 Bake Light and Shadows
Bake Light and Shadows
Scene > Bake Light and Shadows
Use the Bake Light and Shadows module to set parameters for direct and indirect illumination, subdividing polygon meshes, and calculating ambient occlusion. This can improve the visual quality of OpenGL and raytracing precomputed renders.
Use baked lightmaps for storing a static rendered image of lighting that won't change. To edit the UV sets for a lightmap, use the UV Editor.
Another way to access the Bake Light and Shadows module is to right-click the empty space next to the Quick Access Bar and select it from the list.
For information on using the Bake Light and shadows module, see Working with Bake Light and Shadows.
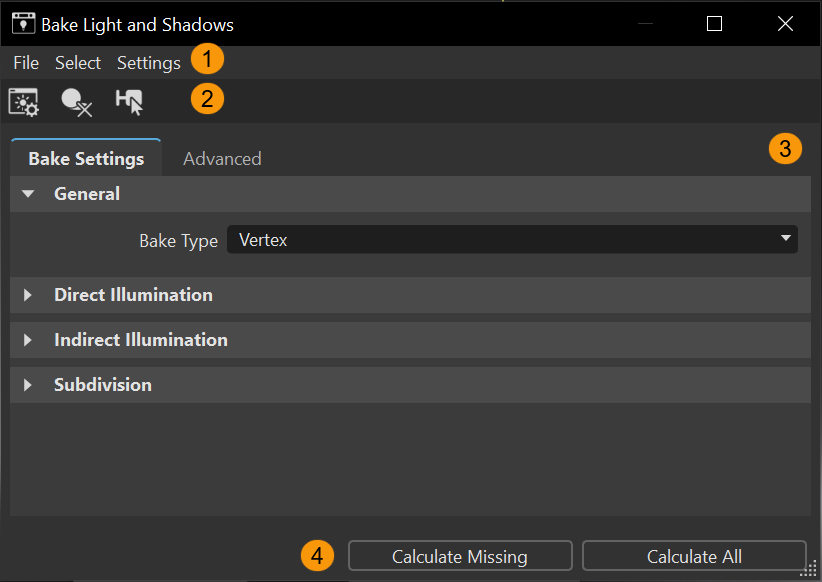
The Bake Light and Shadows module has a menu bar, two tabs (Bake Settings and Advanced), and an QuickActions Bar at the bottom for quick access to commonly used tools.
 QuickActions Bar
QuickActions Bar
This contains three tools that apply to both vertex and texture baking:
 Load Settings from Node - Loads the bake setting from the selected node. It is a shortcut for Load from Node.
Load Settings from Node - Loads the bake setting from the selected node. It is a shortcut for Load from Node. Clear Active - Clears all the active bake type data for the currently selected node hierarchies in the Scenegraph.
Clear Active - Clears all the active bake type data for the currently selected node hierarchies in the Scenegraph. Select Missing - Selects all geometries of the selected Scenegraph hierarchy (or whole scene if nothing selected) without any baking or baking for the selected bake type.
Select Missing - Selects all geometries of the selected Scenegraph hierarchy (or whole scene if nothing selected) without any baking or baking for the selected bake type.
 Bake Settings Tab
Bake Settings Tab
The Bake Settings tab contains parameters for configuring direct and indirect illumination, subdivisions, lightmap behavior, lightmap UV generation, as well as setting the bake type and finally calculating the bake.
General
Bake Type - Sets the type of baking performed. Choose whether the bake results are stored as a color for each vertex of the geometry or in a texture (called a lightmap) that's mapped onto the geometry with lightmap UVs. Both of these support the baking of ambient occlusion, shadows, and direct/indirect illumination; however; there are some differences.
Vertex - Use vertex for solid objects, finely already tessellated objects, or ones with adequate subdivisions, that need shadows for the environment, a simple baked lighting setup, or a neutral look. An advantage of the vertex bake type is shadows are very fast to calculate and no manual reworking is required. See Vertex Baking for more information.
Texture - Use texture with simple geometry for good, high-quality shadows and lightmaps, especially when baked for real-time scenes, while needing to keep the poly count low, but visual quality high. Think construction/manufacturing data and architecture with many planar surfaces. Use it to bake more complex lighting effects, such as reflections or caustics from nearby glass or specular materials. Just ensure Hide Transparent Objects is disabled, so these objects will then be visible during baking.
