Selective Settings
Controls Menu
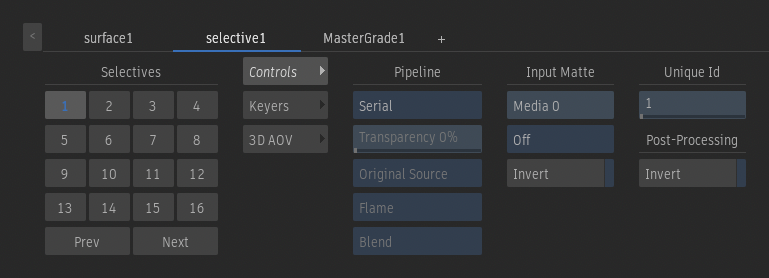
Pipeline Selection option
Select Serial to create a linear pipeline of Matchbox Selective FX, based on the order defined in the Priority Editor. Select Comp for a single Comp operation, regardless of the number of Matchbox nodes, with control on transparency and source. Select Parallel to blend parallel Selective nodes, grouped in the Priority Editor, in an additive process.
Transparency
Sets the transparency of the composition. 0 is transparent, 100 is opaque. Enabled if the Pipeline Selection box is set to Comp.
Original option
Select Original to apply the effects of the selective to the original source. Select Previous Result to apply the effects of the selective to the previous result. Use the Priority Editor to set rendering order. Enabled if the Pipeline Selection box is set to Comp.
Blend Mode option
Select the blend mode to use. A blend mode defines the types of blending available in the Blend Selection box. Enabled if the Pipeline Selection box is set to Comp.
Blend Selection option
Select how the front and matte clip, or the front and back clip, are combined. Enabled if the Pipeline Selection box is set to Comp.
Matte Selection field
Sets the Input Matte used by the selective. The value displayed is a layer index from the Media list.
Input Matte Channel Selection option
Select Off to disable the Input Matte. Select a channel to use the Input Matte: RGB is from the front of the layer, Alpha is the matte of the layer, and luminance is the RGB luma value.
Invert
Enable to invert the Input Matte.
Unique Id field
Identifies the selective. This is the ID used in the Selective Manager, the Schematic, the HUD, and the Priority Editor. An ID is unique to each surface and camera.
Invert
Enable to invert the overall result of the selective, blending together GMasks, Input Matte and Keyer.
GMask Menu
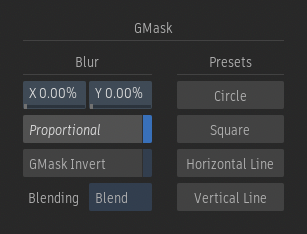
Blur X
Blur the input matte and the GMasks along the x-axis.
Blur Y
Blur the input matte and the GMasks along the Y-axis.
Proportional
Enable to affect the Blur x- and y-axis proportionally.
GMask Invert
Enable to invert the GMasks.
Blending Mode option
Select the blending mode to blend the Input Matte and Gmask together with the selective Keyer and 3D AOV matte. Blend constrains the Keyer and the AOV matte, Add expands, Multiply subtracts.
Create a Circular GMask
Add to the Selective a circular GMask at the centre of the image, with a softness.
Create a Square GMask
Add to the Selective a square GMask at the centre of the image, with a softness.
Create an Horizontal Line GMask
Add to the Selective an horizontal GMask at the centre of the image, with a softness.
Create a Vertical Line GMask
Add to the Selective a vertical GMask at the centre of the image, with a softness.
