HtoA 6.4.6.0
10 February 2026
HtoA 6.4.6.0 is a feature release using Arnold 7.4.5.0 that includes faster USD instancing, volume mip maps and speedups, a nearest points shader, point cloud OSL queries, bloom dispersion, a new render line shader, and much more.
Installation
Download Arnold for Houdini from your Autodesk Account. See Download Arnold for more information about downloading HtoA from your Autodesk Account.
Follow these installation instructions
Enhancements
- Lightweight instancing: Arnold now renders USD instances through a lightweight instancing system that creates fewer Arnold nodes. Instancing is now more memory efficient and time to first pixel is faster, because the scene is quicker to initialize. For example, in the Intel Jungle Ruins scene, the CPU time to first pixel in Houdini Solaris is 85% faster, and the memory usage is 42% lower. usd#2459
-
Arnold Render Settings AOV improvements
-
Exposed per-AOV Filters on Arnold Standard Render Vars and Arnold Render Settings (HTOA-1590)
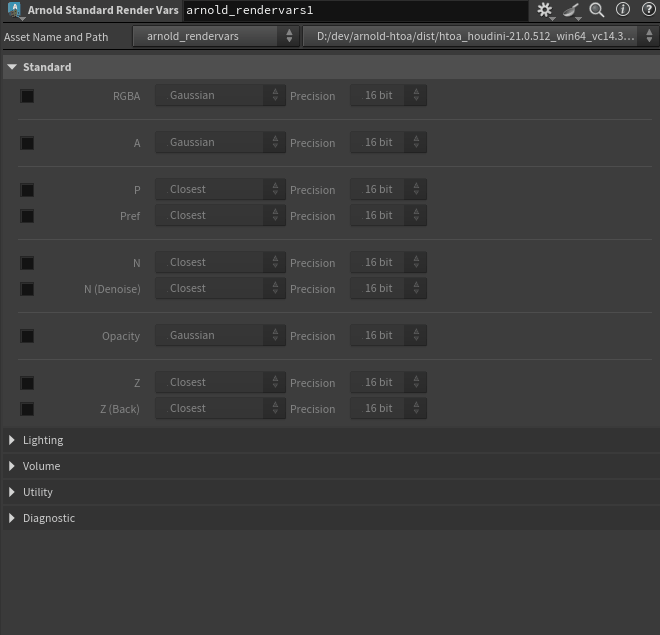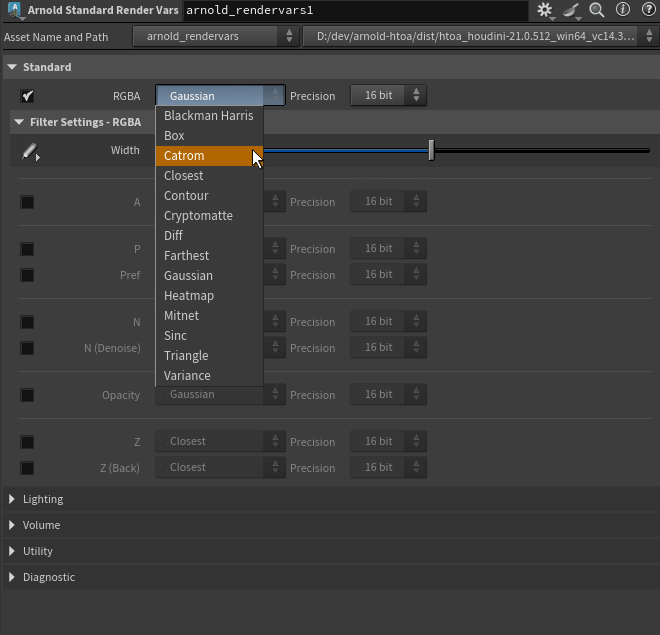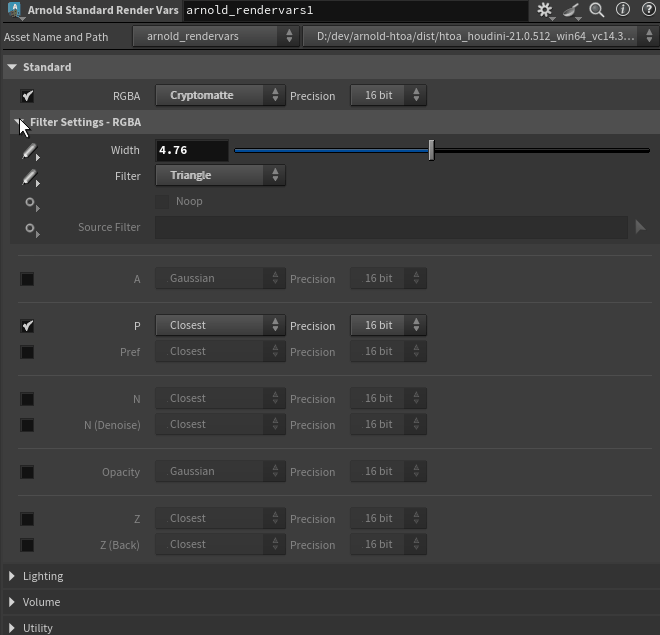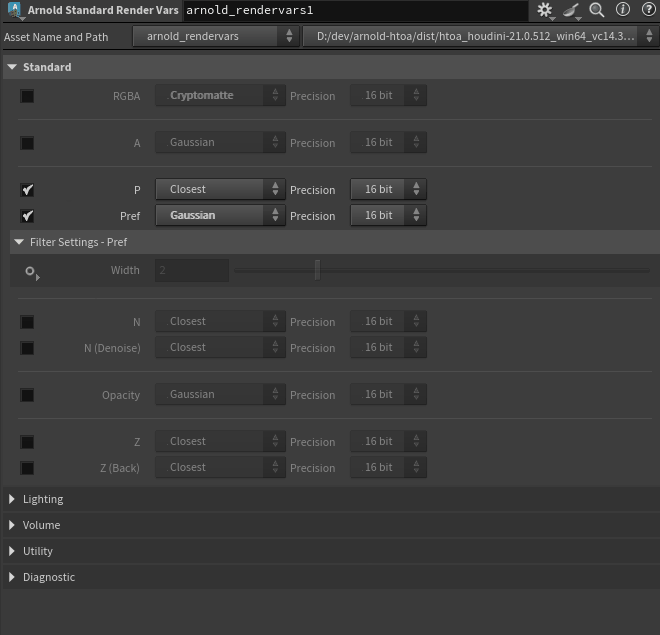
-