Important:Lightmap UVs are needed, so for complex or important objects in direct view, we recommend manually unwrapping UVs. To edit the UV sets for a lightmap, use the UV Editor.
One other advantage is that with texture bake type shadow maps, clones or reference objects can have different lightmaps. See Texture Baking for more information.
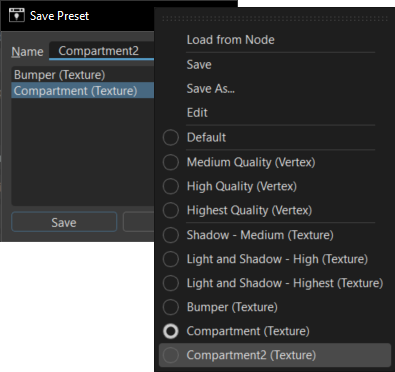
Note:An XML file,
BakePresets, is generated and used to store vertex and texture bake shadow presets. This hleps to avoid issues when adding or deleting presets.- Deleting the
BakePresetsfile removes all non-default presets fron the preset list on your next launch. - If the
BakePresetsfiles doesn't exist inC:\Users\User\AppData\Roaming\VREDPro, VRED will generate one. - If a copy of
BakePresetsis made and then is used to overwrite the original in the folder, the presets in the copy are used by VRED and replace the ones in the preset list.
- Deleting the
Renderer - Only available for the Texture Bake Type. Sets the type of raytracing used. Select CPU or GPU Raytracing. To better understand the differences and choose the best type of raytracing for your needs, check out GPU vs. CPU Raytracing.
Hide Transparent Objects - Only available for the Texture Bake Type. Hides glass and other transparent objects while baking, so they don't cast shadows or contribute to indirect illumination, when enabled. The shadow plane will not be hidden.
Tip:To bake complex lighting effects, such as reflections or caustics from nearby glass or specular materials, ensure this is disabled, making these objects visible during baking.
Direct Illumination
Enables an extra calculation of direct light bounces, which increases the quality of the final result. Think of a spot light illuminating a performer on stage. Only the light source's contribution is used to calculate the light contribution to any given illuminated point.
Shadow Type - Set the type of direct illumination you want baked. Choose from:
Ambient Occlusion - This default setting creates common ambient occlusion shadows. This is independent of light direction and takes the mutual occlusion of visible geometry into account. Ambient occlusion is calculated based on distance (mix/max).
Note:These additional options appear when Ambient Occlusion is selected: Weighting, Minimum Distance, and Maximum Distance.
Shadows - Creates shadows by considering the lighting information from the environment and any light sources listed in the Light Editor.
Note:If there is noise in your shadow baking, a higher sample count can correct this.
Light and Shadows - In addition to the baked shadows, lights are also baked. What is meant by lights is the direct illumination from any active light source, such as a spot light, point light, etc., including the environment. The baked illumination replaces the diffuse real-time precomputed environment lighting after baking. The shadows darken glossy and specular reflections from the real-time precomputed environment lighting in OpenGL and in the Precomputed and Precomputed + Reflections raytracing modes. Later changes to geometry objects, for example, through transformation, do not influence the displayed baked light and shadows.
Note:As of version 2022.1, Enable Separate Illumination is not available when Light and Shadows is selected.
Go a step further and enable Indirect illumination (Indirect Illumination > Enable) to add any indirect illumination. Use the Visualization menu options, Ambient Occlusion Rendering for shadows and Precomputed Illumination Rendering for lights, to display the pure data stored in the textures or vertices.
Enable Separate Illumination - VRED bakes light from the specified light source into a separate lightmap. Bake a specific lighting setup or many indirections from the environment to lighten a scene, along with additional separated lights that can be toggled on and off afterwards. This option shows the correct baking of ambient occlusion/shadows and environment lighting for base illumination and separate direct/optional indirect illumination for separate illumination, when this option and the light source's Bake as Separate Illumination option or geometry light source's option are enabled.
When this option is enabled, the following happens:
Active lights with Bake as Separate Illumination enabled are baked to the separate illumination lightmap.
Active lights with Bake as Separate Illumination disabled are baked to the base lightmap.
When is option is disabled, all active lights are baked, regardless of whether they have Bake as Separate Illumination enabled or disabled.
