Manufacture overview
Use the Manufacture workspace inside Fusion to go from a design model to a programmed part that is ready for manufacture. Create operations and then post process them to get the required G-code that a machine can use to create a part.
The workflow depends on the manufacturing process. Here is an example of a typical workflow when programming a part to be manufactured using CNC milling:
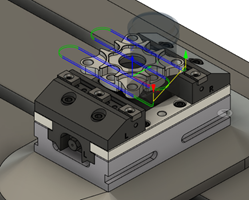
| 1) Create a design | 2) Create a setup | 3) Program the toolpaths |
 |
 |
 |
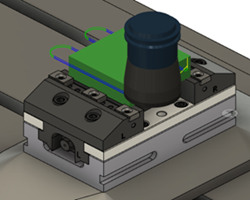
| 4) Simulate the toolpaths | 5) Create the G-code | 6) Make the part |
 |
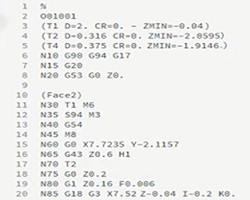 |
 |
Manufacturing processes
Fusion supports additive and subtractive manufacturing processes as well as inspection processes.
Types of processes currently supported by Fusion:
| Subtractive | Additive | Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Milling | Fused filament fabrication (FFF) | Part setting |
| Turning | Stereolithography (SLA) / Digital light processing (DLP) | Part alignment |
| Drilling | Multi-jet fusion (MJF) | Geometric inspection |
| Water jet | Selective laser sintering (SLS) | Surface inspection |
| Laser cutting | Metal powder bed fusion (MPBF) | Manual inspection |
| Electron beam additive manufacturing (eBeam) | ||
| Binder jetting | ||
| Direct energy deposition (DED) |
Access the Manufacture workspace