Added the Output Variance AOVs toggle to create denoising AOVs automatically (HTOA-1590)
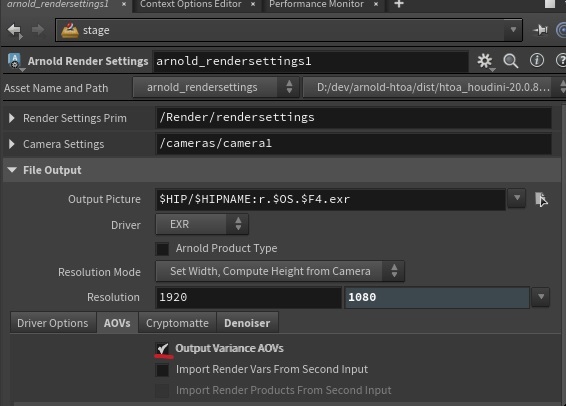
- Changed Render Var default filter from box to gaussian (HTOA-3119)
-
Exposed per-AOV Filters on Arnold Standard Render Vars and Arnold Render Settings (HTOA-1590)
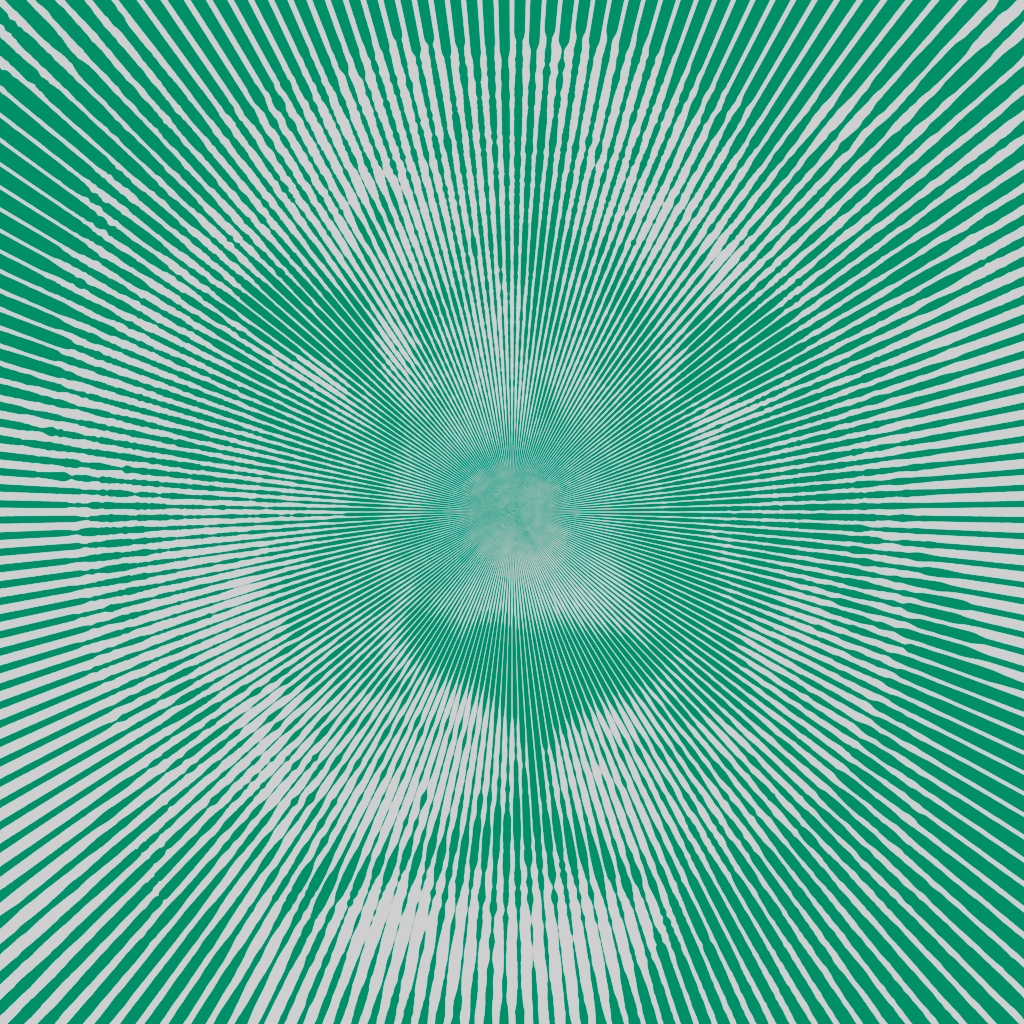
- Line shader:
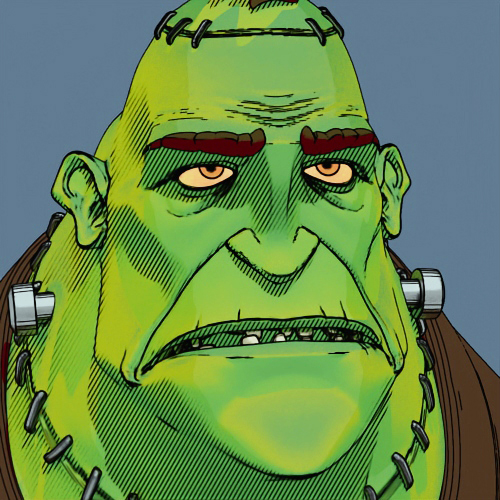
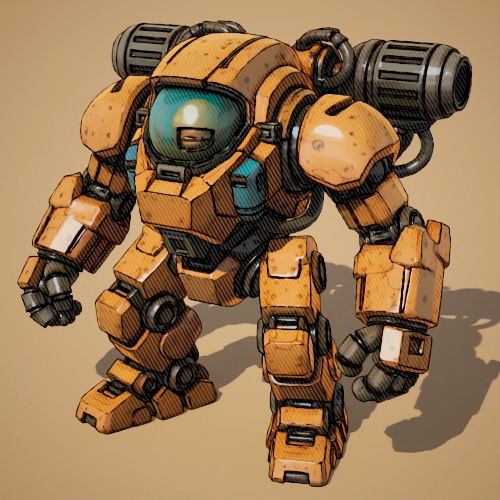
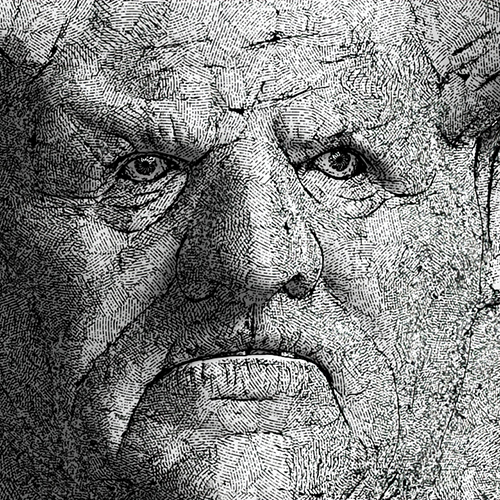



Line → UV Transform (screen space) Line → UV Transform (screen space) Line → Triplanar The new line shader renders lines in various styles to create geometric patterns or brush-stroke-like textures when combined with noise and textures. You can generate complex hierarchical patterns by connecting line shaders together. We recommend using the line shader with uv_transform. (ARNOLD-14976)


Support for mip-mapped OpenVDB files on CPU: The
volumenode now accepts OpenVDB files with mip-mapped grids. You can generate volume mip maps with the Arnold API or with kick (see API Changes below). The different mip-map levels are distinguished by_level_Nsuffixes, whereNis the mip-map level. Arnold then automatically chooses the appropriate mip-map level