. 이 방법은 일반적으로 게임 캐릭터를 생성할 때 수행됩니다.
업데이트
각 프레임에서 게임 캐릭터는 필요에 따라 새 경로 계산을 시작하고 Bot의 현재 상태를 업데이트하고 경로 따르기 시스템의 결과를 해석 및 적용하기 위해 Bot과 상호 작용합니다.
- Bot이 경로를 따르는 동안 캐릭터 클래스는 m_navBot->GetBotOutput().m_outputVelocity를 호출하여 각 프레임에서 제안된 속도를 선택해야 합니다. 애니메이션 및 스티어링 시스템과 호환되도록 필요한 경우 원하는 궤적을 수정합니다. 최종 결과를 게임의 캐릭터에 적용해야 합니다.
- 언제든지 캐릭터의 위치 또는 속도는 변경되며 그에 따라 Bot도 업데이트해야 합니다. Bot 클래스의 구성원 함수를 사용하면 봇 위치 및 속도를 업데이트할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 봇 위치에 액세스하려면 Bot::SetPosition()을 호출하면 됩니다.
- 또한 여러 가지 다른 방법으로 경로 따르기 시스템의 현재 상태를 읽고 응답해야 할 수 있습니다. 아래 예에는 대상에 도달하기 위한 간단한 테스트가 들어 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 경로 따르기 모니터링을(를) 참고하십시오.
파괴
- Bot::RemoveFromDatabase() 메서드를 호출하여 World에 있는 다른 봇의 고려 대상에서 제거합니다.
- 게임에서 Bot 오브젝트에 저장한 모든 포인터를 KY_NULL로 설정합니다. 이렇게 하면 참조 계산 메커니즘이 감소하여 남은 참조가 없는 경우 오브젝트가 투명하게 파괴됩니다.
예
다음은 게임 캐릭터 클래스 MyGameEntity에 의해 Bot 클래스가 사용되는 비교적 간단한 예를 보여줍니다. 생성한 다음에는 캐릭터가 초기 위치 및 지정된 대상 사이에서 앞뒤로 경로를 계획하고 따릅니다.
[Tutorial_FirstIntegration.cpp의 코드]
#include "gwnavruntime/world/bot.h"
...
class MyGameEntity
{
public:
MyGameEntity()
: m_startPosition(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)
, m_destinationPosition(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)
, m_position(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)
, m_velocity(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)
, m_navBot(KY_NULL)
{}
void Initialize(Kaim::World* world, const Kaim::Vec3f& startPosition, const Kaim::Vec3f& destination);
void Destroy();
void Update(KyFloat32 simulationStepsInSeconds);
bool HasArrived();
public:
Kaim::Vec3f m_startPosition;
Kaim::Vec3f m_destinationPosition;
Kaim::Vec3f m_position;
Kaim::Vec3f m_velocity;
Kaim::Ptr<Kaim::Bot> m_navBot;
};
void MyGameEntity::Initialize(Kaim::World* world, const Kaim::Vec3f& startPosition, const Kaim::Vec3f& destination)
{
m_position = startPosition;
m_startPosition = startPosition;
m_destinationPosition = destination;
m_navBot = *KY_NEW Kaim::Bot;
// We initialize the Bot at our desired start position
Kaim::BotInitConfig botInitConfig;
botInitConfig.m_database = world->GetDatabase(0);
botInitConfig.m_startPosition = m_position;
m_navBot->Init(botInitConfig);
...
// We add the Bot to our Database.
m_navBot->AddToDatabase();
...
}
void MyGameEntity::Destroy()
{
m_navBot->RemoveFromDatabase();
m_navBot = KY_NULL;
}
void MyGameEntity::Update(KyFloat32 simulationStepsInSeconds)
{
if (m_navBot->GetFollowedPath() == KY_NULL && m_navBot->IsComputingNewPath() == false) // We need to compute a Path!
{
// Here, we ask the Bot to launch a path computation.
// We should test the return code of this function, but as this tutorial is pretty simple, we are sure it cannot fail:
// - The AStarQuery is set from the default NavigationProfile.
