![]()
At the editable poly Vertex sub-object level, you can select single and multiple vertices and move them using standard methods. This topic covers the Edit Vertices and Vertex Properties rollouts and provides links to the rest.
Procedures
To weld polygon vertices:
-
To use Weld:
If the vertices are very close together, simply click Weld. If they are farther apart, click
 (Settings) to the right of the Weld button. This opens the Weld Vertices caddy, where you can increase the Weld Threshold. Once you change Weld Threshold, it remains at the new value until you change it again, or until the end of the 3ds Max session.
(Settings) to the right of the Weld button. This opens the Weld Vertices caddy, where you can increase the Weld Threshold. Once you change Weld Threshold, it remains at the new value until you change it again, or until the end of the 3ds Max session. -
To use Target Weld:
The two vertices must be contiguous; that is, they must be connected by a single edge.
You can use either of two methods to combine several vertices into one, also known as welding. If the vertices are very close together, use the Weld function. You can also use Weld to combine a number of vertices to the average position of all of them.
Alternatively, to combine two vertices that are far apart, resulting in a single vertex that's in the same position as one of them, use Target Weld.
To select vertices by color:
- In the Vertex Properties rollout
 Select Vertices By group, click the color swatch, and specify the color of vertex you want in the Color Selector.
Select Vertices By group, click the color swatch, and specify the color of vertex you want in the Color Selector. - Specify ranges in the RGB Range spinners. This lets you select vertices that are close to the specified color, but don't match exactly.
- Click the Select button.
All vertices matching the color, or within the RGB range, are selected.
You can add to the selection by holding
 as you click the Select button, and subtract from the selection by holding the
as you click the Select button, and subtract from the selection by holding the  key. Tip: You can select all vertices of the same color by first selecting the vertex you want matched, dragging a copy of the Edit Color swatch to the Existing Color swatch, and then clicking the Select button. (If you want an exact match, be sure to set the RGB Range spinners to 0 first.)
key. Tip: You can select all vertices of the same color by first selecting the vertex you want matched, dragging a copy of the Edit Color swatch to the Existing Color swatch, and then clicking the Select button. (If you want an exact match, be sure to set the RGB Range spinners to 0 first.)
Interface
Selection rollout
See Editable Poly for information on the Selection rollout settings.
Soft Selection rollout
Soft Selection controls apply a smooth falloff between selected sub-objects and unselected ones. When Use Soft Selection is on, unselected sub-objects near your selection are given partial selection values. These values are shown in the viewports by means of a color gradient on the vertices, and optionally on the faces. They affect most types of sub-object deformations, such as the Move, Rotate, and Scale functions, as well as any deformation modifiers (such as Bend) applied to the object. This provides a magnet-like effect with a sphere of influence around the selection.
For more information, see Soft Selection Rollout.
Edit Vertices rollout
This rollout includes commands specific to vertex editing.
 key, but this can create holes in the mesh. To delete vertices without creating holes, use Remove (see the following).
key, but this can create holes in the mesh. To delete vertices without creating holes, use Remove (see the following). - Remove
- Deletes selected vertices and combines the polygons that use them. The keyboard shortcut is
 .
. 
Removing one or more vertices deletes them and retriangulates the mesh to keep the surface intact. If you use Delete instead, the polygons depending on those vertices are deleted as well, creating a hole in the mesh.
Warning: Use of Remove can result in mesh shape changes and non-planar polygons. - Break
- Creates a new vertex for each polygon attached to selected vertices, allowing the polygon corners to be moved away from each other where they were once joined at each original vertex. If a vertex is isolated or used by only one polygon, it is unaffected.
- Extrude
- Lets you extrude vertices manually via direct manipulation in the viewport. Click this button, and then drag vertically on any vertex to extrude it.
Extruding a vertex moves it along a normal and creates new polygons that form the sides of the extrusion, connecting the vertex to the object. The extrusion has the same number of sides as the number of polygons that originally used the extruded vertex.
Following are important aspects of vertex extrusion:
- When over a selected vertex, the mouse cursor changes to an Extrude cursor.
- Drag vertically to specify the extent of the extrusion, and horizontally to set the size of the base.
- With multiple vertices selected, dragging on any one extrudes all selected vertices equally.
- You can drag other vertices in turn to extrude them while the Extrude button is active. Click Extrude again or right-click in the active viewport to end the operation.

Chamfer box showing extruded vertex
-
 Extrude Settings Opens the Extrude Vertices caddy, which lets you perform extrusion via interactive manipulation.
Extrude Settings Opens the Extrude Vertices caddy, which lets you perform extrusion via interactive manipulation. If you click this button after performing a manual extrusion, the same extrusion is performed on the current selection as a preview and the caddy opens with Extrusion Height set to the amount of the last manual extrusion.
- Weld
-
Combines contiguous, selected vertices that fall within the tolerance specified in Weld Vertices caddy. All edges become connected to the resulting single vertex.