during rendering, which gives substantial speedups in volumes with a lot of scattering (for example, clouds) in exchange for mostly small differences in look. Volumes with more mip-map levels can have larger differences in look. Users can also specifymipmap_biason avolumenode or on its instance (by declaring user data of the same name), which adjusts the automatic mipmap selection by that amount. (ARNOLD-14453, ARNOLD-15056)CPU volume mip-mapping speedups wdascloud byc-cloud composition 1 composition 2 sunset clouds original volume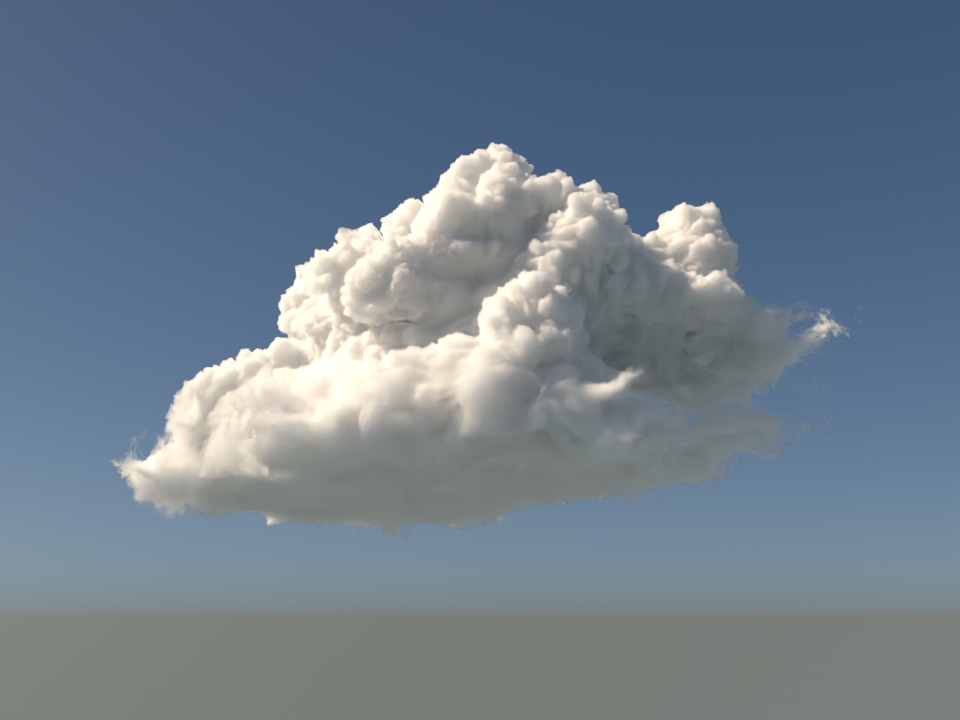 
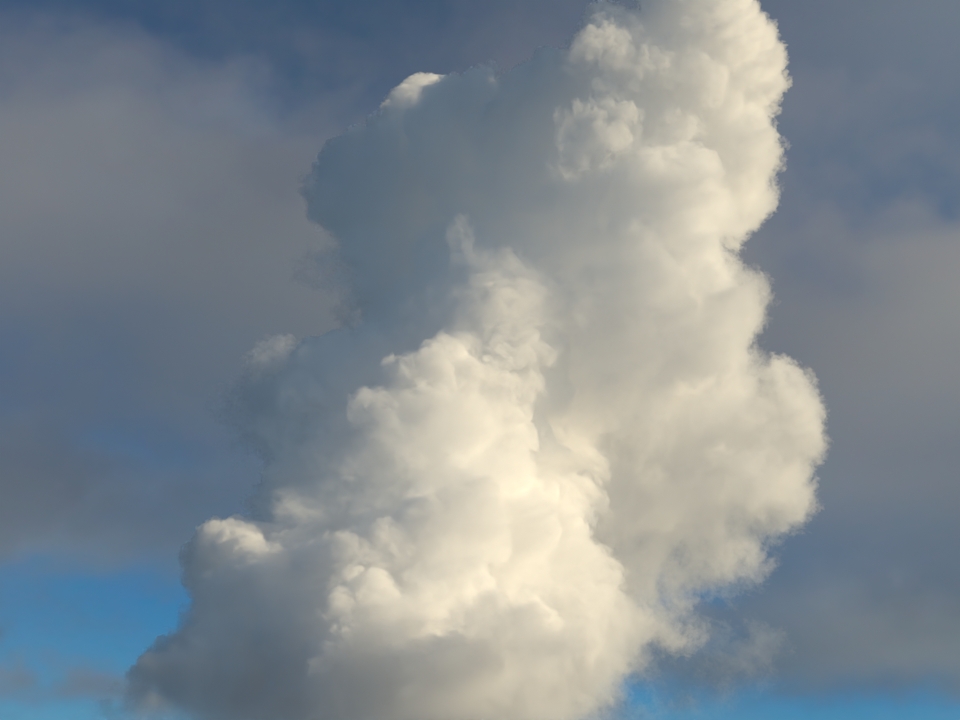
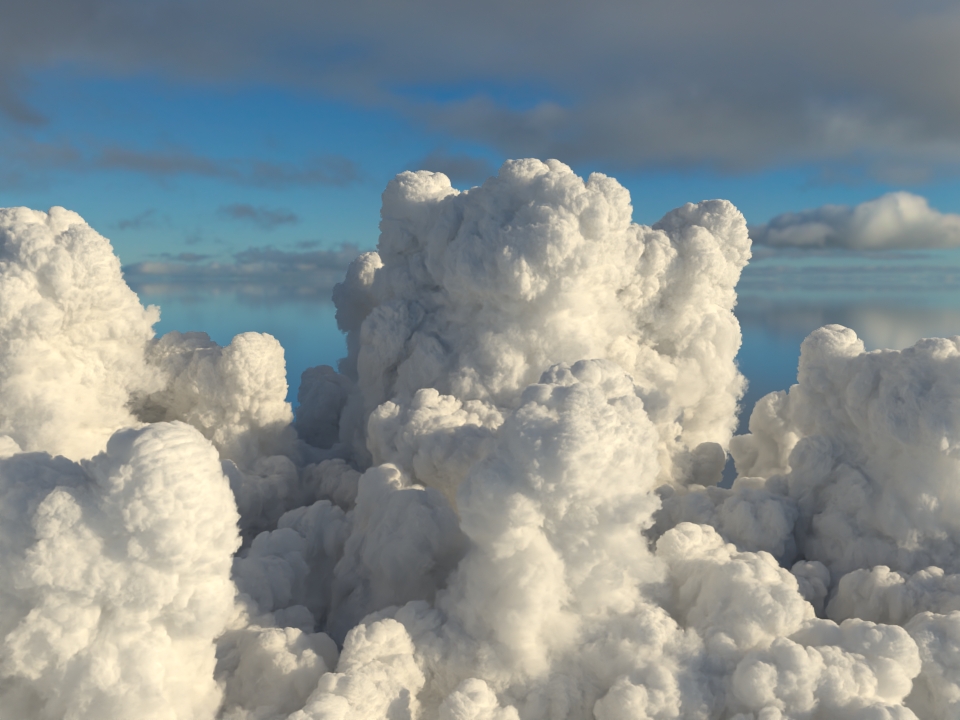
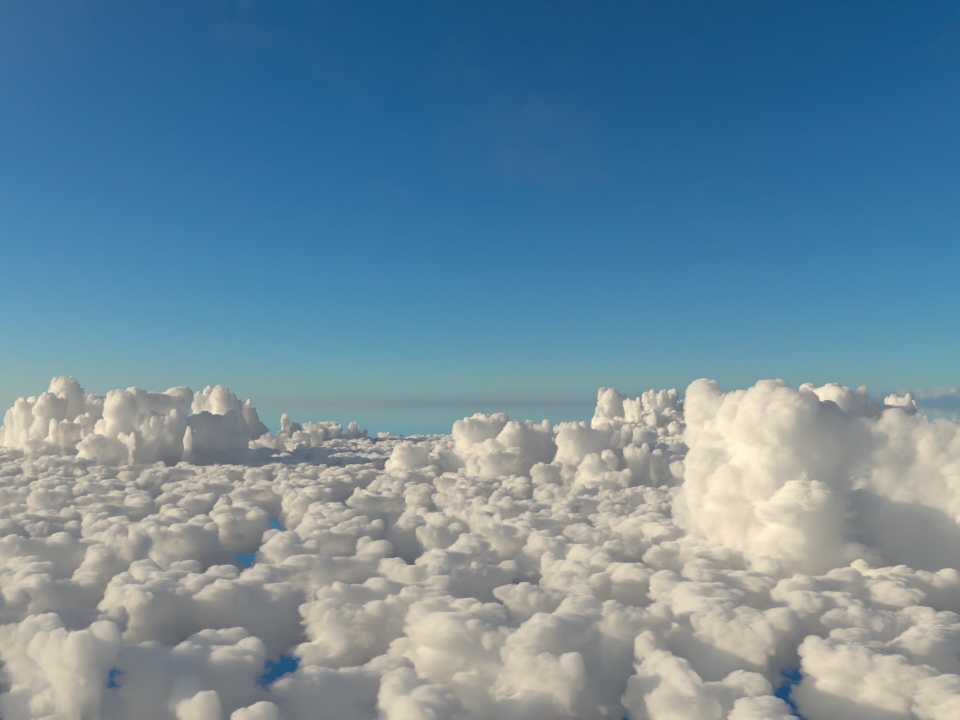
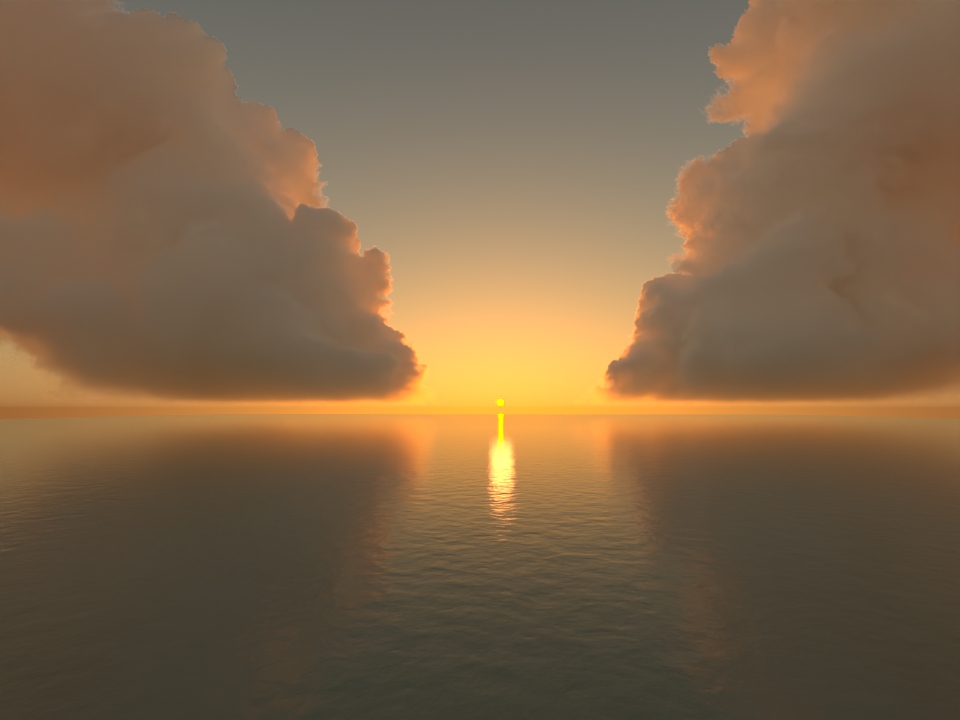




mip-mapped volume (3 levels)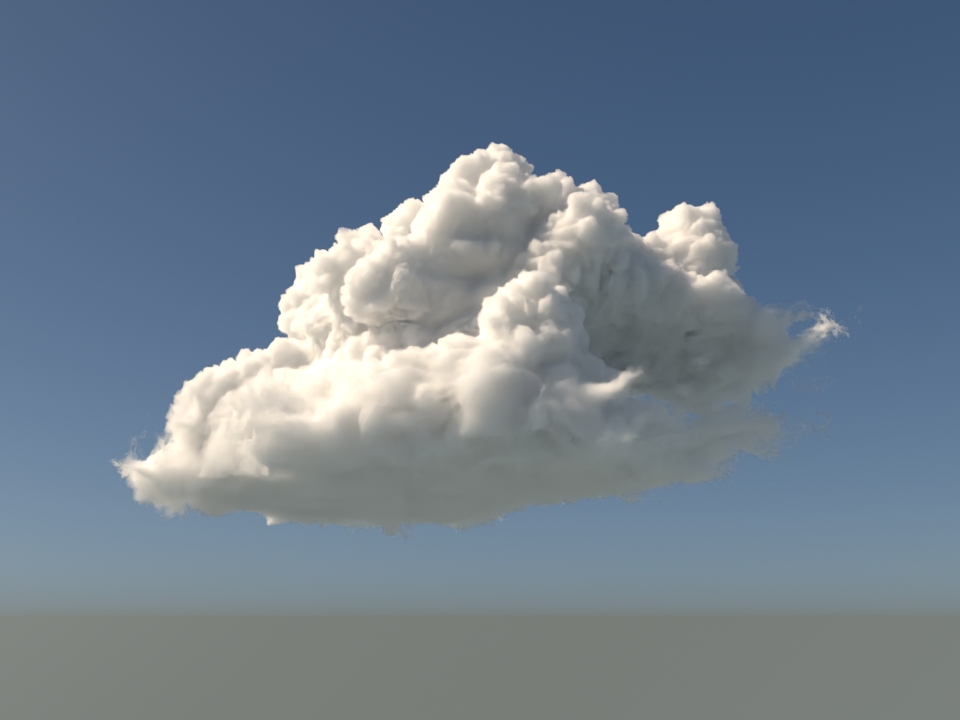 
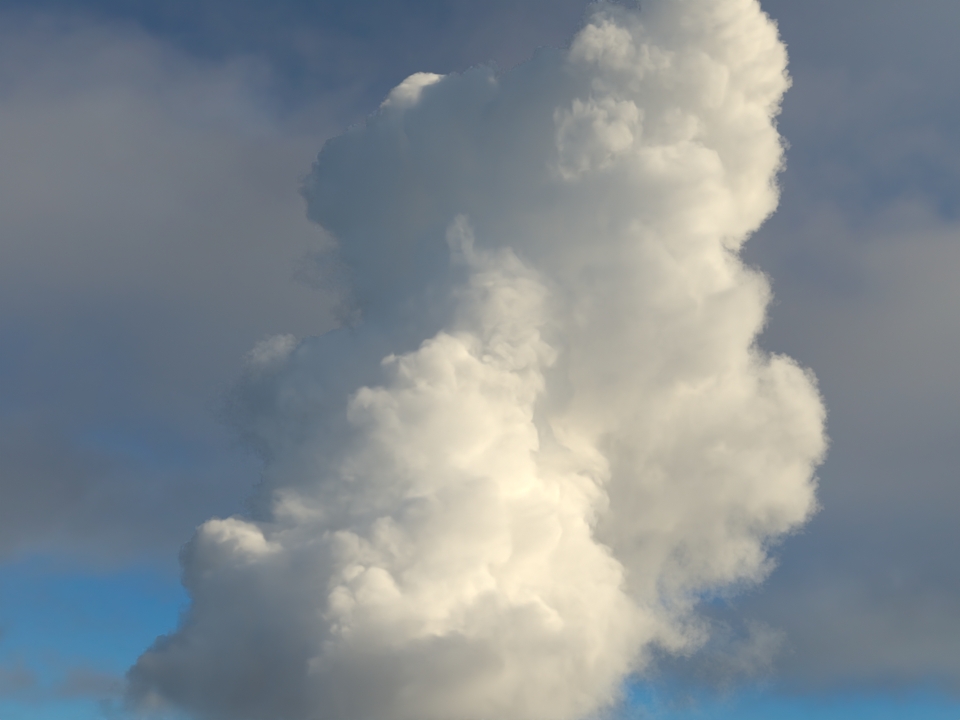
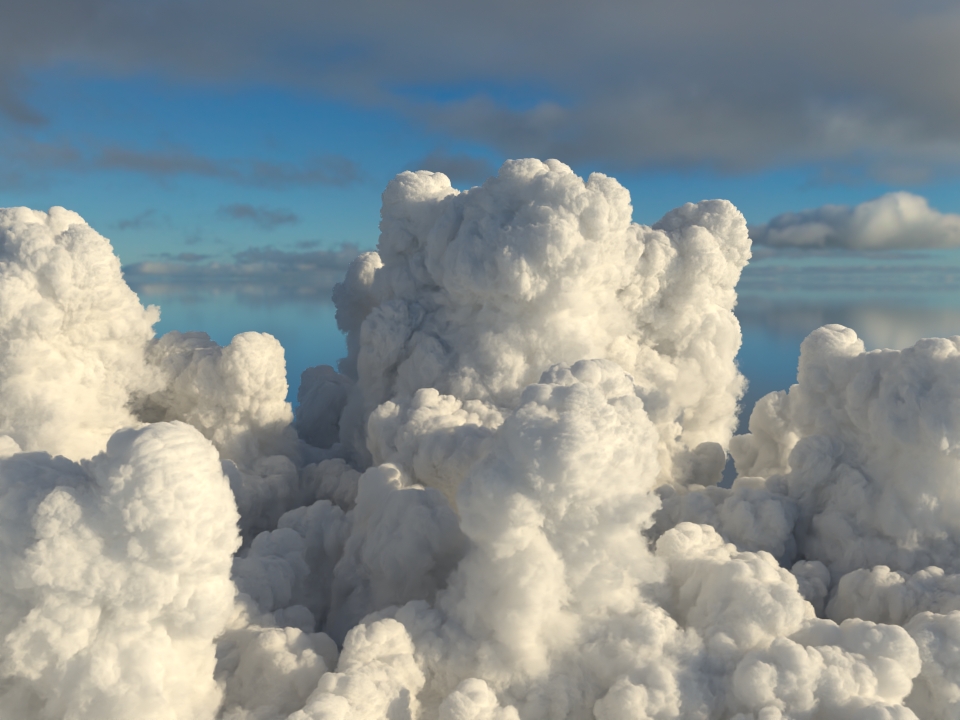
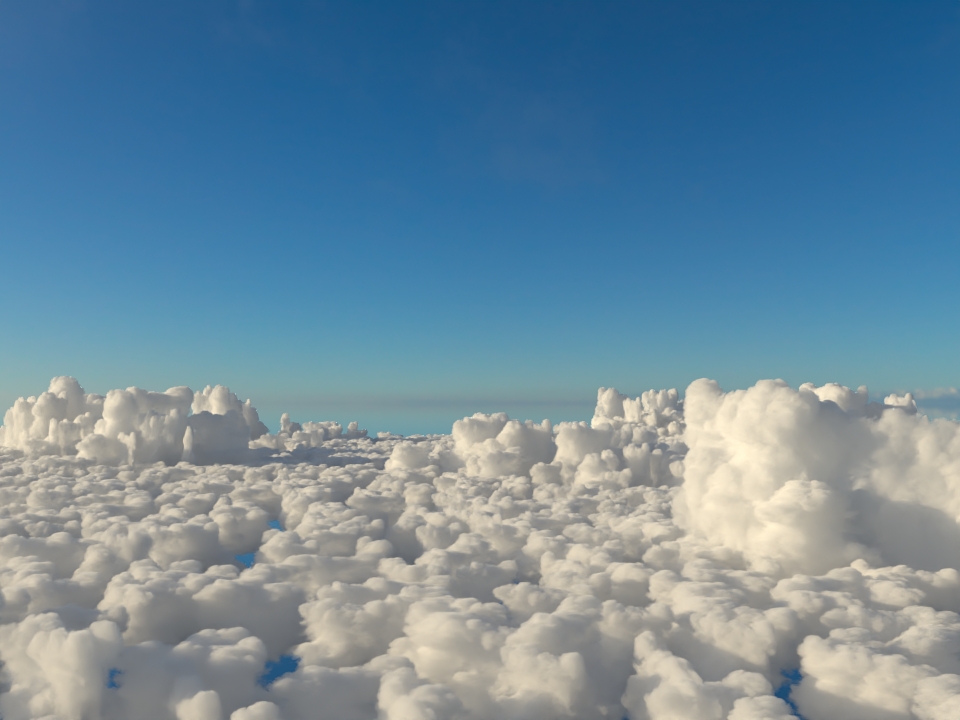
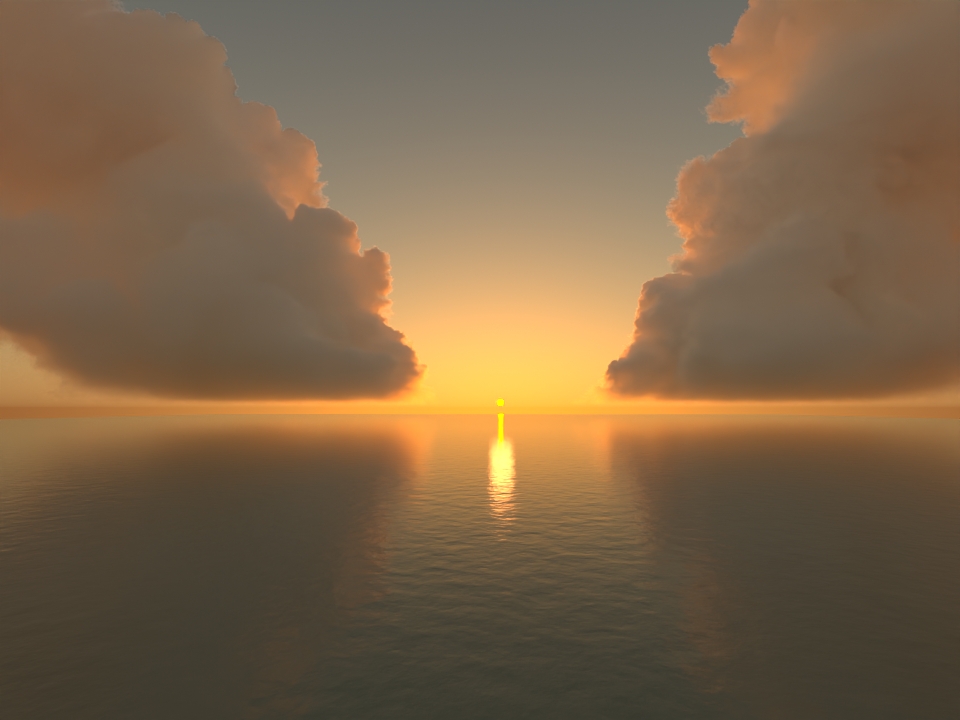




Speedup 1.5x 1.9x 2.6x 2.1x 1.8x mip-mapped volume (6 levels)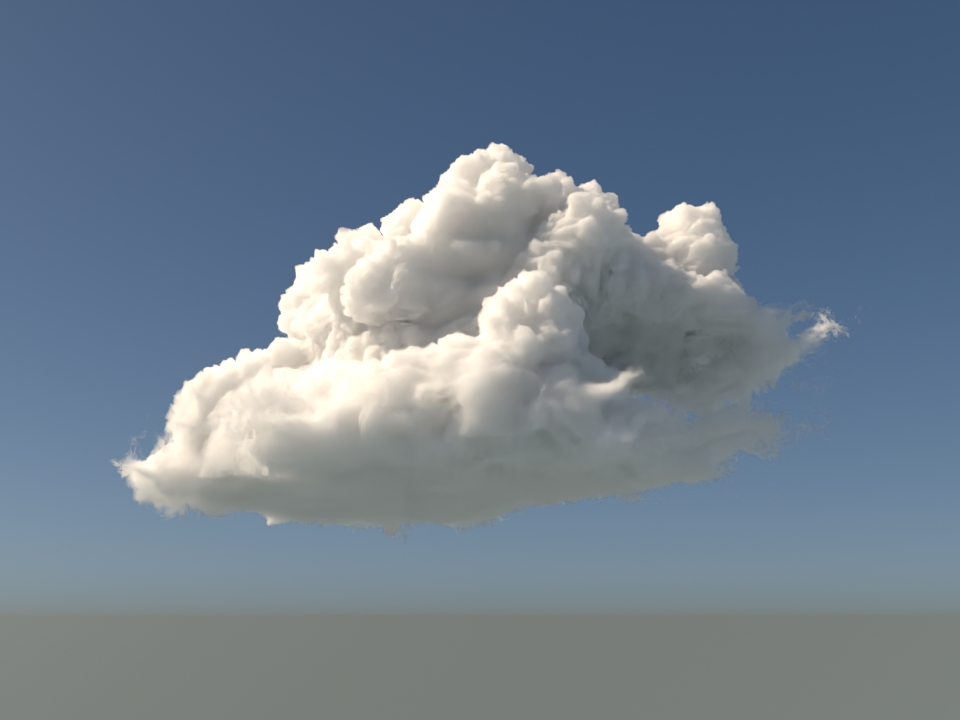 
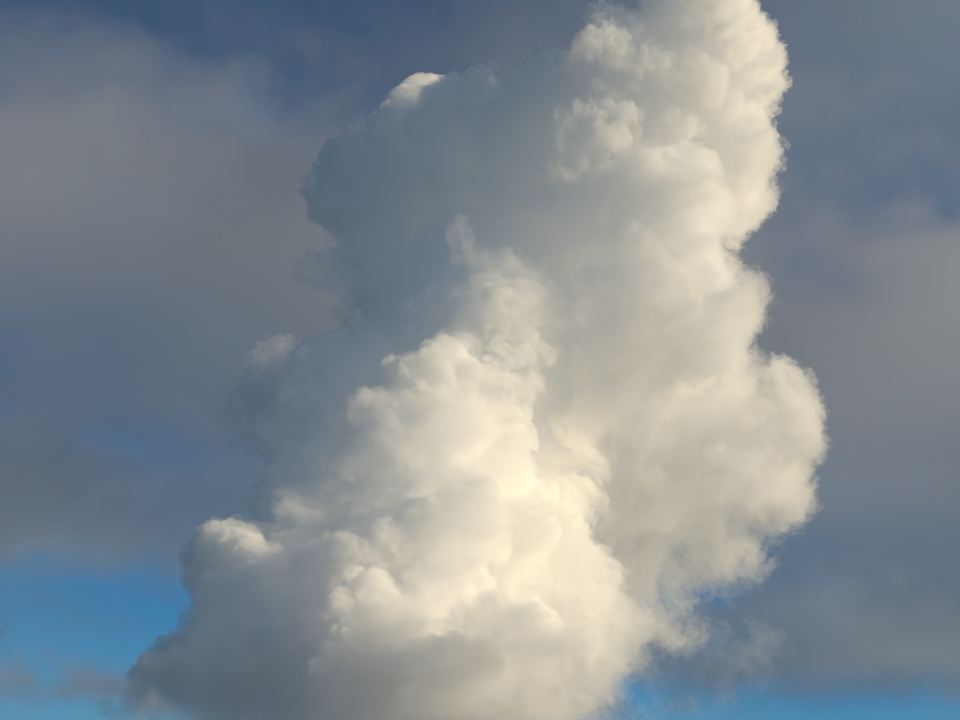
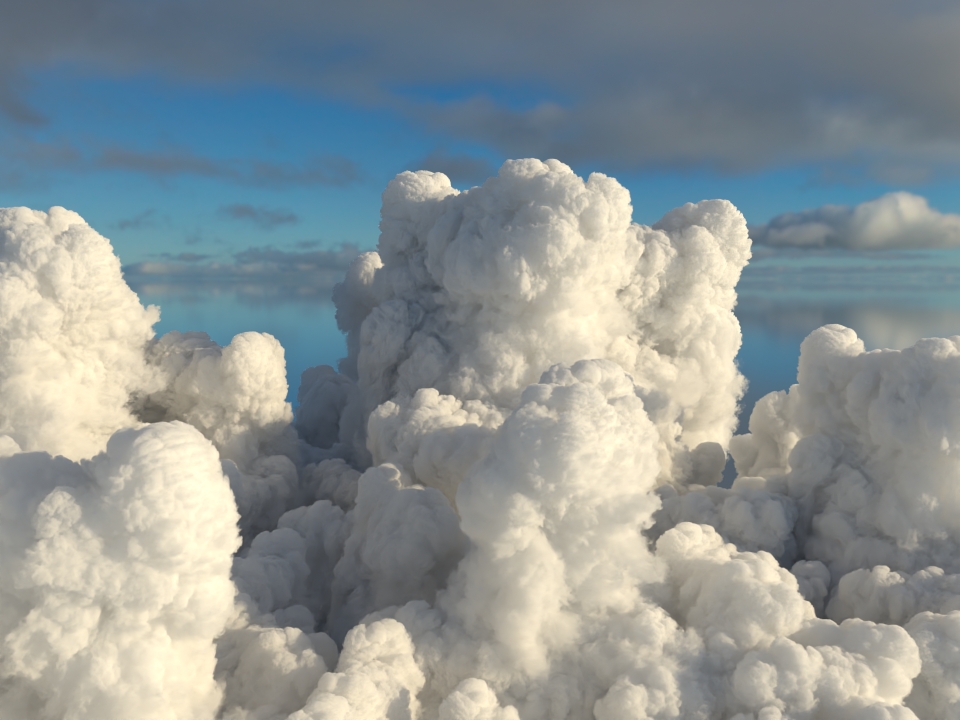
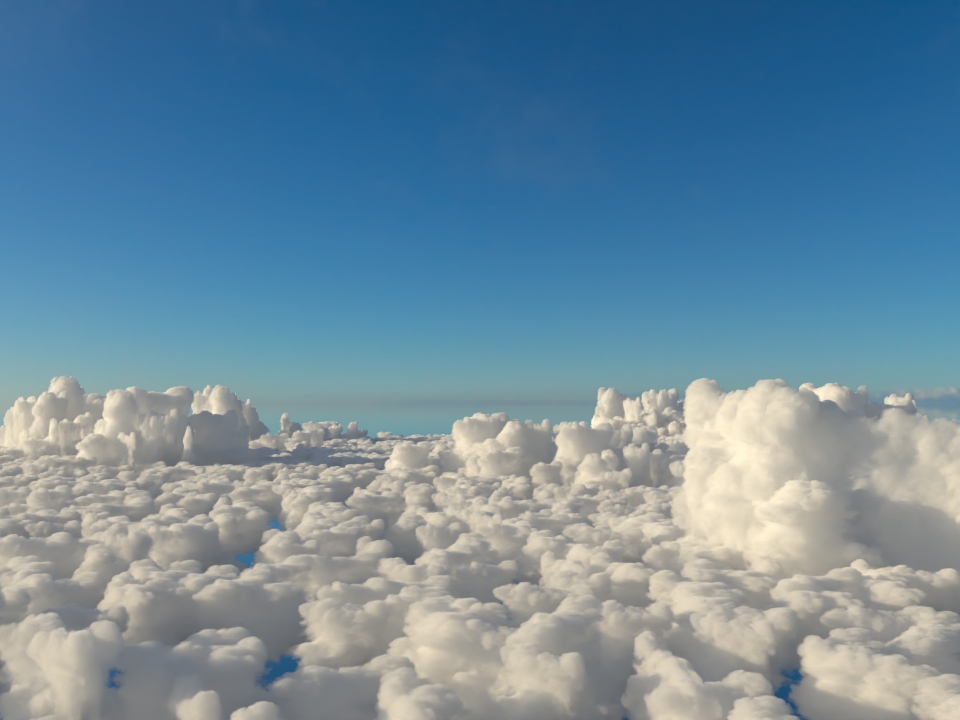