Quality - Sets the number of image samples used to define the direct shadow quality. Ambient Occlusion is a specific not-physically-accurate rendering trick. It basically samples a hemisphere around each point on the face, sees what proportion of a hemisphere is occluded by other geometry and shades the pixel accordingly. Six presets are available, as well as a custom quality setting:
- Preview - 8×8 hemisphere samples (per vertex)
- Low - 16×16 hemisphere samples
- Medium - 32×32 hemisphere samples
- High - 48×48 hemisphere samples
- Highest - 64×64 hemisphere samples
- Ultra High - 128×128 hemisphere samples
- Samples - Only available for the Texture Bake Type. Sets the number of image samples per pixel used for the specified quality preset.
Weighting - Only available with Ambient Occlusion selected. Sets the weighting of the samples while calculating ambient occlusion for both vertex and texture baking. Use this to improve your shadows. Select one of the following:
Uniform - This is the original setting for calculating weighting in VRED 2021.3 and before. All samples while baking are equally weighted.
Cosine - Provides a more realistic real-life result than uniform weighting. Shadows might have more depth and contrast by giving samples in the direction of the surface normals a higher weight.
- Min/Max Distance - Only available with Ambient Occlusion selected. Defines the minimum and maximum distance (mm) between objects that to should be taken into account for the calculation of Ambient Occlusion shadows. The first value defines total black areas where full occlusion takes place. The second defines white areas, where no occlusion takes place. This value can also be seen as the maximum expansion of the virtual hemisphere.
- Clear All - Only available for the Vertex Bake Type. Deletes the Ambient Occlusion calculation of the whole scene.
Clear Visible - Only available for the Vertex Bake Type. Deletes the Ambient Occlusion on selected geometry.
Important:The total calculation time depends on the complexity of the scene and chosen shadow quality preset.
Indirect Illumination
Enables an extra calculation of indirect light bounces, which increases the quality of the final result.
Use Indirect Illumination - Enables/disables the indirect illumination mode. When enabled, extra calculations of indirect light bounces are preformed, which increases the quality of the final result, but increases calculation time.
To see the differences between vertex and texture baking for indirect lights, refer to the following table.
Only for Separate Illumination - Available only for the Texture Bake Type with Enable Separate Illumination enabled. Provides indirect illumination only for the separate illumination and omits the base illumination from baking, increasing the brightness of the scene. If you don't need increased brightness, disable this.
Quality - Only available for the Vertex Bake Type. Sets the quality of indirection. The higher the values, the better the results.
Indirections - The number of indirections defines the number of calculated light bounces. The default value is one, so only one light bounce is calculated.
Important:Higher values produce better quality, but increase calculation time.
- Enable Color Bleeding - Enables the transfer of color between nearby surfaces, caused by the colored reflection of the indirect illumination option. Color bleeding causes a white wall close to a red wall to appear pink because it receives red light from the red wall. When disabled, the illumination color is stored as greyscale.
Override Material - Overrides all non-transparent objects with a chosen flat diffuse material color for indirect illumination calculation.
Note:Displacement textures are not respected when this option is enabled. Baking displacements is only possible with texture baking.
- Color - Sets the color used for the indirect illumination when Override Material is enabled.
- Clear All - Only available for the Vertex Bake Type. Deletes the indirect illumination calculation of the whole scene.
- Clear Visible - Only available for the Vertex Bake Type. Deletes the indirect illumination on the selected geometry.
Lightmap
Only available for the Texture Bake Type. This section contains options for sharing lightmaps for clones, saving textures externally, using a denoiser, and setting for resolution and edge dilation.
Share Lightmaps For Clones - Shares lightmaps for clones in a scene, when enabled. Disable to calculate different lightmaps for clones of the same geometry in the scene, before calculating. With vertex baking, geometries that are clones have the same bake result. With texture baking, these geometry clones can have different lightmaps.
This is the expected behavior for clones with smart references:
Nodes in different file references cannot be cloned - A node in file reference
a.vpbcannot be a clone of a node in referenceb.vpb. Since each file is stored separately, each belongs to the file-respective reference. A node within a file reference can also not be a clone of a node in the regular scene. In these cases, a copy of the node is required. Within the same file references, there are no limitations for clones.All "instances" of a file reference need to be cloned - When reference
a.vpbis used multiple times, alla.vpbare clones. This also means all children of eacha.vpbinstance are clones of all othera.vpbchildren.Lighmaps can be different on clones - When having two clones of a box in the scene, you can calculate different lightmaps for these clones. Just uncheck Share Lightmaps For Clones, before calculating the lightmap.
