Adding Parameters - Arnold for Maya
Here we will add more different parameters to our shader, and they will be integrated into the Maya interface. This will allow us to have an easy way to modify our shader in Maya.
Creating the shader
We can add a new shader to the previous shader loader we created in Creating a Shader Loader:
First, create the shader:
parametersShader.cpp
#include <ai.h>
AI_SHADER_NODE_EXPORT_METHODS(ParametersShaderMtd);
namespace
{
enum ParametersShaderParams { p_int, p_uint, p_bool, p_float,
p_RGB, p_vector, p_point, p_point2,
p_string, p_matrix, p_enum };
const char* enum_list[] =
{
"First value",
"Second value",
"Third value",
NULL
};
};
node_parameters
{
AtMatrix id;
AiM4Identity(id);
AiParameterInt("IntParam", 0);
AiParameterUInt("UIntParam", 0);
AiParameterBool("BoolParam", 0);
AiParameterFlt("FltParam", 0.0f);
AiParameterRGB("RGBParam", 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
AiParameterVec("VecParam", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
AiParameterPnt("PntParam", 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);
AiParameterPnt2("Pnt2Param", 0.7f, 0.7f);
AiParameterStr("StrParam", "");
AiParameterMtx("MtxParam", id);
AiParameterEnum("EnumParam", 0, enum_list);
AiParameterArray("ArrayParam", AiArray(0, 0, AI_TYPE_RGB));
}
node_initialize
{
}
node_update
{
}
node_finish
{
}
shader_evaluate
{
AtRGB color = AiShaderEvalParamRGB(p_RGB);
sg->out.RGB = color;
} Enum values Strings for enum values should not start with a number. So this: "1st value" is not a valid enum value.
You can see that node parameters of different types are defined, but only the RGBParam is used.
Now, to add the shader to the loader, you only need to add this code to the previous loader.cpp file from the previous section:
loader.cpp
extern AtNodeMethods* ParametersShaderMtd;
enum{
MY_SHADER_1 = 0,
MY_SHADER_2,
PARAMETERS_SHADER
};
...
case PARAMETERS_SHADER:
node->methods = ParametersShaderMtd;
node->output_type = AI_TYPE_RGB;
node->name = "parametersShader";
node->node_type = AI_NODE_SHADER;
break; You will be able to compile the loader again as described in the previous section, check that Arnold can load the shader correctly, and copy the compiled shader to the correct folder so that Maya can use it. If you do so, you will discover that it is usable but not well integrated into Maya.
3.2 Integrating the shader in Maya
To integrate this new shader, we can, as in the first section, add information to the metadata file and create a template script for this shader.
3.2.1 Adding metadata information
To add the metadata information, you only have to add this to the loader.mtd file created in the previous section that you placed in this folder: %MTOA_PATH%\shaders\
loader.mtd
[node parametersShader]
desc STRING "Arnold shader to test parameters."
maya.name STRING "aiParametersShader"
maya.id INT 0x00070003
maya.classification STRING "shader/surface"
maya.output_name STRING "outColor"
maya.output_shortname STRING "out"
[attr IntParam]
desc STRING "Integer parameter."
min INT -100
max INT 100
softmin INT -10
softmax INT 10
default INT -10
maya.shortname STRING "int"
maya.name STRING "integer"
[attr UIntParam]
desc STRING "UInteger parameter."
min INT 0
max INT 100
softmin INT 0
softmax INT 10
default INT 0
maya.shortname STRING "uint"
maya.name STRING "uinteger"
[attr BoolParam]
desc STRING "Bool parameter."
default BOOL True
maya.shortname STRING "bl"
maya.name STRING "bool"
[attr FltParam]
desc STRING "Float parameter."
min FLOAT 0
max FLOAT 10
softmin FLOAT 0
softmax FLOAT 1
default FLOAT 0.5
maya.shortname STRING "flt"
maya.name STRING "float"
[attr RGBParam]
desc STRING "RGB parameter."
maya.name STRING "color"
maya.shortname STRING "cl"
[attr VecParam]
desc STRING "Vector parameter."
maya.name STRING "vector"
maya.shortname STRING "vec"
[attr PntParam]
desc STRING "Point parameter."