Speedup 2.0x 2.8x 5.2x 3.2x 2.7x
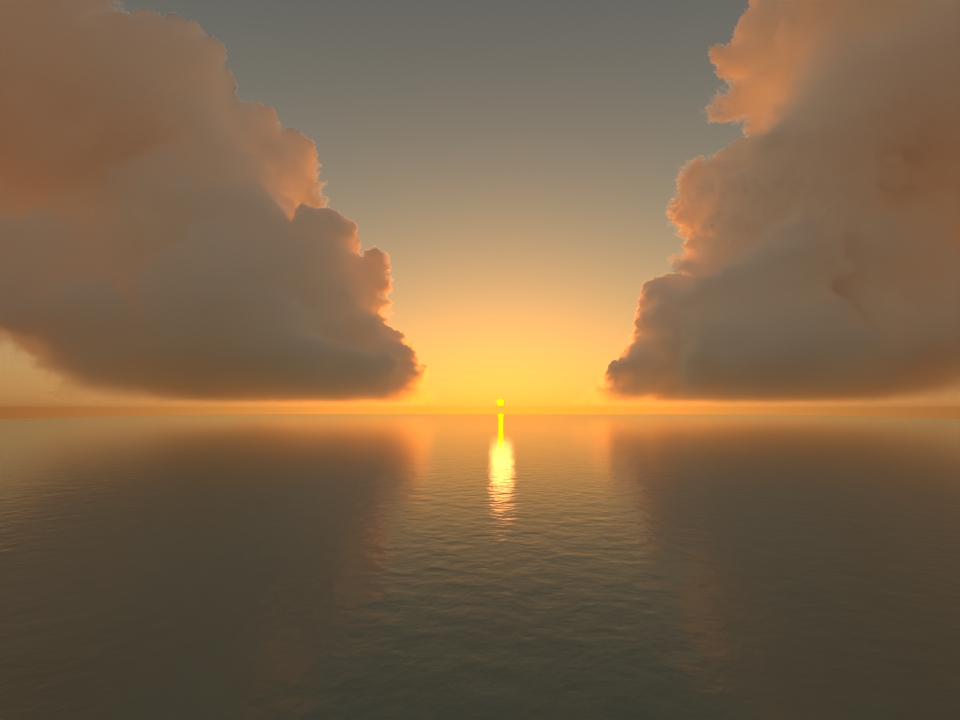
Improved GPU volume rendering performance: GPU rendering of volumes is up to 3.5x faster. (ARNOLD-8936)
GPU rendering speedups wdascloud byc-cloud composition 1 composition 2 sunset clouds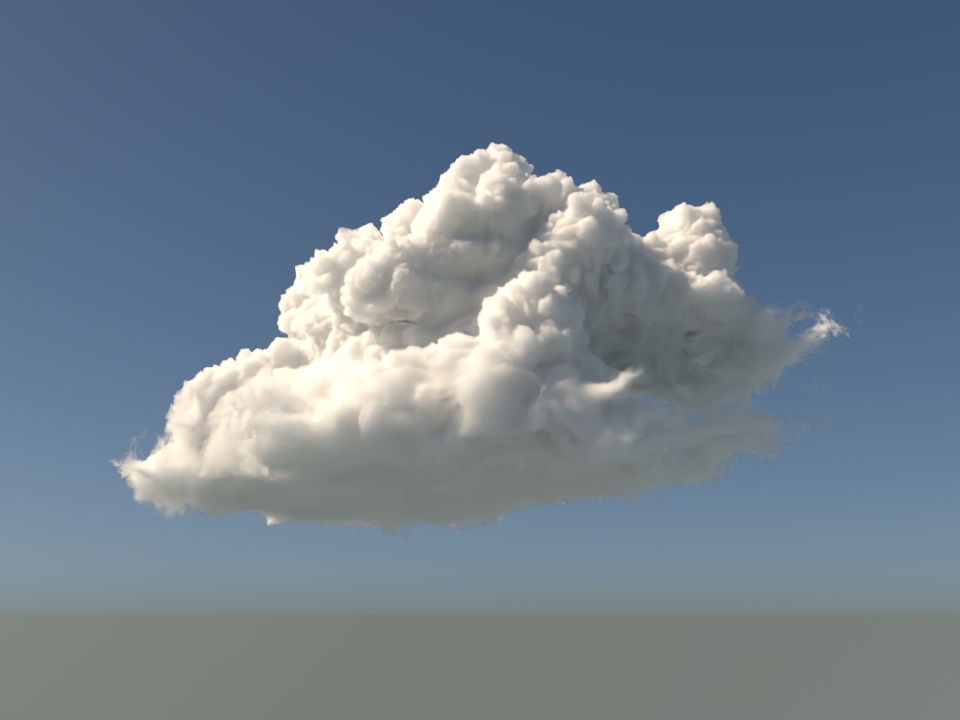 
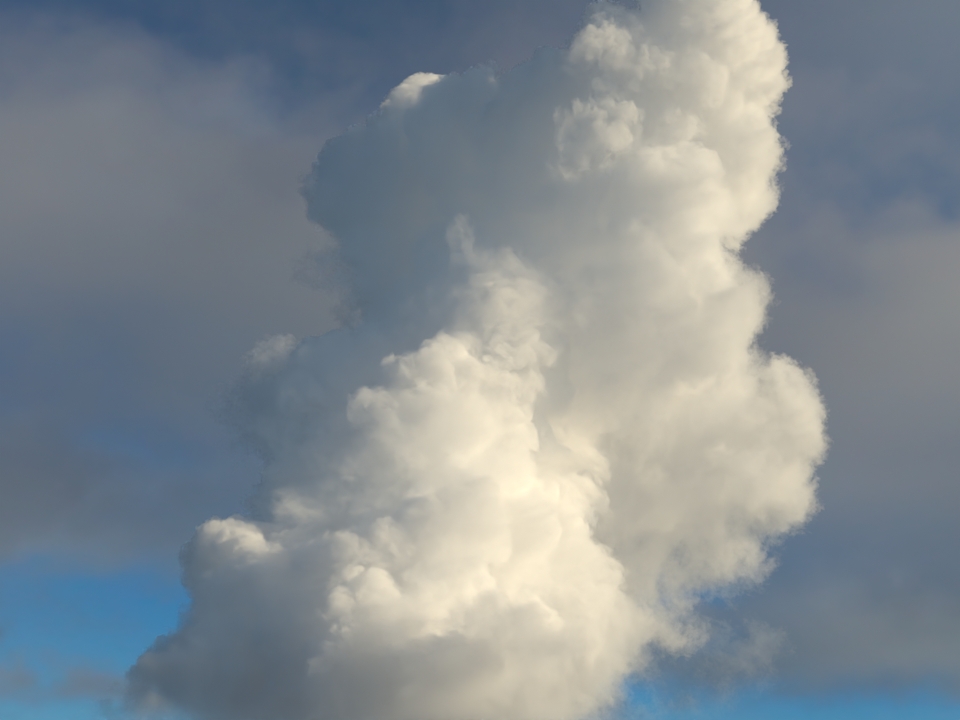
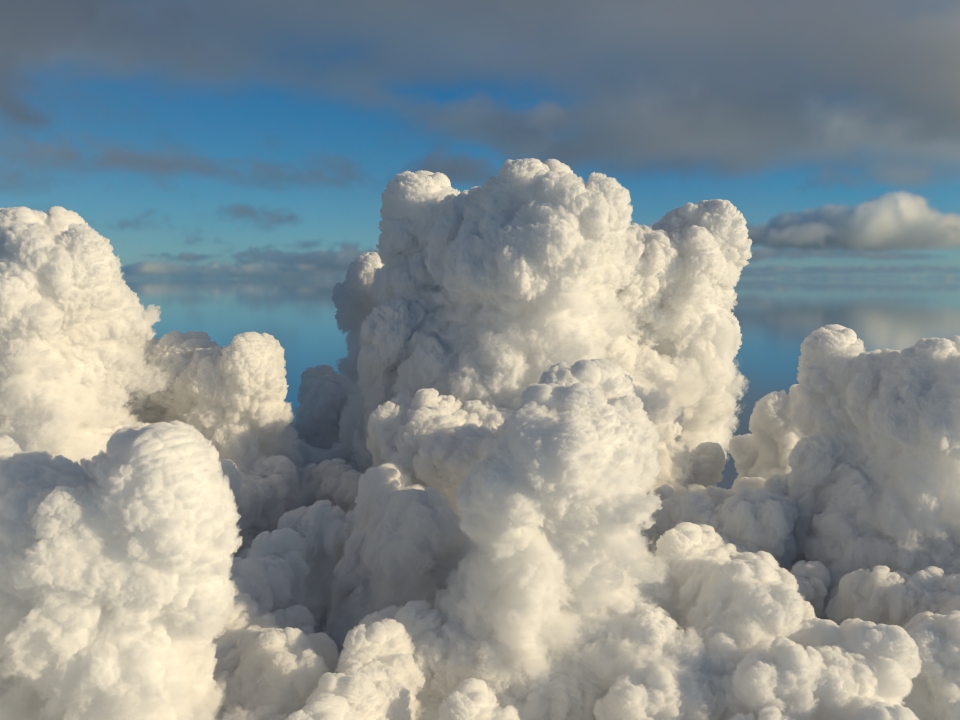
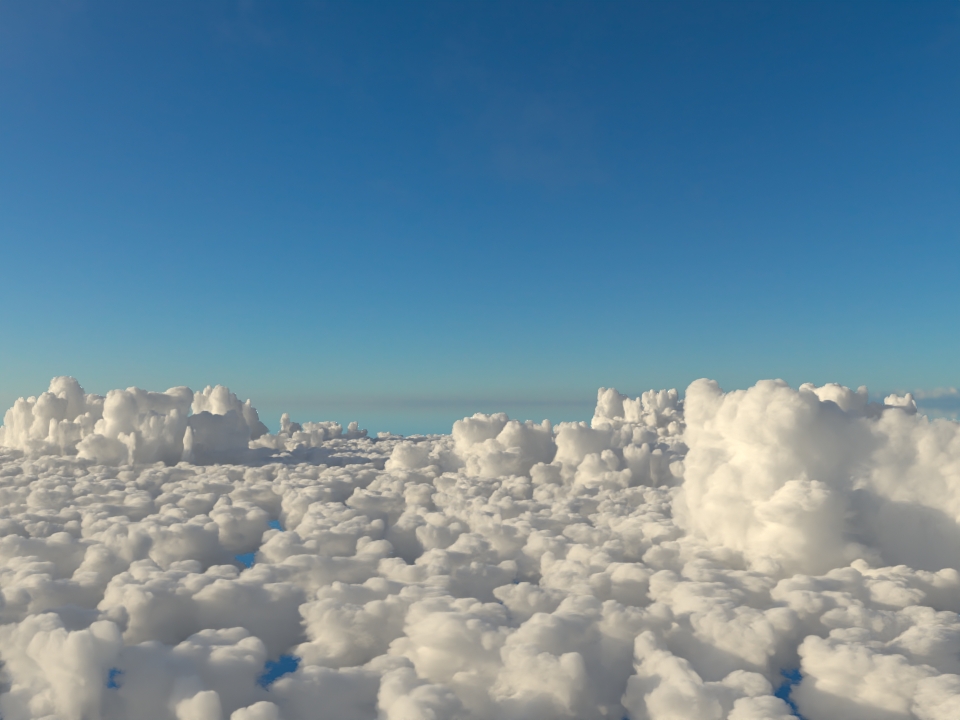
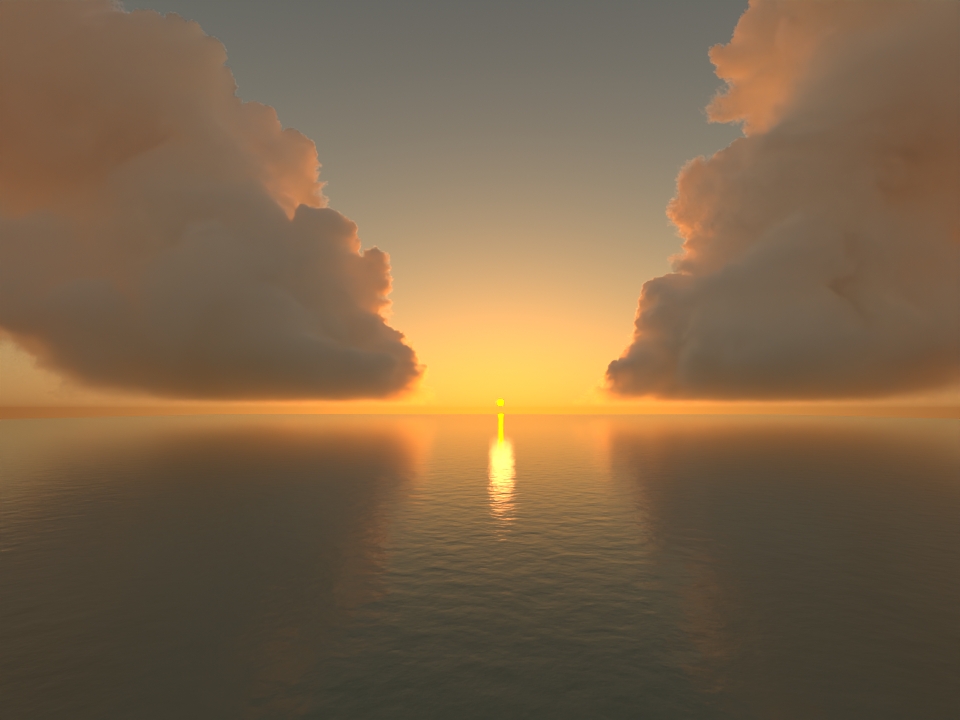




Speedup 2x 1.12x 3.7x 3.5x 1.31x
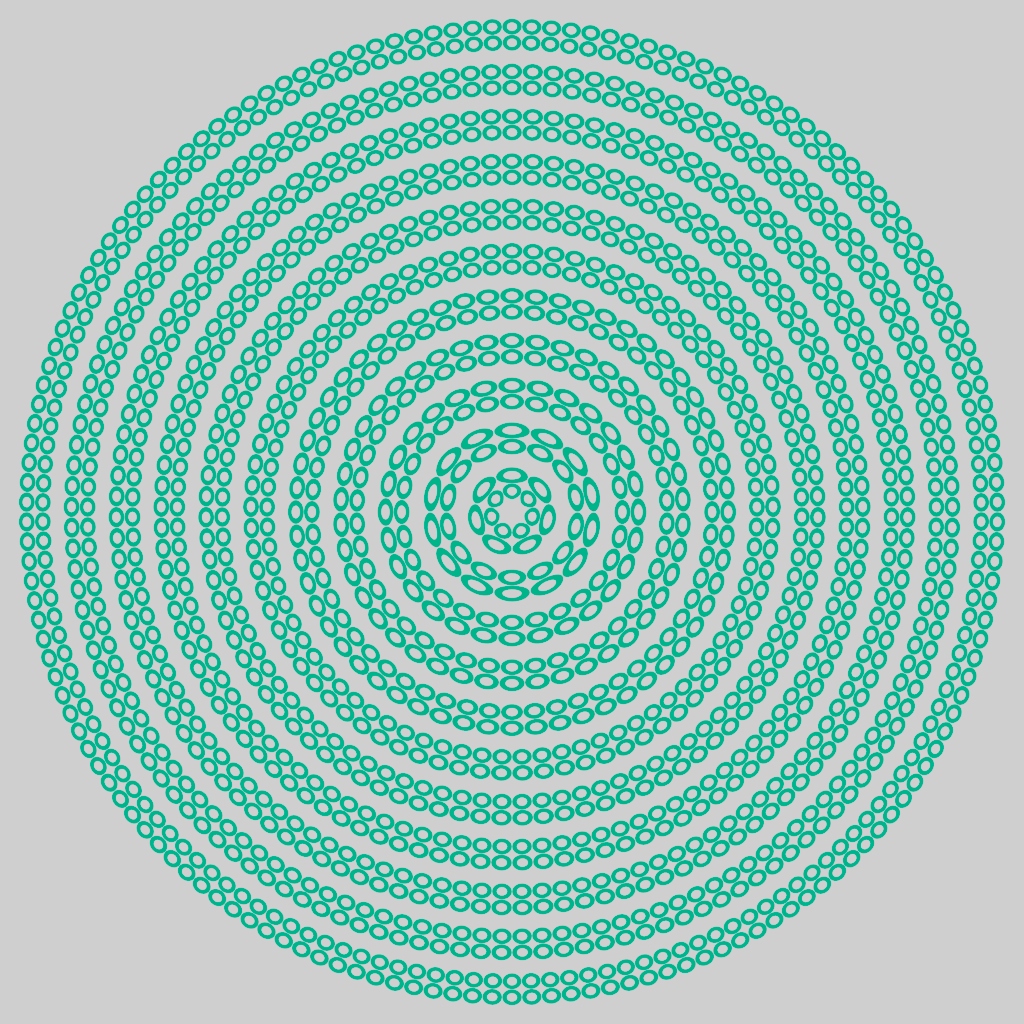
Nearest points shader: The new nearest_points shader samples point clouds from OpenVDB points files, or alternatively, the vertices from points, curves, and polymesh nodes. The shader can output the number of points found, average distance, or an average of a custom user-data attribute from the points. (ARNOLD-15550)


Nearest Points distance → RampRGB (custom) Nearest Points distance → Line → Standard Volume transparent
- pointcloud_search and pointcloud_get OSL support: Support has been added for the
