This panel contains objects that guide the liquid simulation using either a polygon mesh or a cached, lower-resolution simulation.
With guides, you can perform a detailed, high-resolution simulation that is restricted to the top surface layer, reducing the amount of memory and computation time required. Guides are very useful when creating simulations of large fluid bodies such as lakes and oceans.
Guide System rollout
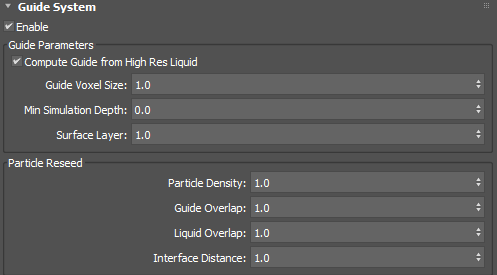
- Enable
- Enables the guide system.
Guide Parameters group
- Compute Guide from Hi Res Liquid
- Computes a final guiding shape that takes the high-resolution liquid into account. This allows colliders to fall into the liquid and penetrate quite deeply without the need to increase Min Simulation Depth (which would affect the number of particles and voxels required across the whole simulation). You can try turning this off if you experience problems, for example, if the simulation does not hold its shape in certain situations. You can also turn this off to speed up computations, but this can result in holes at the main liquid surface if the simulation is very splashy.
- Guide Voxel Size
- Sets a scaling factor for the Master Voxel Size, which is used to voxelize the guide shapes.
- Min Simulation Depth
- Sets the depth to simulate below the top liquid surface in scene units. You may need to change this depending on the scale of the modelled scene.
- Surface Layer
- Sets the height of the simulated layer on top of the guide surface, in scene units. This can be useful for surface splashes.
Particle Reseed group
- Particle Density
- Controls the number of particles to add per voxel in air pockets.
- Guide Overlap
- Multiplies the Master Voxel Size to determine how deeply into the guiding shape and liquid shape to reseed.
- Liquid Overlap
- Multiplies the Master Voxel Size to determine how deeply into the guiding shape and liquid shape to reseed.
- Interface Distance
- Sets the minimum distance in scene units from the air-liquid boundary, below which particles are not reseeded. This prevents noise at the surface.
Guide Mesh Parameters rollout
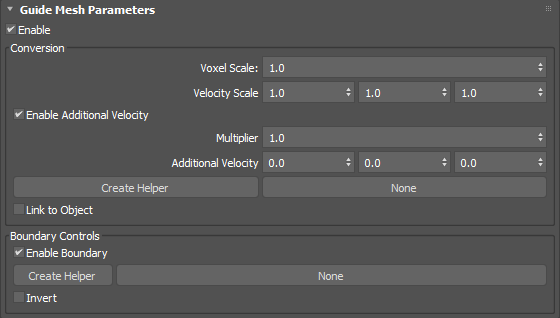
This rollout only appears when an existing guide mesh is selected in top or left pane (depending on whether the Simulation View layout is vertical or horizontal).
Conversion group
- Voxel Scale
- Sets a scaling factor for the Master Voxel Size used to initially voxelize meshes sharing this property.
- Velocity Scale
- Controls the proportion of velocity that is inherited from the emitters' animated transformation and deformation by the fluid at the time of emission in each of the world X, Y, and Z axes.
- Enable Additional Velocity
- Adds extra velocity to any existing velocity from other sources (such as velocity inherited from the emitter's animation).
- Additional Velocity Multiplier
- Sets a multiplier to scale additional velocity uniformly across all axes.
- Additional Velocity
- Sets the base velocity to add in world coordinates.
- Create Helper
- Creates an arrow helper object in the scene. The orientation of the arrow adjusts the direction of the additional velocity.
- Link to Object
- When enabled before creating a Additional Velocity Helper, automatically links the Helper Object to the Scene Object.
Boundary Controls group
- Enable Boundary
- Enables boundary control to limit the area in which the simulation occurs.
Tip: When working with guided simulations, you can use boundaries to preview a smaller area of the simulation in order to save computation time while making adjustments.
- Create Helper
- Creates a Volume helper object in the scene. The valid types for boundaries are Box and Sphere.
- None
- Picks a Volume helper already added to the scene. The button will update with the name of the currently-selected helper.
