Trigonometric Functions
The following functions are useful for working with angles and performing various trigonometric calculations.
degrees
Converts angle units from radians into degrees.
| Syntax | degrees(Angle) |
| Arguments | Angle is the angle in radians that you want to convert. |
| Examples |
|
radians
Converts angle units from degrees into radians.
| Syntax | radians(Angle) |
| Arguments | Angle is the angle in degrees that you want to convert. |
| Examples | radians(225) returns 3.927 (5*PI/4). |
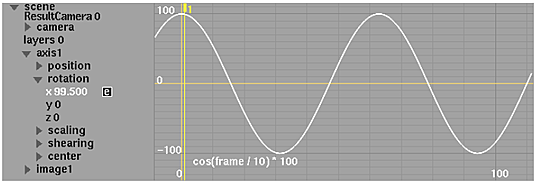
cos
Returns the cosine of a given angle.
| Syntax | cos(Angle) |
| Arguments | Angle is the angle in radians of which you want the cosine. |
| Examples |
|
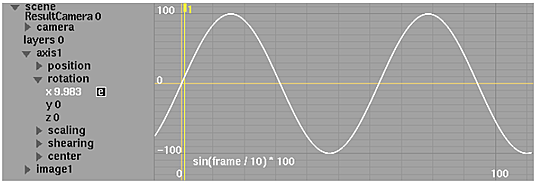
sin
Returns the sine of a given angle.
| Syntax | sin(Angle) |
| Arguments | Angle is the angle in radians of which you want the sine. |
| Examples |
|
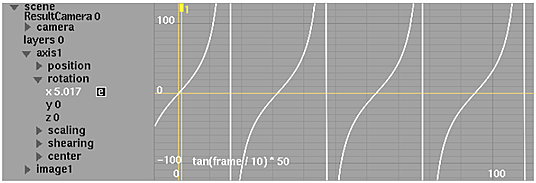
tan
Returns the tangent of a given angle.
| Syntax | tan(Angle) |
| Arguments | Angle is the angle in radians of which you want the tangent. |
| Examples |
|
acos
Returns the arccosine—the inverse function of the cosine—of a given number. The returned angle is given in radians within the range 0 to PI.
| Syntax | acos(Number) |
| Arguments | Number is the cosine of the angle you want and must be between-1 and 1. |
| Examples |
|
asin
Returns the arcsine—the inverse function of the sine—of a given number. The returned angle is given in radians within the range -PI/2 to PI/2.
| Syntax | asin(Number) |
| Arguments | Number is the sine of the angle you want and must be between-1 and 1. |
| Examples |
|
atan
Returns the arctangent—the inverse function of the tangent— of a given number. The returned angle is given in radians within the range -PI/2 to PI/2.
| Syntax | atan(Number) |
| Arguments | Number is the tangent of the angle you want. |
| Examples |
|
atan2
Returns the arctangent of y/x, using the signs of both arguments to determine the quadrant of the return value. The arctangent is the angle from the origin to the vector (x,y). The returned angle is given in radians within the range -PI to PI.
| Syntax | atan2(x, y) |
| Arguments | x and y are the components of the vector to be used in the function. |
| Examples |
|