Use the Automatic Verification page to enable verification of toolpaths on creation. The options on this page are dependent on the selected strategy:
Gouge checking
Model gouge check — Select to gouge check the toolpath against a model even if the model is not directly used in the strategy.
Dimensions
Thickness — Enter the amount of material to be left on the model, within tolerance, when gouge checking. Click the
Thickness
 button to change the
Thickness
box to
Radial thickness
button to change the
Thickness
box to
Radial thickness
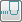 and
Axial thickness
and
Axial thickness
 .
.
 Radial thickness — Enter the radial offset to the tool. When 2.5-axis or 3-axis machining, a positive value leaves material on vertical walls.
Radial thickness — Enter the radial offset to the tool. When 2.5-axis or 3-axis machining, a positive value leaves material on vertical walls.
 Axial thickness — Enter the offset to the tool, in the tool axis direction only. When 2.5-axis or 3-axis machining, a positive value leaves material on horizontal faces.
Axial thickness — Enter the offset to the tool, in the tool axis direction only. When 2.5-axis or 3-axis machining, a positive value leaves material on horizontal faces.
 — Click to display the
Component thickness dialog, which enables you to specify the thicknesses of the different surfaces.
— Click to display the
Component thickness dialog, which enables you to specify the thicknesses of the different surfaces.
Head clearance — Enter the length of the tool tip, shank, and holder combined. If the height of the tool assembly is less than the Head clearance, an additional component is added to the tool assembly. This additional component has the same diameter as the uppermost item in the tool assembly (if Automatic collision checking is On), and a length so that the specified total tool-assembly length is the same as the Head clearance.
- The height of the tool assembly is just the cutter if Automatic collision checking is Off and is the tip, shank, and holder if Automatic collision checking is On.
- If you define a tool assembly which is longer than the Head clearance value, then the Head clearance value is ignored.
- For disc cutters, if a shank is defined, then additional components are added to give the total tool assembly a length equal to the Head clearance value.
Automatic collision checking
Automatic collision checking — When selected, PowerMill collision checks the tool shank and holder during toolpath calculation. The resulting toolpath only contains the non-colliding (safe) sections. This can lead to gaps in the toolpath. When deselected, PowerMill doesn't collision check the tool shank and holder during toolpath calculation.
Collision checking against — Options displayed depend on the strategy you are using. If you selected a Model Area Clearance or Model Rest Area Clearance strategy from the Strategy Selector dialog , you can select to collision-check against the Model and the Stock, or the Model Only. The Model Only option is usually faster to calculate than the Model and Stock option. However, this option does not check for collisions between the tool holder and the stock so take care when running these toolpaths. For all other strategies, this field displays what is being collision checked.
Check against features — Select this option to check for collisions between the tool holder and the feature group.
Check against model — Select this option to check for collisions between the tool holder and the model.
Check against stock — Select this option to check for collisions between the tool holder and the stock. The initial stock used for collision checking depends on the selected strategy.
Output — Select the type of toolpath generated on detecting a collision:
- Safe and unsafe moves —Generates the whole toolpath including the colliding segments.
- Safe split moves — Splits the toolpath into safe and unsafe moves, and only outputs the safe moves.
- Moves in safe holes only — Generates toolpaths only in collision-free holes.
Holder clearance — Enter a specified “safe” area around the tool holder which is taken into account when checking for collisions.
Machine maximum stock — When selected, if a shank or holder collision occurs, the tool tip position is adjusted to avoid the collision whilst removing as much material as possible. When using this option:
- The cutter doesn't need to touch the part, it is as close as possible to the part, and the holder and shank are collision-safe.
- When applied to a constant Z toolpath, the toolpath is moved so it remains a constant Z toolpath.
- When applied to a raster toolpath, the toolpath is moved up Z so the segment remains a typical raster segment.
Keep colliding moves — Select this option to keep colliding sections of the toolpath that are detetcted. Click Home tab > Verification panel > Colliding Sections to display a list of colliding sections for the active toolpath.