If you have shared lightmaps between multiple clones and are unsatisfied with the result on some clones, it is possible to recalculate the lightmaps for the unsatisfactory ones and share the new ones between them. Concerning the clone nodes, the clones still remain clones, even with different lightmaps attached.
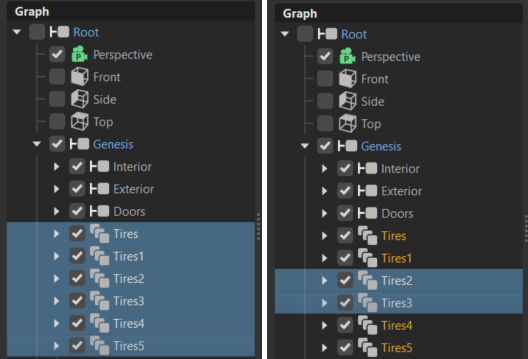
Clones across instances of the same file reference cannot have different lightmaps - A box is used in
a.vpbfile reference and the file reference is used twice in the scene. You cannot calculate different lightmaps for the box, since the file only exists once and is only written once. Therefore, the box is only stored once.You want different lightmaps on clones across instances of the same file reference - Manually change the scene to do this. In most cases, this would mean removing the file references and replacing them with normal group nodes.
Save Texture As External Reference - Enables the storing of all lightmaps and all baked textures in an external file location (non-inlined). Use the Location option to set where they will be stored.
Note:For saving textures non-inlined for specific lightmaps, bake the lightmaps with Save Texture as External Reference activated. Those lightmaps will be saved non-inlined in the vpb, even if the Preference option, Use Inline Textures, is enabled.
Use this option for creating variants for certain geometry. When unchecked, lightmaps and baked textures are saved into the scene file (inlined).
Location - Displays the location where the lightmap textures are saved. Click
 to open a browser and save the lightmap textures in a designated location.
to open a browser and save the lightmap textures in a designated location.Clear All - Deletes all lightmap textures from all selected objects.
Clear Active - Deletes all lightmap textures from all visible selected objects.
Use Denoising - Reduces noise in the final lightmap texture, using either a GPU or CPU denoiser.
Note:VRED will use GPU denoising, if there is a GPU graphics card; otherwise, calculations are done on the CPU.
Sets the denoiser used. Choose from:
GPU/Auto - If the hardware and driver version support it, a GPU-based denoiser will be used; otherwise, a CPU-based denoiser will be used.
Note:If GPU/Auto is chosen and no compatible hardware is found or image resolution is set higher than the GPU denoiser can handle, VRED automatically uses to the CPU denoiser.
CPU - Always uses the CPU-based denoiser.
Use Existing Resolution - Uses previously calculated lightmap resolutions, if valid lightmaps already exists; otherwise, the resolution is calculated based on the current settings.
When nodes have different lightmap resolution settings, their resolutions are preserved, instead of overwritten. Anything without existing settings will have then calculated, using the current settings.
If you want the resolution recalculated for everything, disable this. Any lightmaps that had different resolutions will be changed and might look different.
Resolution - Defines the resolution used as either Static or Dynamic. Lightmap resolutions must be a multiple of four, e.g. 64, 68, 72, etc.
- Static - Uses the specified resolution for all generated lighmap textures.
- Dynamic - Uses the minimum and maximum resolution settings for each texture, which depends on the chosen pixel density, geometry size, and UV space. This is the most commonly used option; however, it requires more rendering time and resources.
Minimum Resolution - the first field sets the static or lowest resolution for each lightmap texture when using Dynamic resolution. The second sets the highest resolution for each lightmap texture when using Dynamic resolution.
Texel Density - Sets the number of pixels per meter for the lightmap texture. The lightmap resolution will be calculated, using this value. Therefore, smaller objects will have a lower density and smaller resolution than larger ones.
Things, such as faces, may need a higher pixel density, due to the amount of detail. Objects out of view can have a lower density. This tool is essential for game development and film production.
Edge Dilation - Prevents seams that can occur when a lightmap has low edge dilation. this means no unintended edges of color from the background around the texture. By increasing the edge dilation of the outermost pixel (ensuring sufficient rays), this eliminates the seam (border). Therefore, there are valid pixels at the borders, which fit.
