Volume Sample Float - Arnold User Guide
 |
The Volume Sample Float shader will sample a volume channel of the new volume API. It should be plugged into one of the components of the Standard Volume shader if you need to further edit the result of the reading of a channel, for instance, to color correct it, etc. For more information on volume workflows, refer to the volume page.
Info: Both the Volume Sample Float and Volume Sample RGB shaders share the same sampling controls, the only difference being the type of output, RGB or float.
These parameters are not texturable due to performance reasons.
- Channel
- Position Offset
- Interpolation
- Volume Type
- Signed Distance Function
- Offset
- Blend
- Invert
- Remap Attributes
- Input Min/Max
- Contrast
- Contrast Pivot
- Bias
- Gain
- Output Min/Max
- Clamp Min/Max
Channel
When not empty, this channel will be used to sample the scattering values for the volume instead of the scattering parameter.
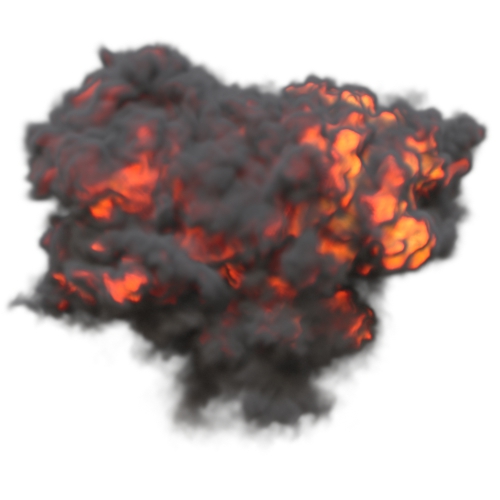
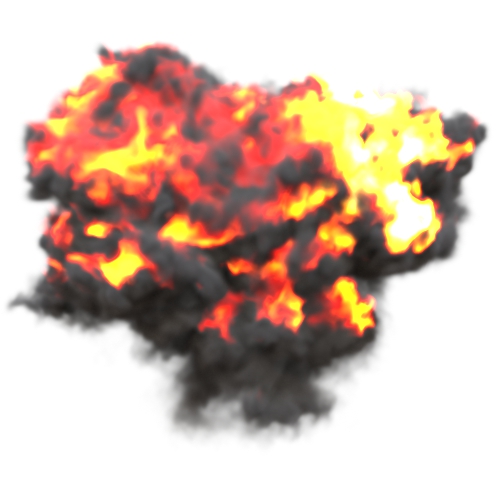
Position Offset
An object space offset to apply to the volume sampling position when using named channels to fetch the volume data. This is useful to displace the volume data.
You will need to connect a noise texture to the position offset to see any result.
 |
 |
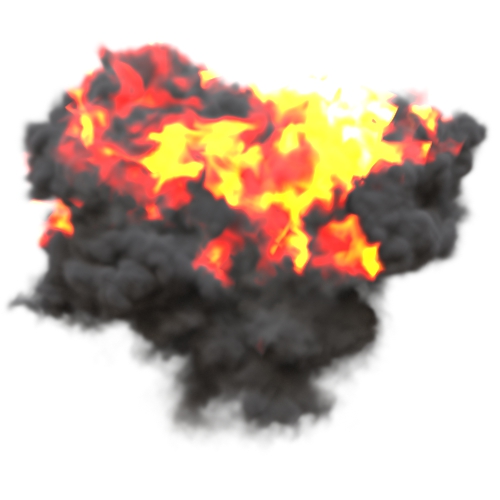 |
| y: 0 | y: -10 | y: -50 |
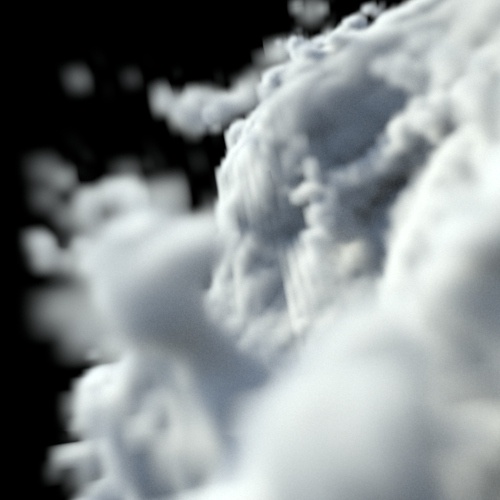
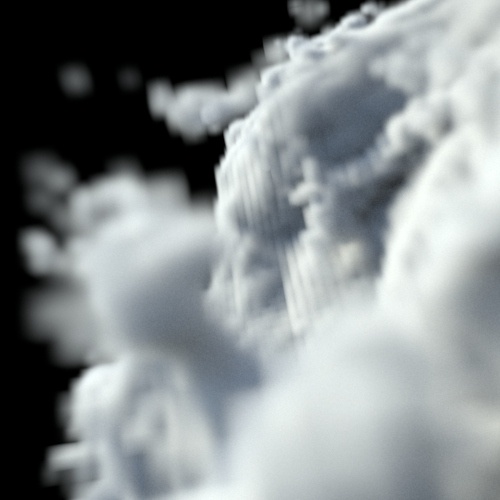
Interpolation
The voxel interpolation to use when sampling the volume data using named channels.