- Invert
- Inverts the area of the boundary.
Guide Emitter Parameters rollout
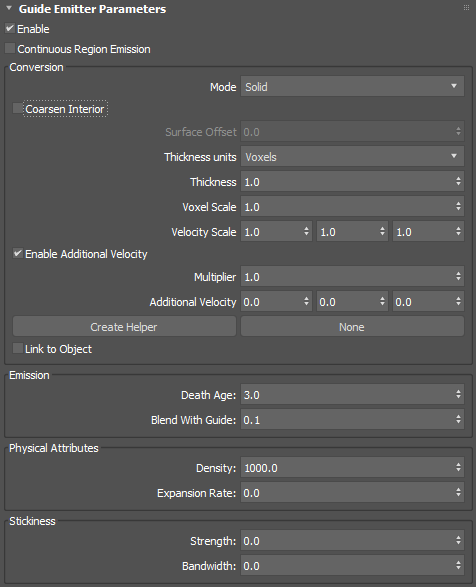
This rollout only appears when an existing guide emitter is selected in top or left pane (depending on whether the Simulation View layout is vertical or horizontal).
- Enable
- Enables liquid emission from the associated emitters.
- Continuous Region Emission
- Refills voxels that become empty with more particles. Enable when simulating liquid sources like spouts and jets; disable for a pool or single drop of liquid.
Conversion group
- Mode
- Controls how the emitter is voxelized, either Solid, Shell, or Solid (Robust).
- Solid creates a solid volume including the mesh interior. The mesh should be both manifold and watertight.
- Shell create a thin shell around the mesh surface. In this mode, Thickness should typically be 1.0 or more.
- Solid (Robust) is an alternative to Solid that usually gives better results for volumes with fine detail, openings leading to cavities, or non-watertight surfaces. However, this setting does not handle fluids inside completely enclosed regions.
- Coarsen Interior
- Saves memory by performing additional coarsening of the voxels inside the volume when the conversion mode is Solid (Robust), especially with self-intersecting meshes.
- Surface Offset
- Sets the distance in voxel widths used to close (dilate and then erode) the solid voxels when the conversion mode is Solid (Robust). The internal minimum is 1.0 so that only greater values have an effect. Note that high values can create artifacts.
- Thickness Units
- Sets whether thickness is in voxels or world-space units. When set to Voxels, the effective thickness depends on the Master Voxel Size of the simulation.
- Thickness
- Sets the amount to thicken the mesh. For solid shapes that are already quite thick, you can use 0.0 for a precise boundary or even negative values to shrink along the surface normals. For thinner volumes and shells, you should use larger values to prevent holes.
- Voxel Scale
- Sets a scaling factor for the Master Voxel Size used to initially voxelize meshes that share this property.
- Velocity Scale
- Controls the proportion of velocity that is inherited from the emitters' animated transformation and deformation by the fluid at the time of emission in each of the world X, Y, and Z axes.
- Enable Additional Velocity
- Adds extra velocity to any existing velocity from other sources (such as velocity inherited from the emitter's animation).
- Multiplier
- Sets a multiplier to scale additional velocity uniformly across all axes.
- Additional Velocity
- Sets the base velocity to add in world coordinates.
- Create Helper
- Creates an arrow helper object in the scene. The orientation of the arrow adjusts the direction of the additional velocity.
- Link to Object
- When enabled before creating a Additional Velocity Helper, automatically links the Helper Object to the Scene Object.
Emission group
- Death Age
- Sets the length of time in seconds that a particle can be outside its emission region before it is deleted.
- Blend With Guide
- Sets the blend weight of the input velocities from the guide. This helps to provide a smooth transition from the simulation to the guide.
Physical Attributes group
- Density
- Sets the physical density of the fluid. For example, water has a higher density than oil.
- Expansion Rate
- Expands or contracts the liquid within the emitter. Positive values push particles out of the emitter in all directions, while negative values pull particles in. A value of 0.0 neither pushes nor pulls.
Stickiness group
- Strength
- Sets the amount that the fluid from this emitter adheres to nearby colliders.
- Bandwidth
- Sets how close the fluid from this emitter needs to be to a collider in order to cause stickiness, in world-space units.