Sampling and Ray Depth - Arnold for 3ds Max
| Further Reading |
|---|
| See also Samples in the Arnold User Guide |
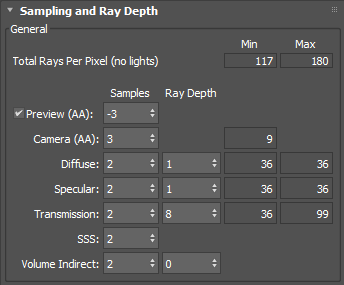
The following information covers sampling and ray_depth settings in MAXtoA.
Further information about sampling and removing noise can be found here.
General
Preview (AA)
The initial AA samples used for the first progressive render. Negative values sub-sample the render, allowing faster feedback in the render window.

Initial Sampling Level from -6 to 0
Adaptive and Progressive Sampling
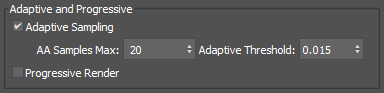
Arnold has the capability of adapting the sampling rate of each pixel when the enable_adaptive_sampling render option is enabled, allowing it to dedicate a greater number of camera samples (and thus also a greater amount of render time) to the pixels that show a greater variation in their sample values.
Ray Depth
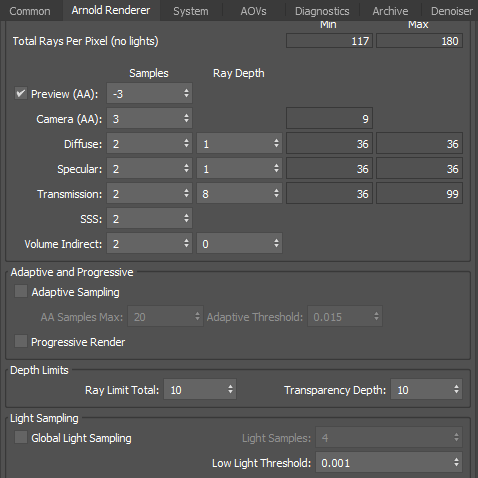
Ray_depth allows you to configure settings that limit the ray recursion based on ray type. Higher values will increase render time.
Global Light Sampling
When enabled, the light sample settings on individual lights are ignored and the overall contribution of all lights together is computed using only the specified number of samples.
It does not apply to environment, directional lights, volumes, and GPU rendering.
Advanced
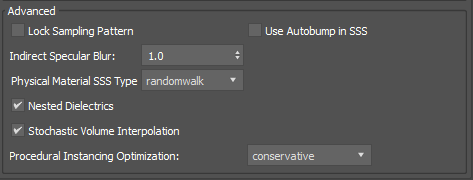
Physical Material SSS Type
The SSS type that is selected when translating the Physical Material's SSS parameters to the Arnold's Standard Surface shader.
Nested Dielectrics
Enables the nested dielectrics system for IOR tracking in scenes with adjacent dielectrics. Defaults to on.
Stochastic Volume Interpolation
The tricubic interpolation mode of AiVolumeSampleXXX() calls, such as those used by the standard_volume shader, now uses a stochastic method of interpolation that greatly reduces the amount of voxel data read in each sample call. This can speed up rendering by as much as 20% in assets such as the WDAS cloud data set. Note that this technique does not always produce a perfectly matching image as a result, and can be toggled via the stochastic_volume_interpolation render option (default is on).
Stochastic Volume Interpolation
The tricubic interpolation mode of AiVolumeSampleXXX() calls, such as those used by the standard_volume shader, now uses a stochastic method of interpolation that greatly reduces the amount of voxel data read in each sample call. This can speed up rendering by as much as 20% in assets such as the WDAS cloud data set. Note that this technique does not always produce a perfectly matching image as a result, and can be toggled via the stochastic_volume_interpolation render option (default is on).
Procedural Optimization
Conservative and Exhaustive modes offer optimizations that enhance the rendering speed of procedurals. Exhaustive mode performs all possible types of optimizations to achieve faster rendering, even if it may result in higher memory usage. On the other hand, Conservative mode applies only those optimizations that boost performance without increasing memory usage. Additionally, the None mode can be used to disable these optimizations and revert to the behavior of previous versions of Arnold.