Shape optimization study
A Shape Optimization study should be used if you are interested in designing lightweight, structurally efficient parts. Shape Optimization provides an intelligent strategy for maximizing part stiffness based on the constraints and loads you specify. The result of a Shape Optimization study is a 3D mesh that can be used to guide your design refinement.
The results from a Shape Optimization Study do not reflect the stress created from the loads. It is important to validate that the new design can withstand the operational loads using a Static Stress Study or other stress related study type.
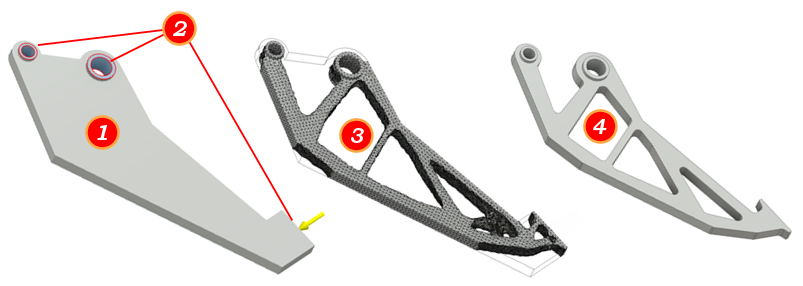
The image below illustrates how Shape Optimization can become part of your design process.
- The first step is to create a build-volume or approximation of the part model. The model should contain requisite contact or constraint points, such as the two pin locations, and the contact faces where the loads are applied.
- With the build-volume defined, you can specify regions to preserve, or hide, from the optimization routine. You can also apply constraints and loads on the model.
- With the design criteria specified, you run a Shape Optimization study which returns a mesh in response to the criteria.
- The mesh serves as a guide to modify the original geometry.
Shape Optimization analysis examples
The following list contains a examples for which a Shape Optimization study might be appropriate:
- Conceptual Design (optimized structures)
- Lightweighting (such as, for aircraft and land vehicle components)
- Determine where to safely remove material to provide wiring, piping, or duct work access with a minimal impact on the structural stiffness and strength.