Using Weld at the Vertex level
Vertices farther apart than the Threshold distance are not welded.
Weld is best suited to automatically simplifying geometry that has areas with a number of vertices that are very close together. Before using Weld, set the Weld Threshold via the Weld caddy. To weld vertices that are relatively far apart, use Target Weld instead.
 Weld Settings Opens the Weld Vertices caddy, which lets you specify the weld threshold.
Weld Settings Opens the Weld Vertices caddy, which lets you specify the weld threshold.
- Chamfer
- Click this button and then drag vertices in the active object. To chamfer vertices numerically, click the Chamfer Settings button and use the Chamfer Amount value.
If you chamfer multiple selected vertices, all of them are chamfered identically. If you drag an unselected vertex, any selected vertices are first deselected.
Each chamfered vertex is effectively replaced by a new face that connects new points on all edges leading to the original vertex. These new points are exactly <chamfer amount> distance from the original vertex along each of these edges. New chamfer faces are created with the material ID of one of the neighboring faces (picked at random) and a smoothing group which is an intersection of all neighboring smoothing groups.
For example, if you chamfer one corner of a box, the single corner vertex is replaced by a triangular face whose vertices move along the three edges that led to the corner. Outside faces are rearranged and split to use these three new vertices, and a new triangle is created at the corner.
Alternatively, you can create open space around the chamfered vertices; for details, see Chamfer.

Top: The original vertex selection
Center: Vertices chamfered
Bottom: Vertices chamfered with Open on
-
 Chamfer Settings Opens the Chamfer caddy, which lets you chamfer vertices via interactive manipulation and toggle the Open option.
Chamfer Settings Opens the Chamfer caddy, which lets you chamfer vertices via interactive manipulation and toggle the Open option. If you click this button after performing a manual chamfer, the same chamfer is performed on the current selection as a preview and the caddy opens with Chamfer Amount set to the amount of the last manual chamfer.
-
- Target Weld
- Allows you to select a vertex and weld it to a neighboring target vertex. Target Weld works only with pairs of contiguous vertices; that is, vertices connected by a single edge.
In Target Weld mode, the mouse cursor, when positioned over a vertex, changes to a + cursor. Click and then move the mouse; a dashed, rubber-band line connects the vertex to the mouse cursor. Position the cursor over another, neighboring vertex and when the + cursor appears again, click the mouse. The first vertex moves to the position of the second and the two are welded. Target Weld remains active until you click the button again or right-click in the viewport.
- Connect
- Creates new edges between pairs of selected vertices.

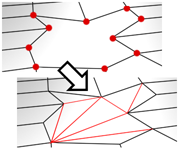
Connect does not let the new edges cross. Thus, for example, if you select all four vertices of a four-sided polygon and then click Connect, only two of the vertices will be connected. In this case, to connect all four vertices with new edges, use Cut.
- Remove Isolated Vertices
- Deletes all vertices that don't belong to any polygons.
- Remove Unused Map Verts
- Certain modeling operations can leave unused (isolated) map vertices that show up in the Unwrap UVW editor, but cannot be used for mapping. You can use this button to automatically delete these map vertices.
[Weight group]
- Weight
- Sets the weight of selected vertices. Used by the NURMS subdivision option and by the MeshSmooth modifier. Increasing a vertex weight tends to pull the smoothed result toward the vertex. Note: When the Select and Manipulate tool is active at the Vertex sub-object level, the caddy appears in the viewport with a control for vertex weight:
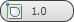 . For instructions for using the caddy, see The Caddy Interface.
. For instructions for using the caddy, see The Caddy Interface.

- Crease
- Sets the crease value of selected vertices. Used by the OpenSubdiv and CreaseSet modifiers. Increasing a vertex crease tends to pull the smoothed result toward the vertex and sharpen the point. Note: When the Select and Manipulate tool is active at the Vertex sub-object level, the caddy appears in the viewport with a control for vertex crease:
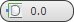 . For instructions for using the caddy, see The Caddy Interface.
. For instructions for using the caddy, see The Caddy Interface.
Edit Geometry rollout
For detailed descriptions of these controls, see Edit Geometry Rollout (Polymesh and Edit Poly).
Vertex Properties rollout
Edit Vertex Colors group
Use these controls to assign the color, and illumination color (shading) of selected vertices.
- Color
- Click the color swatch to change the color of selected vertices.
- Illumination
- Click the color swatch to change the illumination color of selected vertices. This lets you change the illumination without changing the vertex's color.
- Alpha
- Lets you set specific alpha values of selected vertices. These alpha values are maintained by the pipeline and can be used in conjunction with vertex color to provide full RGBA data for export.
Select Vertices By group
- Color/Illumination
- Determines whether to select vertices by vertex color values or vertex illumination values.
- Color Swatch
- Displays the Color Selector, where you can specify a color to match.
- Select
- Depending on which radio button is chosen, selects all vertices whose vertex color or illumination values either match the color swatch, or are within the range specified by the RGB spinners.
- Range
- Specifies a range for the color match. All three RGB values in the vertex color or illumination must either match the color specified by the color swatch in Select By Vertex Color, or be within plus or minus the values in the Range spinners. Default=10.
Subdivision Surface rollout
For information about the Subdivision Surface rollout settings, see Subdivision Surface Rollout (Polymesh).
Subdivision Displacement rollout
For information about the Subdivision Displacement rollout settings, see Subdivision Displacement Rollout (Polymesh).
Paint Deformation rollout
Paint Deformation lets you stroke elevated and indented areas directly onto object surfaces. For more information, see Paint Deformation Rollout (Polymesh).