pointcloud_searchandpointcloud_getOSL built-in functions. To specify a points, curves, or polymesh node, use the node name for the point cloud name. To specify an OpenVDB file, use the formatfilename:gridfor the point cloud name. Note: These functions are not yet available on GPU. (ARNOLD-15550)
-
Bloom color dispersion:
The imager_lens_effect node has a new
aperture_dispersionparameter, which controls the amount of color dispersion when inbloom_mode aperture. Increasing the dispersion value spreads the warmer colors further apart; decreasing it makes the colors progressively cooler. A value of 1 gives realistic dispersion. (ARNOLD-16912)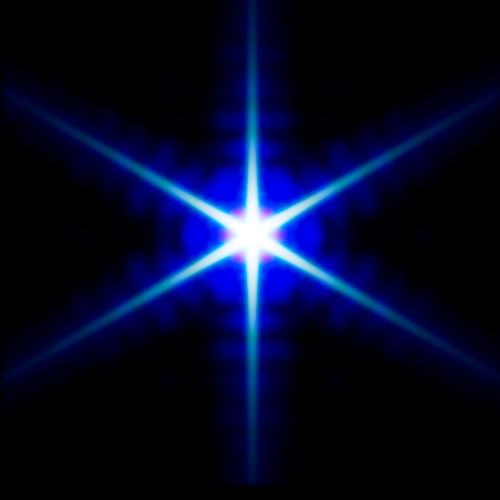
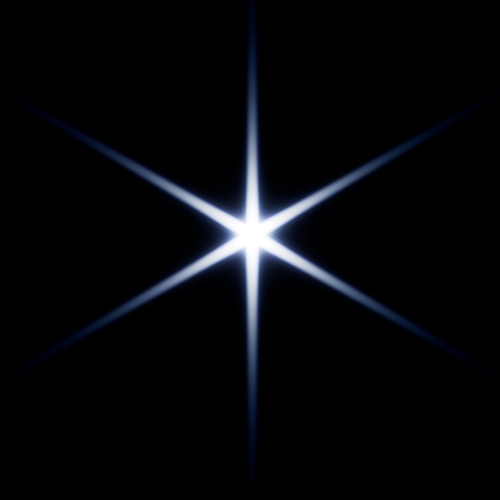
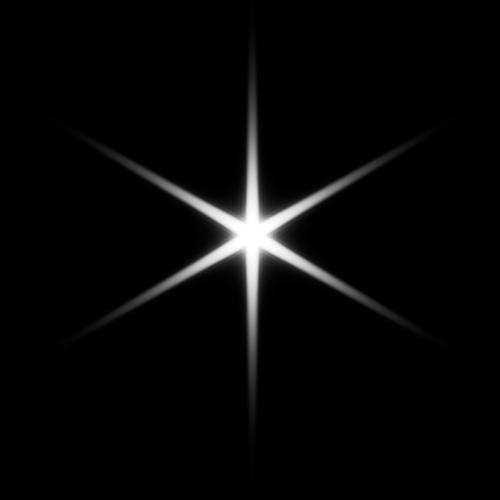
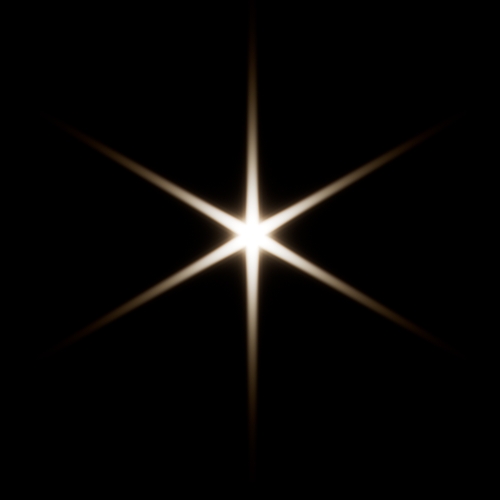
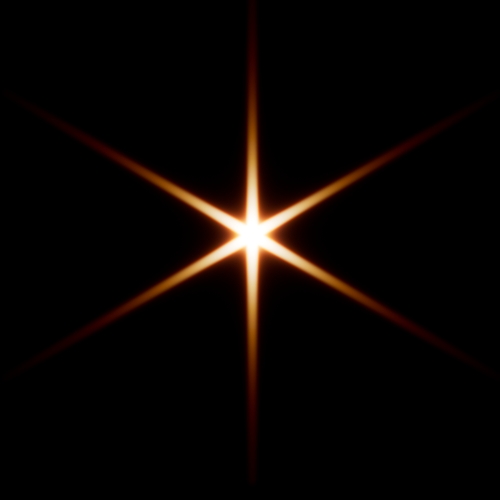




-4 -1 0 1 4
-
Space option in uv_transform:
The uv_transform node now includes a
spaceparameter withtexture(default) andscreenoptions. The texture mode applies transforms to standard texture UVs as before, while the screen mode uses screen UV coordinates. (ARNOLD-14976)
Texture (default) Screen
Cryptomatte option for instances: A new parameter
object_split_instanceswas added to the cryptomatte shader. It determines whether different instances should have different masks or the same one. (ARNOLD-16997)Instancer node instances visible in viewport: Instances created by the
