You can find the point of intersection between two infinite lines from existing points.
After an intersection is found, you can save it by specifying a new point identifier.
To calculate a Bearing/Bearing intersection in the Survey Command Window
- In Toolspace, on the Survey tab, right-click the network to edit, and click Survey Command Window.
- Click Intersections menu
 Bearing/Bearing.
Bearing/Bearing. - Enter the starting point number of the first bearing.
- Enter the bearing from that point.
- Enter the quadrant for the first point.
- Enter an offset for the first points.
- Enter the starting point number of the second bearing.
- Enter the bearing from that point.
- Enter the quadrant for the second point.
- Enter the offset for the second point.
To calculate a Bearing/Bearing intersection, using the survey command language
- In Toolspace, on the Survey tab, right-click the network to edit, and click Survey Command Window.
- At the Command line, enter:
BB [point 1] [bearing 1] [quadrant 1] [offset 1] [point 2] [bearing 2] [quadrant 2] [offset 2]
Command Line Example
NE 1 100 100
NE 2 200 200
BB 1 66.6667 1 50 2 33.3333 2 50
! INTERSECTION # 1 NORTH:100.000000 EAST:200.000000
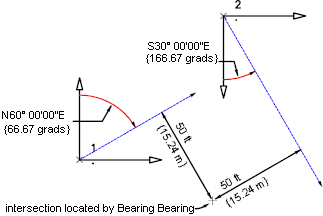
An intersection is located between a bearing of N66.6667"E drawn from point 1, with an offset distance of 50 feet to the right and a bearing of S33.3333"E drawn from point 2 with, an offset distance of 50 to the right.
Command Syntax
BB [point 1] [bearing 1] [quadrant 1] [offset 1] [point 2] [bearing 2] [quadrant 2] [offset 2]
| Parameter | Definition |
|---|---|
| point 1, point 2 | The existing point identifiers that establish the beginning of the bearings. |
| bearing 1, bearing 2 | The bearings for the lines from the existing points. Bearings establish a direction for each vector and are expressed in current angle units. |
| quadrant 1, quadrant 2 | The quadrants in which the bearings exist. The possible values are: 1 (for NE), 2 (for SE), 3 (for SW), and 4 (for NW). |
| offset 1, offset 2 | The offsets from the lines. This acts as if the lines are moved X feet or meters to the left or right. An offset to the right is a positive number, and an offset to the left is a negative number. If you do not want an offset, then use zero. |