Undercuts — Select this option to enable side mill tools to machine undercuts. When Undercuts is enabled, the Machining Side tab is available.
The Undercuts option is unavailable when Interleave spiral paths is enabled.
Continuous spiral — Enable this option to stop the tool lifting from the surface when machining.
Enable Continuous spiral to have a toolpath that stays in constant contact with a surface, reducing the chance of leaving any dwell or witness marks on the surface caused by regular retract and approaches to the surface.
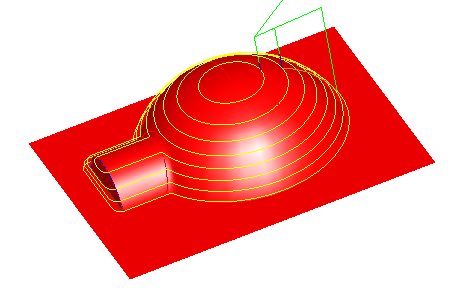
The standard Z level finishing toolpaths creates paths with a constant Z height as shown below. The tool either retracts or feeds along the surface between Z levels.
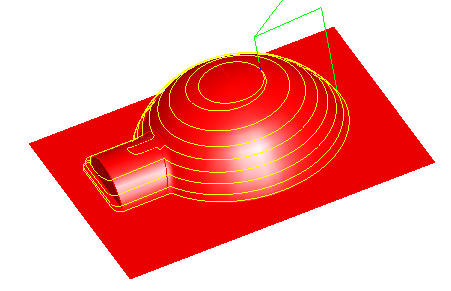
With Continuous spiral enabled, the toolpaths change into a continuous spiral. The toolpaths no longer have a constant Z height.
Bottom up — Enable this option cut the Surface feature from the bottom upwards. Disable it to cut top downwards.
Remachining — Click this button to open the Remachining dialog.
Area Removal
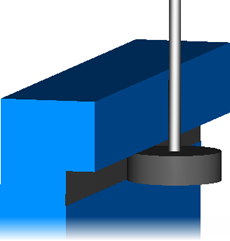
Remove unsafe areas — This removes small toolpath segments to prevent tool damage when using non-center cutting tools. When machining into small pockets, removing small segments stops the central, non-cutting underside of the tool from hitting non-machinable material. Unsafe segment removal filters out the machining of confined areas with small movement of the cutting tool.
Remove area less than — This removes segments that are smaller than the entered percentage of the tool's diameter, unless they surround a Boss feature.
Closed areas only — Select this option to remove segments, in enclosed areas, that are smaller than the Threshold value.
Holder collision clipping — Clips the toolpath where the holder or shank collides with a part surface, check surface, or unmachined stock. When selected, the Holder clearance and Shank clearance attributes are displayed on the Milling tab for the operation.
Machine maximum stock — Use with Holder collision clipping to machine the stock as close to the part without causing a holder collision. This creates smoother toolpaths with fewer retracts, which can improve the surface finish and reduce the machining time, but may cause increased air cutting on some parts.
Z-level finish area removal example:
This cavity part has a small pocket (shown in red):
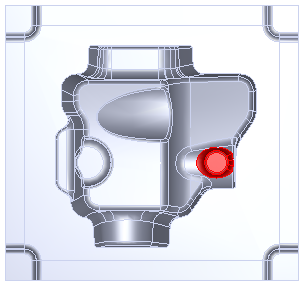
After using a Z-level rough on the part, this is a cutaway front view of a 3D simulation of a Z-level semi-finish with Remove unsafe areas deselected:

The bottom of the pocket is barely bigger than the tool diameter, and the tool hardly moves in this areas. The non-center cutting region of the tool cannot cut the material at the bottom of the pocket.
This is the simulation with Remove unsafe areas selected and Remove area less than set to 80 % of the tool diameter:

The small pocket region is removed from the toolpath. This protects the tool and prevents damage.