maya.name STRING "point"
maya.shortname STRING "pnt"
[attr Pnt2Param]
desc STRING "2D Point parameter."
maya.name STRING "point2"
maya.shortname STRING "pnt2"
[attr StrParam]
desc STRING "String parameter."
maya.name STRING "string"
maya.shortname STRING "str"
default STRING "empty"
[attr MtxParam]
desc STRING "Matrix parameter."
maya.name STRING "matrix"
maya.shortname STRING "mtx"
[attr EnumParam]
desc STRING "Enumeration parameter."
default INT 1
maya.name STRING "enumeration"
maya.shortname STRING "enum"
[attr ArrayParam]
desc STRING "Color Array parameter."
maya.name STRING "colorarray"
maya.shortname STRING "carray" This describes attributes that will be used for the Maya representation of the parameters like name, shortname, slider limits, descriptions, and default values.
3.2.2 Adding a Maya template
The last task to do is to create a Maya template for this shader. This is similar to the one created in the first section: self.addControl(parameterName, label="Parameter Label"). But adding the rest of the controls. The correct control for each attribute will be created automatically.
Create an aiParametersShaderTemplate.py file in MTOA_PATH\scripts\mtoa\ui\ae\ or in any folder that is defined in MTOA_TEMPLATES_PATH
aiParametersShaderTemplate.py
import maya.mel
from mtoa.ui.ae.shaderTemplate import ShaderAETemplate
class AEaiParametersShaderTemplate(ShaderAETemplate):
def setup(self):
self.addSwatch()
self.beginScrollLayout()
self.addCustom('message', 'AEshaderTypeNew',
'AEshaderTypeReplace')
self.beginLayout("Parameters list", collapse=False)
self.addControl("integer", label="Integer Param")
self.addControl("uinteger", label="Unsigned Int Param")
self.addControl("bool", label="Bool param")
self.addControl("float", label="Float param")
self.addControl("color", label="Color param")
self.addControl("vector", label="Vector param")
self.addControl("point", label="Point param")
self.addControl("point2", label="2D Point param")
self.addControl("string", label="String param")
self.addControl("matrix", label="Matrix param")
self.addControl("enumeration", label="Enumeration param")
self.addControl("colorarray", label="Color Array param")
self.endLayout()
maya.mel.eval('AEdependNodeTemplate '+self.nodeName)
self.addExtraControls()
self.endScrollLayout() When you use the ParametersShader in Maya, you will be able to see this Attribute Editor for it.
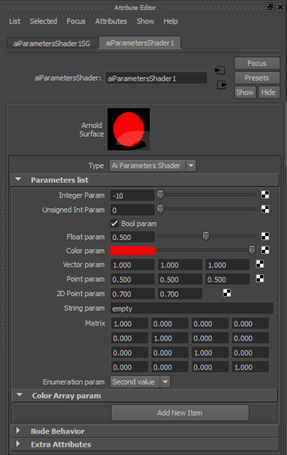
Figure 4: ParametersShader Template
Now you will be able to configure your shader's input parameters from Maya.
Avoid Space Optimization in the Template
Maya automatically tries to optimize the layout space, for example, if in the previous code you change from this:
aiParametersShaderTemplate.py
...
self.addControl("uinteger", label="Unsigned Int Param")
self.addControl("bool", label="Bool param")
self.addControl("float", label="Float param")
... To this:
aiParametersShaderTemplate.py
...
self.addControl("uinteger", label="Unsigned Int Param")
self.addControl("bool", label="Bool param 1")
self.addControl("bool", label="Bool param 2")
self.addControl("float", label="Float param")
... You will see this result:
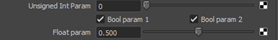
Figure 5: Optimized Template
To avoid this, we can use this code instead:
aiParametersShaderTemplate.py
...
self.addControl("uinteger", label="Unsigned Int Param")
self.beginNoOptimize()
self.addControl("bool", label="Bool param 1")
self.addControl("bool", label="Bool param 2")
self.endNoOptimize()
self.addControl("float", label="Float param")
... And you will get this result:
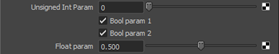
Figure 6: Optimized Template
Method called when an attribute is changed
Sometimes we may need a certain action to be performed everytime an attribute is changed. For example to evaluate that the introduced value is correct. Let's imagine we require that the value of the uinteger attribute is always greater or equal to the integer attribute. We can try to achieve this with the following code.
