Use Collision objects to redirect fluid particles and cause splash effects.
Collider Conversion Parameters
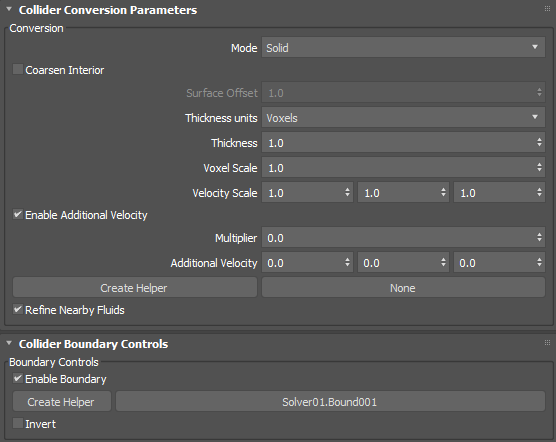
Conversion group
- Mode
- Controls how the collider is voxelized, either Solid, Shell, or Solid (Robust).
- Solid creates a solid volume including the mesh interior. The mesh should be both manifold and watertight.
- Shell create a thin shell around the mesh surface. In this mode, Thickness should typically be 1.0 or more.
- Solid (Robust) is an alternative to Solid that usually gives better results for volumes with fine detail, openings leading to cavities, or non-watertight surfaces. However, this setting does not handle fluids inside completely enclosed regions.
- Coarsen Interior
- Saves memory by performing additional coarsening of the voxels inside the volume when the conversion mode is Solid (Robust), especially with self-intersecting meshes.
- Surface Offset
- Sets the distance in voxel widths used to close (dilate and then erode) the solid voxels when the conversion mode is Solid (Robust). The internal minimum is 1.0 so that only greater values have an effect.
Note: High values can create artifacts.
- Thickness Units
- Sets whether thickness is in voxels or world-space units. When set to Voxels, the effective thickness depends on the base voxel size of the simulation.
- Thickness
- Sets the amount to thicken the mesh. For solid shapes that are already quite thick, you can use 0.0 for a precise boundary or even negative values to shrink along the surface normals. For thinner volumes and shells, you should use larger values to prevent holes.
- Voxel Scale
- Sets a scaling factor for the base voxel size used to initially voxelize meshes that share this property.
- Velocity Scale
- Controls the proportion of velocity that is inherited from the emitters' animated transformation and deformation by the fluid at the time of emission in each of the world X, Y, and Z axes.
- At the default value of 1.0, any fluid that collides with a mesh reacts normally to the mesh's animation.
- At 0.0, the fluid reacts as if the mesh is motionless, regardless of the mesh's actual animation.
- Between 0.0 and 1.0, the fluid reacts as if the mesh is moving more slowly. For example, this can be used to dampen the splashes created by a fast-moving collider hitting a volume of water.
- Above 1.0, the fluid reacts as if the mesh is moving more quickly. This can be used to exaggerate the splashes from a collider hitting a volume of water.
- Below 0.0, the fluid reacts as if the mesh is moving in the opposite direction from its actual animation.
- Enable Additional Velocity
- Adds extra velocity to any existing velocity from other sources (such as velocity inherited from the emitter's animation).
- Multiplier
- Sets a multiplier to scale additional velocity uniformly across all axes.
- Additional Velocity
- Sets the base velocity to add in world coordinates.
- Create Helper
- Creates an Arrow helper object in the scene. The orientation of the arrow adjusts the direction of the additional velocity.
- None
- Picks an Arrow helper already added to the scene. The button will update with the name of the currently-selected helper.
- Refine Nearby Fluids
- Prevents the coarsening of fluid resolution in areas close to the collider when Spatial Adaptivity is enabled in the Solver Properties. Disable this option for colliders where less detail is required.
Collider Boundary Controls
Boundary Controls group
- Enable Boundary
- Enables boundary control to limit the area of effect of the collider.
- Create Helper
- Creates a Volume helper object in the scene. The valid types for boundaries are Box and Sphere.
- None
- Picks a Volume helper already added to the scene. The button will update with the name of the currently-selected helper.
- Invert
- Inverts the area of the boundary.