Adding a GMask to a Selective
| Function | Flame Shortcut | Smoke Classic Shortcut |
|---|---|---|
| Create Circle GMask Selective Preset | Space - S | Not assigned |
| Create Square GMask Selective Preset | Ctrl - Space - S | Not assigned |
| Create Horizontal Line GMask Selective Preset | Shift - Space - S | Not assigned |
| Create Vertical Line GMask Selective Preset | Shift - Ctrl - Space - S | Not assigned |
Keyers Menu
Diamond Keyer
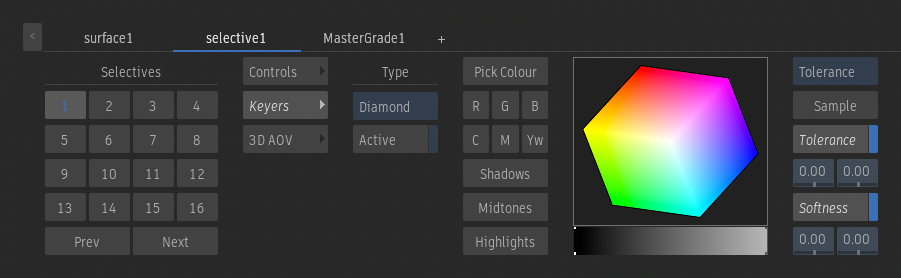
Keyer Type option
Select the keyer to create a matte for the selective.
Active
Enable to apply the key to the selective.
Pick Colour
Define the matte based on a sample from the image. Drag the cursor over the image to define the initial matte.
Red
Define the matte range based on the red channel.
Green
Define the matte range based on the green channel.
Blue
Define the matte range based on the blue channel.
Cyan
Define the matte range based on the cyan channel.
Magenta
Define the matte range based on the magenta channel.
Yellow
Define the matte range based on the yellow channel.
Shadows
Define the matte range based on the dark areas in the image.
Midtones
Define the matte range based on the midlevel areas in the image.
Highlights
Define the matte range based on the bright areas in the image.
Adjustment option
Select Tolerance to add tolerance to the matte, +Softness to add softness to the matte, or -Softness to remove softness from the matte using the Sample button.
Sample
Define the Tolerance, +Softness, or -Softness. The edited value depends on the selected Adjustment option.
Tolerance
Enable to apply the grey tolerance indicator on the hue widget.
Low Tolerance field
Displays the minimum value for the tolerance range.
High Tolerance field
Displays the maximum value for the tolerance range.
Softness
Enable to apply the black softness indicator on the hue widget.
Low Softness field
Displays the minimum value for the softness range.
High Softness field
Displays the maximum value for the softness range.
Tracer Keyer
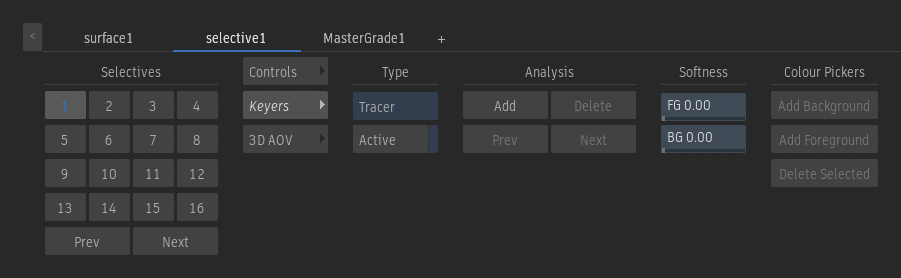
Keyer Type option
Select the keyer to create a matte for the selective.
Active
Enable to apply the key to the selective.
Add
Add a tracer at a specific frame.
Delete
Delete an existing tracer.
Previous
Jump to the previous tracer.
Next
Jump to the next tracer.
Foreground Softness field
Displays the amount of 3D colour volume around the foreground colour range.
Background Softness field
Displays the amount of 3D colour volume around the background colour range.
Add Background Sampling
Add more background colour sampling boxes to define the background 3D colour volume.
Add Foreground Sampling
Add more foreground colour sampling boxes to define the foreground 3D colour volume
Delete Selected
Delete the current colour sampling box selection, and remove it from either the foreground or background 3D colour volume.