Note:The resolution of the lightmap can also play a roll in a seam appearing. To improve this further, increase the resolution of the lightmap, using Maximum Resolution, then pressing Calculate All.
UV calculations are done before lightmap sampling is started, therefore, if lightmap calculation are cancelled after this, the new UVs might not match the old lightmaps.
Lightmap UV
Only available for the Texture Bake Type. This section sets the method used for UV generation and provides the option for using existing UV sets.
UV Generation - Use this first time you bake new geometry without lightmap UVs. It automatically generate s UVs. Just select the method used for generating the lightmap UV Sets before the baking process, if Use Existing Lightmap UV Set is unchecked or the geometry has no lightmap UVs. Select one of the following:
Triplanar & Layout - Generates the lightmap UV Sets using the Triplanar function from the UV Editor. With triplanar mapping, there is a blend zone where the projections overlap on the surface. If this does not give the desired result, try the Unfold & Layout option.
The created UV texture coordinates are then laid out as per the current Layout settings, with the exception of the Island and Tile Padding, as these are controlled by Edge Dilation.
Note:The Fewer Islands option in the UV Editor is automatically enabled when Triplanar & Layout is selected, to reduce the number of islands for a UV layout.
Unfold & Layout - Generates the lightmap UV Sets using the Unfold & Layout function from the UV Editor. This tries to flatten the surface in UV space. This can only succeed if the surface is not a closed object or has been cut beforehand; otherwise, try the Triplanar & Layout option.
The created UV texture coordinates are then laid out as per the current Layout settings, with the exception of the Island and Tile Padding, as these are controlled by Edge Dilation.
Use Existing Lightmap UV Set - Use if your geometry already has lightmap UVs and you want the existing lightmap UV layout reused. When enabled, it will use the previously created UV set. This is the default state, since most people want to use the existing lightmap UVs.
Warning:When disabled, any existing calculations are lost and cannot be retrieved. New lightmap UV set creations replace the existing one, which could result in layout and bake results that differ from the previous ones.
Subdivision
Only available for the Vertex Bake Type. Use these settings to subdivide the mesh for polygons that cannot be retessellated, but have shadow results that need improvement.
Use Subdivision - Enables/disables the subdivision mode. When enabled, the Quality, Minimum Edge Length, and Intensity Threshold options become available. Subdivides existing polygon mesh into smaller triangles. This option should be turned on to avoid ragged edges on shadow illustration. This feature is helpful when NURBS data for re-tessellation is not available, but a refined mesh is required. Subdividing generates more complex objects - it should only be used when required.
Quality - Causes geometries to be refined during the ambient occlusion calculation process, when the Enable subdivision check box is checked. Extra vertices are inserted into the meshes to try and get smoother results on the geometry. Three presets are available:
- Low - Subdivides up to two times, if the difference in intensities between the vertices of an edge is above the intensity threshold.
- Medium - Subdivides up to two times, if the difference in intensities between the vertices of an edge, or the edge midpoint of the triangle edge, is above the intensity threshold.
- High - Subdivides up to four times, if the difference in intensities between the vertices of an edge, or the edge midpoint, is above the intensity threshold.
- Minimum Edge Length - Defines the threshold of the subdivision. If the length of an edge between two vertices is below the defined value, it is not subdivided and no additional vertices are added.
Intensity Threshold - Sets the threshold of intensity values of two vertices, to force a subdivision of the triangle edge.
Caution:Enabling this feature increases calculation time and the polygon count of the scene.
 Calculate Buttons
Calculate Buttons
- Calculate Missing - Calculates ambient occlusion, shadows, or light and shadows for all visible and selected nodes in the Scenegraph hierarchy without baking or baking of the selected bake type. When complete, the viewport will update to display the baked lights and shadows. Use this to select nodes more automatically, instead of searching for and selecting them one at a time.
- Calculate All - Calculates ambient occlusion, shadows, or lights and shadows for all visible and selected nodes in the Scenegraph hierarchy. Geometry with existing baking of the selected bake type are recalculated. When complete, the viewport will update to display the baked lights and shadows.
 Advanced Tab
Advanced Tab
The Advanced tab contains an overview of settings used for baking and shows what can be seen in the viewport, such as the light baking textures.
To see the light baking textures directly on the model, from the Visualization menu, select Precomputed Illumination Rendering.
Properties
Displays the bake properties and states for the selected nodes.