instancernode can now be displayed in the viewport, making it easier to visualize and work with instanced geometry during scene setup and interactive rendering. (ARNOLD-16778)Faster handling of interrupted mesh pre-processing: Interrupting mesh pre-processing during IPR (by for instance moving the camera while the scene is loading) no longer causes slowdowns and wasted work. Speedups are expected to increase with core count and mesh size. We have observed savings measured in minutes. (ARNOLD-16978)
Options node included in JSON statistics: The
optionsnode parameters are now written to the JSON statistics file, making it easier to understand what render settings were used when you analyze performance data. (ARNOLD-8558)Consistent unit rounding in Render Report: The Arnold Render Report now rounds values to a consistent unit, improving readability and comparability. Previously, different statistics could be displayed in mixed units (for example, sometimes in milliseconds and others in seconds), which made comparisons difficult. (ARNOLD-17036)
-
New node-based AOV workflow:
A new
render_outputnode replaces the old string-basedoutputstatements. The global Arnoldoptionsnode has a newdriversparameter that links to thedrivernodes, and eachdrivernode has a list ofrender_outputnodes. (ARNOLD-5774)The
render_outputnode has the following structure:Type Name Unlinkable Default Bounds ------- ------------------- ------- ------ Inputs STRING aov_name RGBA ENUM type rgba NODE filter null STRING layer_name BOOL half_precision false NODE camera null STRING nameFor example,
optionsnode like this:options { outputs 2 1 STRING "RGBA RGBA my_filter driver_output" "diffuse RGBA my_filter driver_output" } driver_exr { name driver_output filename "render.exr" }would become:
options { drivers 1 1 NODE "driver_output" } driver_exr { name driver_output render_outputs 2 1 NODE "my_RGBA_output" "my_diffuse_output" filename "render.exr" } render_output { name my_RGBA_output aov_name "RGBA" type "rgba" filter "my_filter" } render_output { name my_diffuse_output aov_name "diffuse" type "rgba" filter "my_filter" }NOTE: The APIsAiSceneWriteandAiSceneLoadfor.assfiles by default do not export with these nodes. To do so, add the booleanconvert_string_outputsset totruein theAtParamValueMapfor theparamsflag.
