Results analysis for a Process Simulation study
This feature is part of an extension. Extensions are a flexible way to access additional capabilities in Fusion. Learn more.
When you solve a Process Simulation study, you can choose to view the results for displacement and recoater clearance and risk, and check the different types of structure that make up the build.
Displacement
Displacement is the extent to which a part warps or distorts during the additive manufacturing process. This is mainly caused by the cycles of heating and cooling that takes place during the process. Extremely hot temperatures cause thermal expansion of material and then rapid cooling allows material to contract, which induces warpage.
A Scale Factor lets you exaggerate the visual displacement on the canvas to help make it clear where the part changes in shape the most.
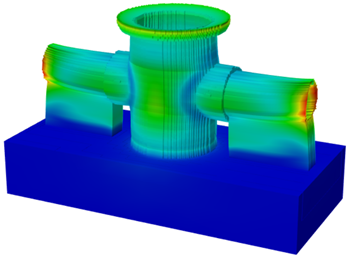
You can export an .stl file or a .3mf file of the warped part that reflects the displacement predicted by the solved Process Simulation study. You can use these files and compare the predictions with scans of the real, physical part to validate the study, or use them to check that a part fits within an assembly. The .3mf file stores the color-coded displacement information.
You can also export an .stl file, or create a mesh body, of the reverse-warped part that automatically compensates for the displacement predicted by the solved Process Simulation study. When additively manufacturing a compensated part, the part warps to the originally desired shape.
Recoater clearance and risk
The recoater of an additive machine deposits the layers of metal powder particles on a build platform. Interference with a recoater can occur when the top of the fused part distorts up through the powder layer and into the path of the recoater blade.
Recoater clearance is the percentage of the powder layer that is free of upward distortion. Typically, the smallest acceptable threshold is 80%, but the acceptable level of clearance should be decided based on material, processing conditions, recoater type, and acceptable risk.
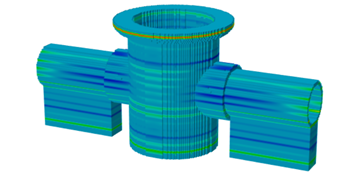
Structure type
The structure type identifies the part itself, the supports, and the build platform. It is used to investigate any areas of the mesh that are under constrained, which means a more accurate mesh is required.