Loads reference
Access
Ribbon: Stress Analysis tab  Loads panel, click a load type.
Loads panel, click a load type.
or
In the browser, right-click the Loads node ![]() , and click a type.
, and click a type.
Load types
 Force
Force
Applies a force of the specified magnitude to the selected faces, edges, or vertices. When selecting multiple entities, the selection is limited to the same type as your first selection.
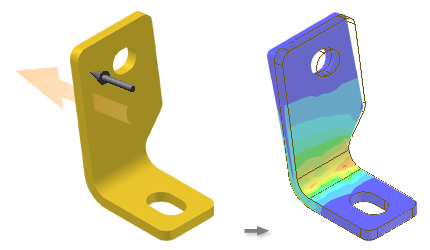
 Bearing Load
Bearing Load
Bearings loads vary greatly over the size and directions of forces that they can support. Forces can be predominately axial (thrust bearings) or radial.
 Gravity
Gravity
This gravity load direction can be normal (perpendicular) to the face and with the magnitude value.
 Pressure
Pressure
Applies a pressure load.
 Moment
Moment
Moment loads are applied around the axis and perpendicular to the face.
 Remote Force
Remote Force
Applies either a Normal or directional force. A Normal force is applied perpendicular to the face and with the amplitude value
 Body
Body
The Linear tab defines linear acceleration for the model. The Angular tab defines angular velocity or angular acceleration for the model.
Options
Only the appropriate options for each load type are available.
 Location
Location
Specifies the face, edge, or vertex on which to apply the load.
Faces
Specifies a face for the load. For a Bearing load, cylindrical faces are the only valid input for .

 Direction
Direction
Specifies the load direction. The default direction is normal to the selected face and with the magnitude value. Magnitudes are applied into the face.
The Direction Selector is automatically active allowing you to select geometry to define the vector.
The Direction Selector is automatically active allowing you to select geometry to define a different load direction.
The Direction Reverse command inverts the direction of the selected vector.
For a Gravity load, when an edge is selected, the loads are applied parallel to the selected edge.
For a Bearing load, the default is the axial direction. You can use vector components or a geometry selection to specify an alternate direction.
For a Body load, Linear tab, specifies the acceleration vector. Applies a Normal vector perpendicular to the face and with the magnitude value. Loads are applied parallel to selected edges.
For a Body load, Angular tab, Specifies the direction of angular velocity or angular acceleration. A Normal vector is applied perpendicular to the face and with the magnitude value.
Magnitude
Specifies the magnitude of the load.
Remote Point (Remote load)
Specifies the X, Y, and Z components of the remote force location.
Location (Body loads)
You can change the location of the initial Velocity and/or Acceleration selection, and maintain the specified orientation. Select a vertex and the location you choose is common to both the Velocity and Acceleration selections.
(More) 
Expands the dialog box to reveal more controls for specifying the load vector and controlling glyph display.
Use Vector Components
Enables vector controls so that you can define more explicitly the load vector. Specify the magnitude for the appropriate vector components for:
Vector Components
- Fx = X component
- Fy = Y component
- Fz = Z component
Vector Components
- Fx = X component
- Fy = Y component
- Fz = Z component
Vector Components
- X component
- Y component
- Z component
Display Glyph
When checked, displays the load glyph in the graphics region.
Scale
Specifies scale of the load glyph. You can increase or decrease the glyph size.
![]() Specifies the load glyph color.
Specifies the load glyph color.
Name
Specifies a name for the load. The name you specify displays in the browser.