Semantic Keyer
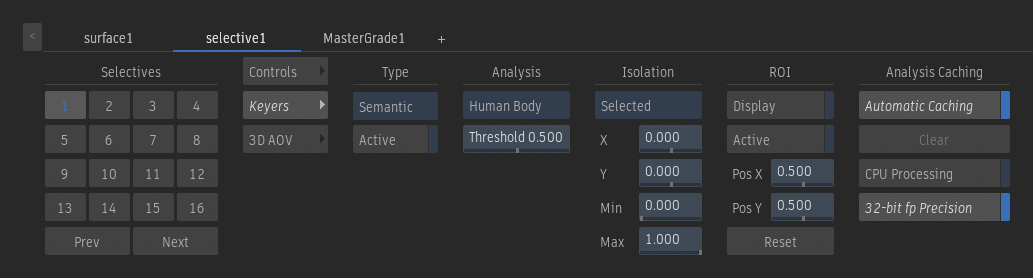
The Semantic keyer uses a machine learning model to automatically extract a matte out of skies, human bodies, human faces, or human heads.
Analysis Type option
Select the feature to detect.
Threshold
Default value (0.5) has no effect. Move toward 0.0 to fill semi-transparent regions with black. Move toward 1.0 to fill with white.
Human Face Isolation option
The face feature to detect. If there is more than one talent in the shot, use the Selective Input view (F9) to select the talent with the widget.
Target Isolation option
All creates a matte with every human head or body in the surface. Selected allows you to choose the human head or body to include in the matte. Use the Selective Input view (F9) to display the widget and select the subject.
Position X fied
Sets the X position of the widget used to choose the human head or body to include in the matte.
Position Y field
Sets the Y position of the widget used to choose the human head or body to include in the matte.
Minimum Brightness field
Sets the minimal brightness to include in the matte. Clean up the matte by removing semi-transparency from undesirable features. Enabled when Target Selection is set to Selected.
Maximum Brightness field
Sets the maximal brightness to include in the matte. Clean up the matte by strengthening the transparency of the selected subject. Enabled when Target Selection is set to Selected.
Salient Position X field
Sets the X position of the Salient Bounding Box. View the Bounding Box in the Selective views (F9).
Salient Position Y field
Sets Y position of the Salient Bounding Box. View the Bounding Box in the Selective views (F9).
Salient Width field
Sets Width of the Salient Bounding Box. View the Bounding Box in the Selective views (F9).
Salient Height field
Sets Height of the Salient Bounding Box. View the Bounding Box in the Selective views (F9).
Reset Bounding Box
Reset the Salient Bounding Box.
Display ROI
Display the region of interest (ROI). The ROI can only appear in a viewport set to Object (F8) or Selective (F9) view.
Active ROI
Enable to analyze only the area defined by the Region Of Interest (ROI). A well-defined ROI can improve performance, caching, and the quality of the analysis.
ROI Position X field
Sets the centre position of the Region Of Interest along the x-axis.
ROI Position Y field
Sets the centre position of the Region Of Interest along the y-axis.
Reset ROI
Reset the Region Of Interest (ROI) to the full image and delete any ROI keyframe.
Automatic Caching
Enable to cache the analysis as each frame is displayed, making scrubbing or playback faster. Turn off if you run out of space on your framestore.
Clear
Cear the cache.
CPU Processing
Enable to perform the analysis with the CPU instead of the GPU. Using the CPU helps with stability on computers equipped with minimal amounts of VRAM.
32-bit fp Processing
Enable to analyze with 32-bit fp floating point precision. Disable this option if you run out of framestore space because of caching. The cache will use less space, but use 16-bit floating point precision.
Keyers Rendering Controls
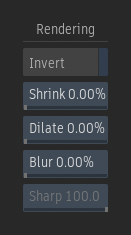
Invert
Enable to invert the result of the key.
Shrink field
Use to reduce the spatial extent of the keyer's result.
Dilate field
Use to increase the spatial extent of the keyer's result.
Blur field
Sets the blur amount applied to the keyer's result.
Sharpness field
Sets the sharpness amount of the Diamond keyer's key.
3D AOV Menu
Type
3D AOV Type option
Set the 3D AOV image segmentation type. Each type requires a specific AOV data pass, such as Distance requires a Z-depth map.
Active
Activate the image segmentation. Automatically turns on when you edit any of the Controls.
