Action uses shaders to compute the colour, lighting, shadows, and other attributes of each pixel or vertex of objects in the scene. Shaders use the processing pipeline of the GPU to accelerate object-specific rendering effects. You can use shaders to control the interaction between surfaces or models and the lights in the scene to contribute to the realism of a material simulated in a texture.
You can use any media to map textures to Action surfaces and geometries, thus adding detail such as depth and reflections to your 3D composites.
Working With Textures in Map Nodes
You create maps in Action (such as Diffuse and Reflection maps) based on media from the Media list. In some cases, such as with Substance Textures, the media is automatically applied to map nodes. To specify different media as the texture source, select the media in the Media menu, then click Apply. If the media you want to use resides elsewhere on your filesystem, you can use the Read File tab of the map menu to load the texture, and then decide if you want the texture to be managed by Action, or not.
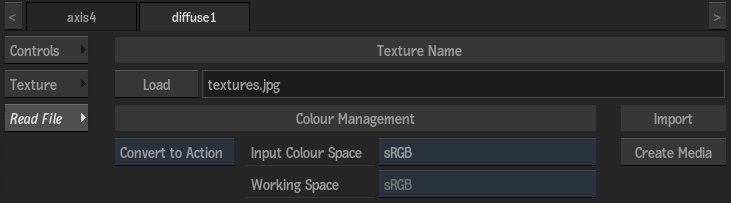
- Load button
- Click to open a browser to select an external texture for the map.
- Name field
- This locked field displays the name of an externally loaded texture.
- Create Media button
- Click to convert the external texture into an Action-managed texture. The Texture Name is removed from this menu, and the texture appears in the Action Media list instead, assigned as a proper layer to the texture in the schematic.