Update CER: The Customer Error Reporting (CER) library is updated to v7.2.4. (ARNOLD-16796)
OpenColorIO 2.5: Arnold now includes OpenColorIO 2.5.0. The upgrade brings support for built-in ACES 2 configs and many other improvements and fixes. See the full release notes for more details. (ARNOLD-17107)
USD Enhancements
Lightweight instancing: Arnold now renders USD instances through a lightweight instancing system that creates fewer Arnold nodes. Instancing is now more memory efficient and time to first pixel is faster, because the scene is quicker to initialize. For example, in the Intel Jungle Ruins scene, the time to first pixel in Houdini Solaris is 85% faster, and the memory usage is 42% lower. usd#2459
USDLux standardization: The Arnold
optionsnode has a newusdlux_versionparameter that enables USDLux compatibility. Settingusdlux_versionto25.05activates the current Arnold implementation of the USDLux standard for USD lights. This early development preview includes support for IES orientation and brightness normalization.Asset resolver: The Autodesk asset resolver is now integrated into the USD procedural. You can now render USD files containing asset-resolving directives, such as tokens and path replacements, using a mapping file and the environment variables described in the Maya documentation.
Volume fieldIndex: Rendering VDB volumes now supports the
fieldIndexattribute of theOpenVDBAssetprimitive. You can now render a specific grid instead of all grids with a given name. usd#2394
API Changes
- Mip-mapped volume generation: You can now generate mip-mapped volumes either with the Arnold API, or with kick. The Arnold API includes a new
AiVolumeFileMakeLODsfunction. kick has a new-makevolumelodscommand-line flag. Both the API and the kick flag take three arguments: the input file, the output file, and the maximum number of levels to generate. The actual number of levels generated maybe lower than the number requested. (ARNOLD-17114)
-
Asset API:
New API functions allow you to query file dependencies (assets) defined in an
Arnold universe (
AiUniverseGetAssetIterator), scene file (AiSceneGetAssetIterator), or procedural (AiProceduralGetAssetIterator). (ARNOLD-16891)For example, querying assets of
scene.ass:AtAssetIterator* it = AiSceneGetAssetIterator("scene.ass"); while (!AiAssetIteratorFinished(it)) { const AtAsset* asset = AiAssetIteratorGetNext(it); // do something with the asset } AiAssetIteratorDestroy(it);
-
Assets in custom scene formats:
Plugin developers can now implement the
scene_get_assetsmethod in their scene format plugin to return file dependencies (assets) specific to that format. This method is optional, and if it is not implemented, Arnold loads the scene and queries assets from the generated Arnold universe. (ARNOLD-16891)For example, this code returns 2 assets:
scene_get_assets { AtAsset* asset1 = AiAsset("/path/to/mytexture.exr", AtFileType::Asset); AiAssetAddReference(asset1, "mytexture.exr"); AtAsset* asset2 = AiAsset("/path/to/myvolume.vdb", AtFileType::Asset); AiAssetAddReference(asset2, "myvolume.vdb"); AtArray* assets = AiArrayAllocate(2, 1, AI_TYPE_POINTER); AiArraySetPtr(assets, 0, asset1); AiArraySetPtr(assets, 1, asset2); return assets; }
File type metadata: A new
file_typemetadata can be defined on file path parameters to tell how the path needs to be resolved. If not defined, the file type is guessed from the supported extensions of the parameter (extensions metadata) or the extension of the specified file, if any. Available values arecustom,asset,texture,procedural,osl, andplugin(seeAtFileTypeenum). (ARNOLD-17289)Point cloud API: New API functions allow C++ shaders to perform point cloud queries that are very similar to the OSL specification for its
pointcloud_searchandpointcloud_getfunctions. The typical usage pattern is to callAiPointCloudSearchto get a list of indices and a count of nearest points, and then call theAiPointCloudGetfamily of functions to query particular attributes from those points. To specify a points, curves, or polymesh node, use the node name for the point cloud name. To specify an OpenVDB file, use the formatfilename:gridfor the point cloud name. (ARNOLD-15550)Mip-mapped volume generation: The Arnold API and kick can now generate mip-mapped volumes . The Arnold API includes a new
AiVolumeFileMakeLODsfunction. kick has a new-makevolumelodscommand-line flag. Both the API and the kick flag take three arguments: the input file, the output file, and the maximum number of levels to generate. (ARNOLD-17114)
Incompatible Changes
Required NVIDIA driver version must be newer than 582.16/580.126: GPU rendering and OptiX denoising do not work with driver versions 582.16/580.126 (windows/linux) and older, and will log an error and abort the render. Note that you can use New Feature Branch drivers. (ARNOLD-17405)
color_jittershader now correctly installed as RGB type: Thecolor_jittershader was mistakenly installed as an RGBA type instead of the correct RGB type, which caused unnecessary complexity when linking it to other shaders in DCC tools. (ARNOLD-17095)
-
Standard Volume channel references to OpenVDB indexed grids: Channel parameters like standard_volume.density_channel now use grid names without a grid index. (ARNOLD-16753)
For example, density_channel density works with these volume.grids:
- density
- density, density[1]
- density[0], density[1]
- dens*
A standard_volume channel with an index, like density_channel density[1], returns all zeroes. If you need different shaders on different grids, you can have different volume nodes for each grid index, and one standard_volume applied to each volume.
Bug Fixes
- HTOA-3015 - The Houdini help browser now works as expected when HtoA is installed
- HTOA-3104 - Fixed issue where the position of the first point in an rgb ramp could not be changed
- HTOA-3177 - Fixed a subnet crash when connecting an input
- ARNOLD-17291 - Fix out-of-bounds access when sampling mesh lights
- ARNOLD-17349 - Volumes appear more accurate under large camera rotation blur
- ARNOLD-17341 - Random crash while GPU rendering and interactively modifying OSL shaders
- ARNOLD-17350 - Fixed incorrect bounding of lights with nearly co‑directional surface normals
- usd#2469 - Authored primvars should not have elementSize set to the array size
- usd#2476 - log_verbosity setting should affect both console and file logs
- usd#2492 - Fix path resolving issue for OCIO config with absolute paths
- usd#2504 - Ensure geom subsets don't get appended to USD in animated exports
System Requirements
Houdini, Houdini FX, Houdini Indie and Houdini Education
- 20.0.896
- 20.5.684
- 21.0.596
Linux with at least glibc 2.17 and libstdc++ 11.2.1 (gcc 11.2.1) for Houdini 20/20.5. This is equivalent to Rocky 8.
macOS 11 or later
Apple Mac models with M series chips are natively supported by HtoA
x86-64 CPUs need to support the SSE4.1 instruction set. Apple Mac models with M series chip are supported natively mode.
GPU rendering works on Windows and Linux only and requires an NVIDIA GPU with the Maxwell architecture or later.
- On Linux, we recommend 590.48 or higher drivers.
- On Windows, we recommend 591.28 or higher drivers.
Optix™ denoiser requires an NVidia GPU with CUDA™ Compute Capability 5.0 and above.
Intel OIDN GPU support is limited to:
- MacOS
- Apple native CPUs (M1 and newer)
- Windows
- Intel Xe dedicated and integrated GPUs
- NVIDIA GPUs using Turing or newer architectures
- MacOS