Create Map
Attach to the surface the map required by the 3D AOV Mode box, such as Z-depth for Distance, and set the map to the Analysis mode.
Controls - Range
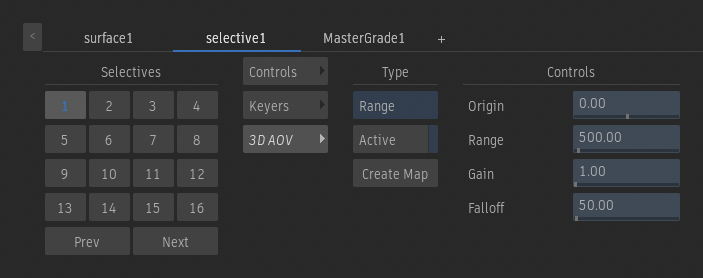
Origin field
Sets where the segmented volume starts in the camera space.
Range field
Sets the depth of the segmented volume.
Gain field
Applies a gain to control the intensity of the output segmentation.
Falloff field
Controls the smoothness of the transition to and from the segmented volume.
Controls - Distance
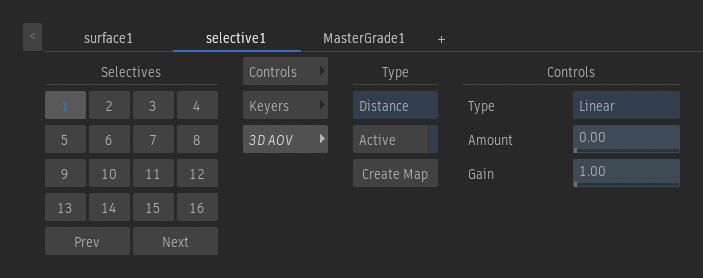
Type option
Select the algorithm that decays the transition between the near and far clipping planes.
Amount field
Modulates the rate at which the transition decays for the chosen decay algorithm.
Gain field
Applies a gain to control the intensity of the output segmentation.
Controls - Near/Far
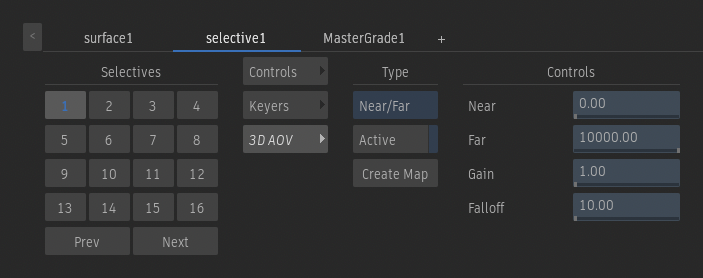
Near field
Sets the near clipping plane for the depth segmentation.
Far field
Sets the far clipping plane for the depth segmentation.
Gain field
Applies a gain to control the intensity of the output segmentation.
Falloff field
Controls the smoothness of the transition to and from the segmented volume.
Controls - Normals
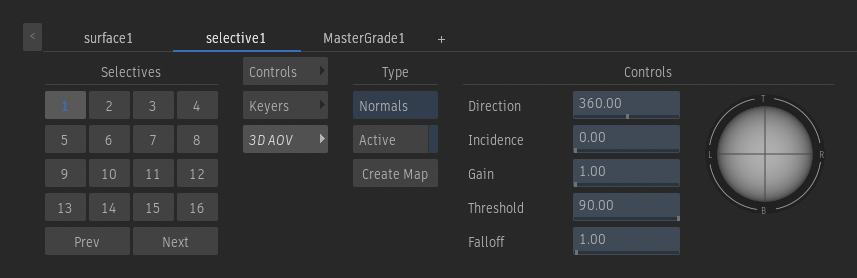
Direction field
Sets the direction of the incoming light.
Incidence field
Sets the slant, from the z-axis, of the incoming light. The higher value, the more oblique the incoming light is.
Gain field
Applies a gain to control the intensity of the output segmentation.
Threshold field
Sets the range of the normals used to segment the image. Matches the dark area on the trackball.
Falloff field
Controls the smoothness of the transition to and from the segmentation.
