The method of calculating deep beams is based on the following presented principles, as defined in Appendix E5 to the French BAEL 91 code.
- The deep beam height should equal at least a half of the calculation span.
- The deep beam should be stiffened in the near-support zone by means of brackets or other deep beams, able to provide the required transversal support.
- A load applied to a deep beam is a uniform load distributed over each span and it is applied to the upper part of the deep beam.
- Moments of inertia of cross-sections are identical for each span.
- The proportion of successive span lengths should fall within the range <0.8 and 1.25>
- Cracking is treated as not severe.
The following symbol definitions have been adopted in the description of the methods of calculating reinforcement area for deep beams:
|
lt |
Deep beam length in the axes of supports. |
|
lo |
Deep beam length at the face of supports. |
|
l |
Calculation length of the deep beam = min(lt; 1,15lo). |
|
h |
Deep beam height. |
|
bo |
Deep beam width. |
|
z |
Arm of internal forces. |
|
p |
An uniform load, recognizing load coefficients for constant and variable loads. |
|
|
A moment originating from the "p" load. |
|
|
Shear force originating in the operation of "p" load. |
 |
Shear stress equal: 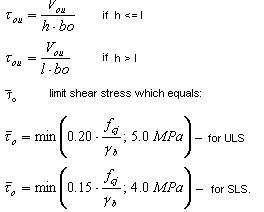 |
See also