aiParametersShaderTemplate.py
import pymel.core as pm
import maya.cmds as cmds
from mtoa.ui.ae.shaderTemplate import ShaderAETemplate
class AEaiParametersShaderTemplate(ShaderAETemplate):
def checkInteger(self, nodeName):
intAttr = self.nodeAttr('integer')
uintAttr = self.nodeAttr('uinteger')
intValue = cmds.getAttr(intAttr)
uintValue = cmds.getAttr(uintAttr)
if intValue > uintValue:
cmds.setAttr(uintAttr,intValue)
def setup(self):
self.addSwatch()
self.beginScrollLayout()
self.addCustom('message', 'AEshaderTypeNew',
'AEshaderTypeReplace')
self.beginLayout("Parameters list", collapse=False)
self.addControl("integer", label="Integer Param",
changeCommand=self.checkInteger)
self.addControl("uinteger", label="Unsigned Int Param")
... Now everytime that the integer attribute is updated, if it has a value greater than the uinteger value, this will be increased to be equals to that value. But, of course, if you decrease the uinteger parameter, this could be lower than the integer one. To deal also with this case, we can easily write this code:
aiParametersShaderTemplate.py
import pymel.core as pm
import maya.cmds as cmds
from mtoa.ui.ae.shaderTemplate import ShaderAETemplate
class AEaiParametersShaderTemplate(ShaderAETemplate):
def checkInteger(self, nodeName):
intAttr = self.nodeAttr('integer')
uintAttr = self.nodeAttr('uinteger')
intValue = cmds.getAttr(intAttr)
uintValue = cmds.getAttr(uintAttr)
if intValue > uintValue:
cmds.setAttr(uintAttr,intValue)
def checkUinteger(self, nodeName):
intAttr = self.nodeAttr('integer')
uintAttr = self.nodeAttr('uinteger')
intValue = cmds.getAttr(intAttr)
uintValue = cmds.getAttr(uintAttr)
if intValue > uintValue:
cmds.setAttr(intAttr,uintValue)
def setup(self):
self.addSwatch()
self.beginScrollLayout()
self.addCustom('message', 'AEshaderTypeNew',
'AEshaderTypeReplace')
self.beginLayout("Parameters list", collapse=False)
self.addControl("integer", label="Integer Param",
changeCommand=self.checkInteger)
self.addControl("uinteger", label="Unsigned Int Param",
changeCommand=self.checkUinteger)
... Enabling and Disabling a Control
Sometimes some parameters do not have any meaning depending on other attributes values. For example, let's imagine that the float attribute only makes sense when the bool attribute is true. We can make this clear for the user if disabling the float attribute when bool is false. To do this, first we can define a changeCommand method as in the previous section, and use there the arnoldDimControlIfFalse method to disable the attribute. Here is an example:
aiParametersShaderTemplate.py
import maya.mel
import maya.cmds as cmds
import mtoa.ui.ae.utils as aeUtils
from mtoa.ui.ae.shaderTemplate import ShaderAETemplate
class AEaiParametersShaderTemplate(ShaderAETemplate):
def changeBool(self, nodeName):
aeUtils.arnoldDimControlIfFalse(nodeName, "float", "bool")
def setup(self):
self.addSwatch()
self.beginScrollLayout()
self.addCustom('message', 'AEshaderTypeNew',
'AEshaderTypeReplace')
self.beginLayout("Parameters list", collapse=False)
self.addControl("integer", label="Integer Param")
self.addControl("uinteger", label="Unsigned Int Param")
self.addControl("bool", label="Bool param",
changeCommand=self.changeBool)
self.addControl("float", label="Float param")
... If we want the opposite, making the float attribute to be enabled only when bool if false, you can use aeUtils.arnoldDimControlIfTrue instead of aeUtils.arnoldDimControlIfFalse. But in some cases, the condition to enable or disable an attribute could be more complex. For example, we may enable the float value only in the case that the red component of the color is greater than 0. You can write code like this for that case:
aiParametersShaderTemplate.py
import maya.mel
import maya.cmds as cmds
import mtoa.ui.ae.utils as aeUtils
from mtoa.ui.ae.shaderTemplate import ShaderAETemplate
