Use the Probed Circle item to measure a full or partial circle on a part. You must probe a minimum of three points distributed around the circumference of the circle.
To create a Probed Circle item:
- Open a Geometric group in the Sequence Tree.
- Click Home tab > Create panel > Geometry > Probed Circle.
The Probed Circle dialog contains the following areas:
Name — Enter a name for the item. The name is used in the inspection sequence, in the Report and Info tabs, and when referencing the item in other items.
Use nominals — Select this check box to enter or change the item nominals, and to compare the item measurements to their nominal values. Deselect this check box to disable comparisons with the item nominals.
When this check box is selected, an in-tolerance
 or out-of-tolerance
or out-of-tolerance
 indicator is displayed on the measured item's icon in the inspection sequence; the border of the item
label is coloured to indicate whether the measurements are within tolerance; and the tolerance, nominal, deviation, and error values of the item are shown in the report.
indicator is displayed on the measured item's icon in the inspection sequence; the border of the item
label is coloured to indicate whether the measurements are within tolerance; and the tolerance, nominal, deviation, and error values of the item are shown in the report.
When this check box is deselected, the Nominal boxes are disabled, no tolerance indicators are displayed and no tolerance, nominal, deviation, and error values are shown in the report for this item.
 and select
From CAD Entity. To replace the nominals with the item's measurements in the current Measure, click the button and select
From Active Measure.
and select
From CAD Entity. To replace the nominals with the item's measurements in the current Measure, click the button and select
From Active Measure.
Visible — Select this check box to display the item in the CAD view.
Output in report — Select this check box to include the item in the report.
Coordinate system — Select the alignment relative to which the item's measurements are to be reported.
To specify the alignment during the inspection, select <Active Alignment>. You can then select the alignment from the Active alignment list, or by adding an Active Alignment item to the inspection sequence.
 Start angle — Enter the start angle of the feature relative to the
Orientation vector. You can enter the angle in degrees or radians.
Start angle — Enter the start angle of the feature relative to the
Orientation vector. You can enter the angle in degrees or radians.
 End angle — Enter the end angle of the feature relative to the
Orientation vector. You can enter the angle in degrees or radians.
End angle — Enter the end angle of the feature relative to the
Orientation vector. You can enter the angle in degrees or radians.
Material side — Choose the side from which you want to probe the feature. Select:
- Hole (ID) to probe an internal feature.
- Boss (OD) to probe an external feature.
- Not specified to leave the probing direction unrestricted.
Fitting algorithm — Choose the algorithm with which you want to calculate the item. Select:
- Least square to create the feature that minimizes the deviation across all probed points.
- Maximum inscribed to create the largest feature that fits within the probed points.
- Minimum circumscribed to create the smallest feature that fits around the outside of the probed points.
- Minimax to create the feature by averaging the maximum inscribed and minimum circumscribed features that have the same centre.
Reference plane — Select the plane on which you want to project the feature.
Centre — Enter the nominal and tolerances for the position of the feature's centre point.
Diameter — Enter the nominal and tolerances for the Radius or Diameter of the feature.
 to hide the label, and click
to hide the label, and click
 to redisplay it.
to redisplay it.
Offset/Thickness — By default, the feature is projected onto the reference plane. To specify the position of the feature relative to the reference plane, enter its average height. To calculate the average height of the feature from the measurement, select the Calculate from measurement check box.
Circularity — Enter the Maximum acceptable difference between the points with greatest positive deviation and greatest negative deviation from the best-fit circle. If the difference between the greatest positive deviation and greatest negative deviation exceeds the Maximum value, the circularity is out-of-tolerance.
To measure circularity, PowerInspect calculates the best-fit circle, C1, through the points. It then runs two concentric circles through the points furthest from the new circle in each direction, shown as C2 and C3:
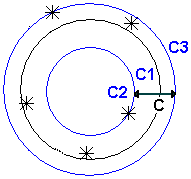
The Circularity value is the difference between the radii of C2 and C3.
Guided measure — Select this check box to restrict the probed points to the reference plane when measuring the feature with an articulated arm. Only points taken within the Capture tolerance (specified in the Feature Probing dialog) are recorded. To adjust the plane along its normal, such as when probing a hole, enter an Offset distance. This check box has no effect when probing the part with a CMM.
Orientation — Select the vector from which the Start angle and End angle are calculated when creating a partial circle.
Auto-accept enabled — Select this check box to save the item measurements as soon as you have probed the number of points specified in the Points box. If you played the item as part of the inspection sequence, PowerInspect automatically plays the next item. Deselect the check box to choose how many points to probe and save your measurements manually. This option is available only when an item has no probe path.
Point sources — Select this tab to use probed points from other items to measure this item.
For example, you can use the tab to create a measured cylinder by combining measurements from probed circles at the top and bottom of the feature.
To specify the sources for the probed points, select one or more items in the
Available sources list, and then click
 to add them to the Selected
sources
list.
to add them to the Selected
sources
list.
To remove sources, select the items in the
Selected sources list, and then click
 .
.
Click OK to close the dialog and save your changes.
 to
to