Controls - Motion
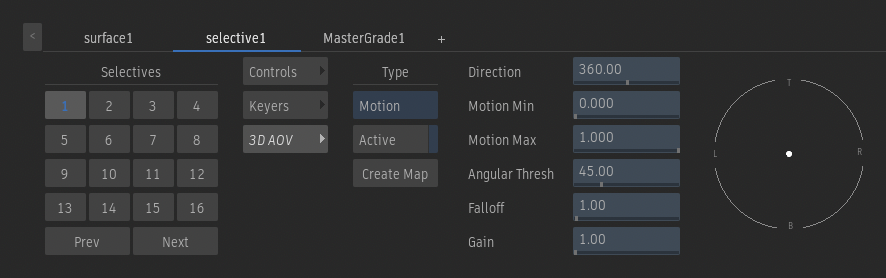
The Motion mode requires access to Motion Vector data. The data can come from a Motion Vector texture map (if connected to the Surface) or from the Action Motion Vector output (if connected to the Camera). The Motion mode isolates part of the Motion data using direction and motion min/max fields, and then create a matte out of it.
Direction field
Controls what direction of the motion is included in the resulting matte.
Motion Min field
Filters out smaller motions from the selected direction the resulting matte.
Since the process of creating Motion Vector results includes a lot of small motion, you'll probably need to increase this value to get a precise motion segmentation result.
Motion Max field
Filters out the larger motions from the selected direction in the resulting matte.
Angular Threshold field
Defines the angle of the motion range included in the defined Direction.
Falloff field
Sets the shape of the curve that defines the motion range from the centre of the define direction and the limit of the Angular Threshold. While Linear interpolation is the default, increasing the Falloff creates a logarithmic-type interpolation.
Gain field
Applies a gain to control the intensity of the output segmentation.
Motion Vector widget
Controls the Direction and Motion Min settings.
Controls - Primitive
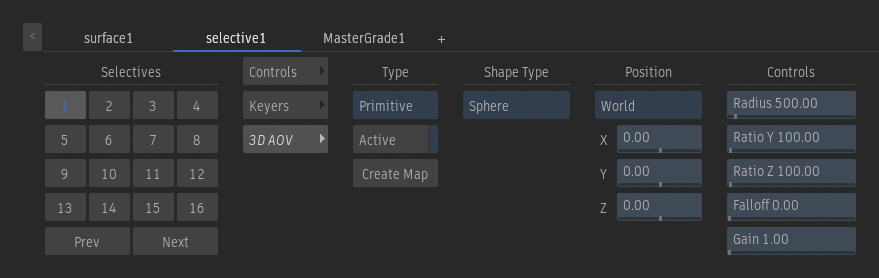
Use a primitive to precisely extract an object from the depth, something that cannot be done with other depth-based segmentation tools.
Shape Type option
Set the shape used to isolate part of the depth data. Grey in the shape indicates areas that do not circumscribe any depth information. Yellow indicates areas that circumscribe some depth information. Use the F8 or F9 views to display the shape.
Position button
Use World to position the shape using absolute XYZ coordinates. Use Camera to position the shape relative to the camera.
Position X field
Sets the shape position along the x-axis.
Position Y field
Sets the shape position along the y-axis.
Position Z field
Sets the shape position along the z-axis.
Relative Position X field
Sets the shape position relative to the camera, along the x-axis.
Relative Position Y field
Sets the shape position relative to the camera, along the y-axis.
Relative Depth field
Normalizes the distance from the camera to the centre of the shape.
Radius field
Sets the size of the shape
Ratio Y field
Changes the 3D Shape along the y-axis.
Ratio Z field
Changes the 3D Shape along the z-axis.
Falloff field
Sets the smoothness of the transition to and from the segmented volume.
Gain field
Applies a gain to control the intensity of the output segmentation.
Selectives Navigation Panel
Go To Selective
Click a blue number to display the Selective. Click a grey number to create Selective.
Previous Selectives
Displays the previous set of Selectives.
Next Selectives
Displays the next set of Selectives.