class AEaiParametersShaderTemplate(ShaderAETemplate):
def changeColor(self, nodeName):
redAttr = self.nodeAttr('colorR')
redValue = cmds.getAttr(redAttr)
dim = not (redValue > 0)
cmds.editorTemplate(dimControl=(nodeName, "float", dim))
def setup(self):
self.addSwatch()
self.beginScrollLayout()
self.addCustom('message', 'AEshaderTypeNew',
'AEshaderTypeReplace')
self.beginLayout("Parameters list", collapse=False)
self.addControl("integer", label="Integer Param")
self.addControl("uinteger", label="Unsigned Int Param")
self.addControl("bool", label="Bool param")
self.addControl("float", label="Float param")
self.addControl("color", label="Color param",
changeCommand=self.changeColor)
... Creating a custom control
MtoA will automatically create a control for the attributes based on its type, but sometimes you may need more flexibility and create a custom control for a certain attribute. For example, let's imagine that the string attribute in the previous example is used to point to a file. Then you may want a control with a button that shows a file explorer so you can enter the file name in a more intuitive way. Here is an example to get that behavior:
aiParametersShaderTemplate.py
import pymel.core as pm
import maya.cmds as cmds
from mtoa.ui.ae.shaderTemplate import ShaderAETemplate
class AEaiParametersShaderTemplate(ShaderAETemplate):
def filenameEdit(self, mData) :
attr = self.nodeAttr('string')
cmds.setAttr(attr,mData,type="string")
def LoadFilenameButtonPush(self, *args):
basicFilter = 'All Files (*.*)'
ret = cmds.fileDialog2(fileFilter=basicFilter, dialogStyle=2,
cap='Load File',okc='Load',fm=4)
if ret is not None and len(ret):
self.filenameEdit(ret[0])
cmds.textFieldButtonGrp("filenameGrp", edit=True, text=ret[0])
def filenameNew(self, nodeName):
path = cmds.textFieldButtonGrp("filenameGrp", label="File Name",
changeCommand=self.filenameEdit, width=300)
cmds.textFieldButtonGrp(path, edit=True, text=cmds.getAttr(nodeName))
cmds.textFieldButtonGrp(path, edit=True, buttonLabel="...",
buttonCommand=self.LoadFilenameButtonPush)
def filenameReplace(self, nodeName):
cmds.textFieldButtonGrp("filenameGrp", edit=True,
text=cmds.getAttr(nodeName) )
def setup(self):
self.addSwatch()
self.beginScrollLayout()
self.addCustom('message', 'AEshaderTypeNew',
'AEshaderTypeReplace')
self.beginLayout("Parameters list", collapse=False)
...
self.addCustom('string', self.filenameNew, self.filenameReplace)
... Summary of Template Commands
Here we will summarize all the previously used template methods and add some new ones:
addSwatch
As previously seen, this command creates a Swatch in the Attribute Editor that shows a preview of the Shader.
beginScrollLayout endScrollLayout
Begins and ends a Vertical Scroll Layout where you can place sections and attributes.
beginLayout endLayout
Begins and ends a Layout. You can give it a name and define if it is collapsed or not by default.
self.beginLayout("Section Name", collapse=False)addControl
Creates a control for a shader attribute. It automatically creates the correct control depending on the type of attribute. You can define alabel and a changeCommand.
self.addControl("attrname", label="My Attr", changeCommand=self.changeAttr])addCustom
Creates a custom control for a shader attribute.
self.addCustom(attrName, newMethod, replaceMethod)addSeparator
Adds a separator in the layout.
beginNoOptimize endNoOptimize
Stops and starts again the layout space optimization.
addBumpLayout
Creates a section that will allow you to connect a bump normal mapping to the shader.
addExtraControls
All extra attributes will be grouped in an "Extra Controls" section.
addCustom('message','AEshaderTypeNew','AEshaderTypeReplace')
Creates a "Type" scroll list where you can change the shader type of the node.
maya.mel.eval('AEdependNodeTemplate '+self.nodeName)
Creates the "Node Behavior" section in the shader template.