Changing the Select option or manually selecting something else, changes the content listed in this section.
Name - Displays the name of the selected node. If multiple are selected, the name field changes to blue, indicating the name differs among the selected nodes.
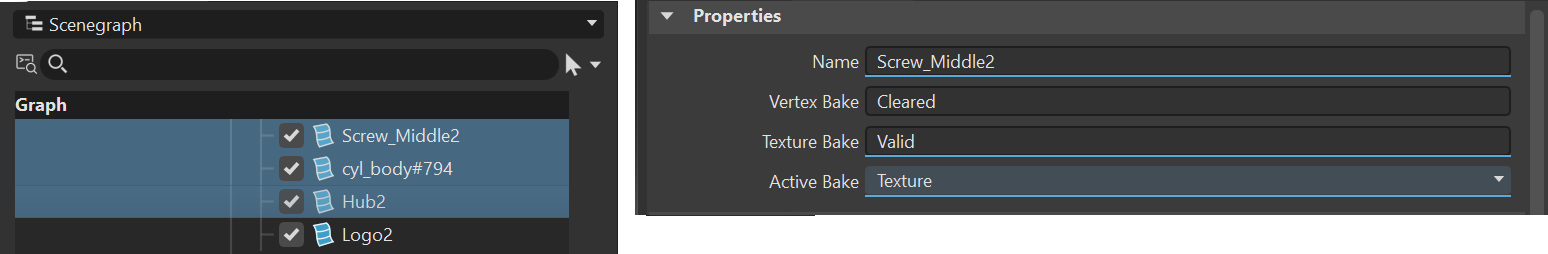
Vertex Bake and Texture Bake - Displays the current bake state of the selected node. There are three states that can be set:
-
- For Vertex Bake, no vertex baking has been calculated on this node.
- For Texture Bake, no lightmap has been calculated on this node.
-
- For Vertex Bake, vertex baking has been calculated and can be rendered.
- For Texture Bake, lightmap has been calculated and can be rendered.
Cleared
For Vertex Bake, vertex baking was cleared, since the Clear All button was pressed. The last used baking calculation settings can still be reloaded.
For Texture Bake, the lightmap was cleared, since the Clear All button was pressed. The last used baking calculation settings can still be reloaded.
Note:What makes None different from Cleared, is that there was never something baked on that node and, therefore, no Bake Settings are available to display.
-
Active Bake - Sets the active type of baking (vertex or texture) which is rendered in the viewport. Select None to toggle baked light and shadows off.
Note:Another way to set the active bake type is to right-click within the Scenegraph to access the context menu, select Edit > Baked Light and Shadows, then choose Use No Bake, Use Vertex Bake, or Use Texture Bake.
Lightmap
Only available for nodes where texture bake calculations were performed.
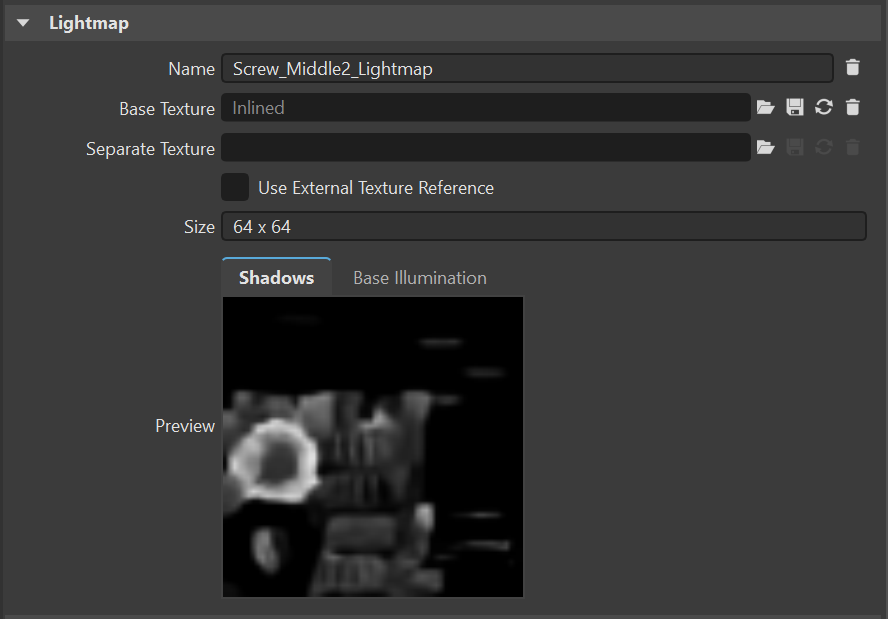
This section displays the shadow and illumination maps for the geometry selected in the viewport.
