Options and settings explained
Jump to:
- Show slim faces
- Volumetric remeshing
- Uniform remeshing
- Adaptive remeshing
- Quad remeshing
- Manifold remeshing
- Display and settings
Show slim faces
This section colorizes triangles by their smallest angle. Very narrow triangles can be prone to self-intersections and are also problematic for the FEA calculations used by Local Simulation and Optimization Utility which typically require a retriangulation with more regular triangles.
Options
- Colored (checkbox): Enables or disables the coloring.
- Smallest angle (slider and input field): Set a threshold between 0° and 20°. Triangles with angles smaller than this number are colored in yellow-to-red tint.
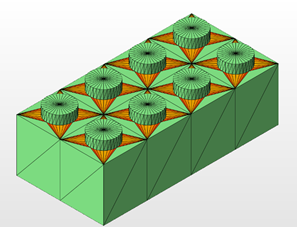
Use the Slim Faces option to identify very narrow triangles
Volumetric remeshing
This is a very simple and fast remeshing algorithm that can be sufficient for simple tasks. It uses a 3D, or volumetric, raster to generate the nodes required to replicate the original surface.
Options
- Target edge length: The remesher tries to adhere to this edge length but may deviate if the geometry requires it.
- Fast mode: Switching this on disables a postprocessing step that corrects for small errors in the positions of the newly generated nodes. The remeshing is completed even faster but it can create a shape that is slightly deformed from the original one.
Uniform remeshing
Attempts to reproduce the original shape from triangles as regular in size and angles as possible.
Uniform remeshing can be used even when meshes have holes.
Options
- Target edge length: The remesher tries to adhere to this edge length but may deviate if the geometry requires it.
- Smoothing: Based on surrounding nodes, an adjusted position is calculated to flatten irregularities.
Note: This setting is quite sensitive. Try low values up to 0.1 at first.
- Maintain edge if angle is greater than and Angle: This is the threshold of the angle between normals of the triangles forming the edge. Edges of this or greater angles are smoothed. This ignores the signs of the normals, so both types of edges, concave or convex, are be affected by this, if eligible.
Adaptive remeshing
This is a way to remesh that maintains intricacies where needed while saving on triangles where the surface is less detailed.
Options
- Small and Large edge length: The remesher tries to adhere to this minimum and maximum edge length but may deviate if the geometry requires it. The lower and upper values for these settings are calculated from the outbox size of the part.
- Smoothing: Based on surrounding nodes, an adjusted position is calculated to flatten irregularities.
Note: This setting is quite sensitive. Try low values up to 0.1 at first.
- Smooth Edge if angle is greater than and Angle: This is the threshold of the angle between normals of the triangles forming the edge. Edges of this or greater angles are smoothed. This ignores the signs of the normals, so both types of edges, concave or convex, may be affected by this.
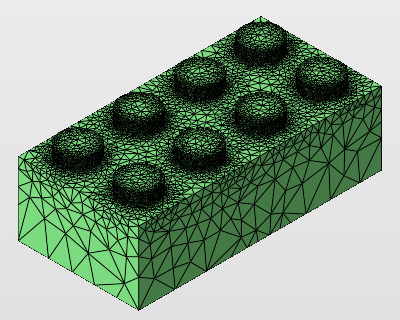
Remeshing adaptively maintains finer detail while saving on triangles in less detailed areas.
Quad remeshing
Recreates the original surface with pairs of triangles in such a way that, if at all possible, nodes have only 6 neighboring nodes. Quads are also necessary for external BREP conversion.
Options
- Target edge length: The remesher tries to adhere to this edge length but may deviate if the geometry requires it.
Note: Highly noisy meshes may lead to a much finer quad mesh than the target you set. In such cases, the remesher stops and provides a message. In such cases, we recommend to begin with the highest setting for Target edge length at first and then adjust to finer settings if needed.
- Colorize quadmesh after mesh manipulation: Selecting from a range of yellow-to-brown shades, this adds color information to the mesh, coloring triangles belonging to the same quad with identical colors.
Manifold remeshing
This reconstructs the original mesh with new, regular triangles. Holes formed by open triangle edges are wrap around to the inside to generate a thickness to the mesh and close the seam. This way, while not closing the holes themselves and making the mesh fully solid, the method ensures that the part on the whole becomes printable, if hollow.
Options
- Target edge length: The remesher tries to adhere to this edge length but may deviate if the geometry requires it.
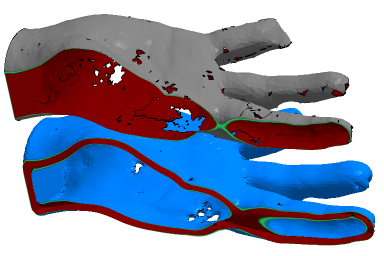
The flawed mesh (top) has been turned into a closed mesh with a thickness (bottom).
Display and settings
These are global settings that apply to all three tabs, Triangle reduction, Smoothing, and Remesh.
Options
- Highlight triangles: Switches triangle borders to be highlighted by a black line.
- Show original mesh: After having performed any mesh manipulation, hold this button to compare with the original mesh.