// - We do not ask for a path computation while another path computation is in process.
// Note that Kaim::Bot::ComputeNewPathToDestination() will run the query during the Kaim::World::Update().
m_navBot->ComputeNewPathToDestination(m_destinationPosition);
}
// If we are arrived...
if (HasArrived())
{
m_velocity = Kaim::Vec3f::Zero();
// Clear the followed path.
m_navBot->ClearFollowedPath();
// Swap the positions.
Kaim::Vec3f swap = m_destinationPosition;
m_destinationPosition = m_startPosition;
m_startPosition = swap;
// Restart a move.
m_navBot->ComputeNewPathToDestination(m_destinationPosition);
}
// Retrieve the velocity suggested by the path following system, if available.
m_velocity = m_navBot->GetBotOutput().m_outputVelocity;
// Perform a simple integration.
m_position += m_velocity*simulationStepsInSeconds;
// Inform our Bot that the entity has moved.
// Note that the update will be effective after next World::Update() call
m_navBot->SetPosition(m_position);
m_navBot->SetVelocityAndFrontDirection(m_velocity);
}
bool MyGameEntity::HasArrived()
{
KyFloat32 arrivalPrecisionRadius = m_navBot->GetConfig().m_pathProgressConfig.m_checkPointRadius;
if (m_navBot->HasReachedPosition(m_destinationPosition, arrivalPrecisionRadius))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
class MyGameLevel
{
public:
...
void Update(float deltaTimeInSeconds);
...
protected:
...
MyGameEntity m_entity;
};
bool MyGameLevel::Initialize(Kaim::World* world)
{
... Do all other initializations
// Initialize my entity
m_entity.Initialize(world, Kaim::Vec3f(-11.5963f,1.06987f,10.4563f), Kaim::Vec3f(-16.636f,-26.7078f,8.10107f));
...
return true;
}
...
void MyGameLevel::Update(float deltaTimeInSeconds)
{
...
m_entity.Update(deltaTimeInSeconds);
}
void MyGameLevel::Destroy()
{
// Destroy my entity.
m_entity.Destroy();
... Do all other destructions and releases.
}
위의 코드는 대부분 경로 따르기 시스템의 기본 동작을 사용합니다. 그러나 경로 따르기 시스템은 매우 구성이 용이합니다. 여러 가지 방법으로 사용자 정의하고 캐릭터가 경로를 따를 때 발생하는 이벤트에 반응하고 필요한 경우 관련된 클래스의 고유한 구현을 작성하여 게임의 요구 사항에 맞도록 조작할 수 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 경로 찾기 및 경로 따르기을(를) 참조하십시오.
테스트
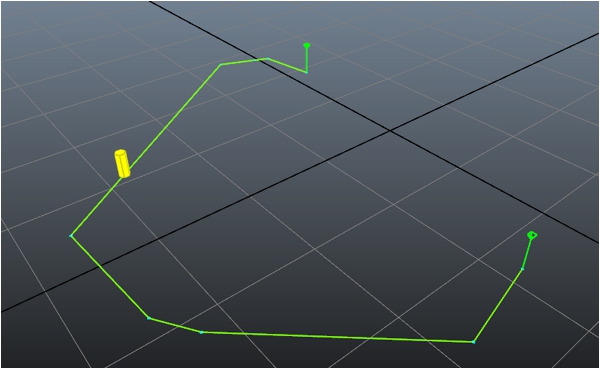
Navigation Lab을 게임에 연결한 다음 AstarQuery에 설정된 시작점과 끝점 사이에서 앞뒤로 이동하는, 캐릭터를 나타내는 노란색 원통이 표시되어야 합니다. 예를 들면 다음과 같습니다.
- 캐릭터를 지면에 계속 클램프되도록 하는 물리학이 게임에 아직 없는 경우 캐릭터가 지세를 통과해 떨어지거나 떠다닐 수 있습니다.
- NavMesh를 통한 경로가 미세 조정되는 방식에서 약간 차이가 있기 때문에 경로는 양방향에서 정확하게 동일할 수 없습니다.