The Properties section cannot display multiple lightmaps. Therefore, you must select one thing at a time to preview the textures. To select another image file, click the Open icon ![]() , select another image, then Open. The new texture is loaded into the Lightmap section. Be aware that the UV layout must be identical to the new loaded texture and Lightmap UV set to achieve the correct results.
, select another image, then Open. The new texture is loaded into the Lightmap section. Be aware that the UV layout must be identical to the new loaded texture and Lightmap UV set to achieve the correct results.
If you are expecting to see a lightmap and there is none, ensure the texture and/or vertex bake have a Valid state in properties and that Active Bake is not set to None.
Name - Provides an auto-generated name for the lightmap of the selected node. Notice that the name is a combination of the node name followed by
_Lightmapand followed by_numeration, if several lightmaps were baked on nodes with the same name. This name is used when saving the lightmap as an external reference.Tip:If you see a yellow highlighted field, this indicates that multiple nodes are selected with different names.
 Note:
Note:Use
 when you've renamed a node after baking and want VRED to generate a new name with a new calculation that matches the renamed node. This will make it easier for the artist to identify which lightmap is assigned to which node.
when you've renamed a node after baking and want VRED to generate a new name with a new calculation that matches the renamed node. This will make it easier for the artist to identify which lightmap is assigned to which node.Base Texture and Separate Texture - Provides controls for loading, refreshing, and deleteing base and separate lightmap image, as well as they're location.
To load the texture image from a file, click
 .
.To save the texture image to a file, click
 .
.To reload the texture image, click
 .Note:
.Note:If you have a missing non-inlined texture (you see a pink and black checkboard texture) and know where the missing file is located on disk, load the file, using these texture control, then try repathing the lightmaps.
To delete the texture image, click
 .
.
Use External Texture Reference - Stores the texture outside VRED in an external location when saving the file. The image data is then not stored within the project file.
Note:If the referenced texture file cannot be found when saving the project, the texture will be included in the project file. You need to save a currently inlined texture, first, using File > Save Lightmaps to a folder outside VRED to set up a referenced file location.
Size - Provides the dimensions of the lightmap.
Preview - Shows a preview of the lightmap for the tab selected.
Shadow - Shows a preview of the shadow lightmap for the baked texture.
Base Illumination - Shows a lightmap for the baked texture that captures all illumination from the real-time environment (base).
Separate Illumination - Shows a lightmap for the baked texture that captures the illumination from everything baked separately, using Enable Separate Illumination and Bake Separate Illumination.
Texture Bake Settings and Vertex Bake Settings
Provides an overview of the settings used for baking the selected object (parameters from the Bake Settings tab). Find the mode set, whether indirect illumination, color bleeding, material override, and subdivisions are enabled, the number of indirections, the quality settings for direct and indirect quality, and much more.
These are a part of the same settings seen in the Bake Settings tab, if you select the Settings menu, then Load from Node.
A quick way to access this tool is to use ![]() , found in the QuickActions Bar.
, found in the QuickActions Bar.
Mode - Displays the type of mode used for baking.
Weighting - Only available with Ambient Occlusion selected. Shows the type of weighting used for vertex baking.
Indirect Illumination - Indicates whether indirect illumination is enabled for baking.
Indirections - Shows the number of calculated light bounces set for baking.
Note:Higher values produce better quality, but increase calculation time.
Color Bleeding - Indicates whether color bleeding is enabled for baking.
Material Override - Indicates whether materials will be overwritten for baking.
Renderer - Indicates the type of renderer used for texture baking.
Samples - Indicates the number of samples used for texture baking.
Denoising - Indicated whether denoising is enabled for texture baking.
Denoiser Type - Indicates the type of denoiser used for texture baking, if Denoising is enabled.
Edge Dilation - Indicates the setting used for edge dilation for texture baking.
Direct Quality - Indicates the direct illumination quality level set for baking.
Indirect Quality - Indicates the indirect illumination quality level set for baking.
Subdivision - Only available for the Vertex Bake Type. Indicates whether subdivisions are set for baking.
 Menus
Menus