 |
 |
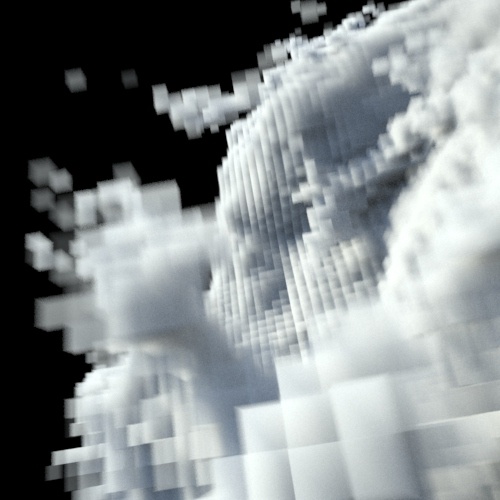 |
| tricubic | trilinear (default) | closest |
Volume Type
Interpret the volume data as fog (density) or SDF (signed distance function). In SDF mode, the inside is converted to a constant density of 1.
Signed Distance Function
Offset
Offset the SDF values by this distance, allowing to dilate or erode the SDF boundary shape.
 |
 |
 |
| Negative offset | Zero offset (default) | Positive offset |
Blend
The distance over which to smooth out the edges of the SDF.
 |
 |
 |
| 0 (default) | Low Blend | High Blend |
Invert
By default, positive distances represent space outside of the boundary while negative distances mean inside. This parameter lets you invert this convention.
Remap Attributes
These are useful parameters to remap the float sampled values to an arbitrary range. The operations are applied in the same order as the parameters.
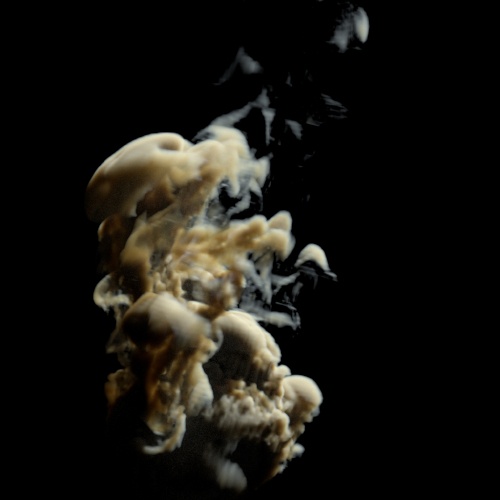
Input Min/Max
The range of input values that will be mapped internally to [0, 1]. The internal values are not clamped.
 |
 |
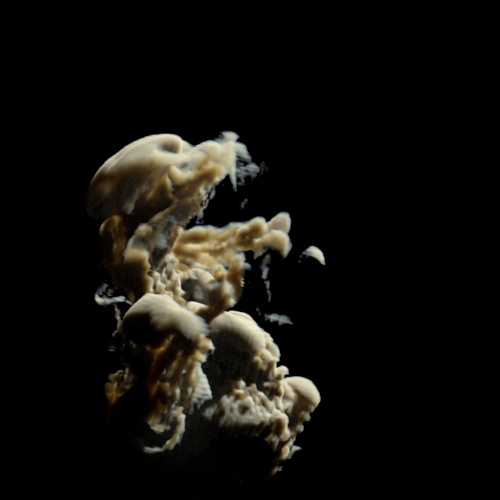 |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.75 |
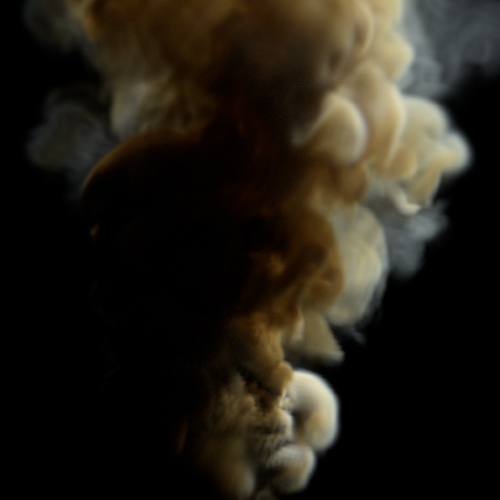
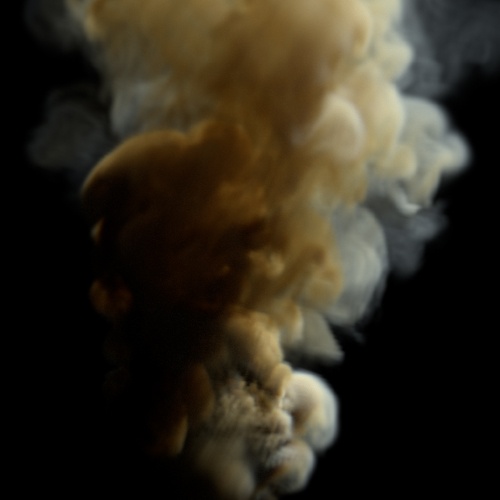
Input Min
 |
 |
 |
| 0.5 | 1 (default) | 1.5 |
Input Max
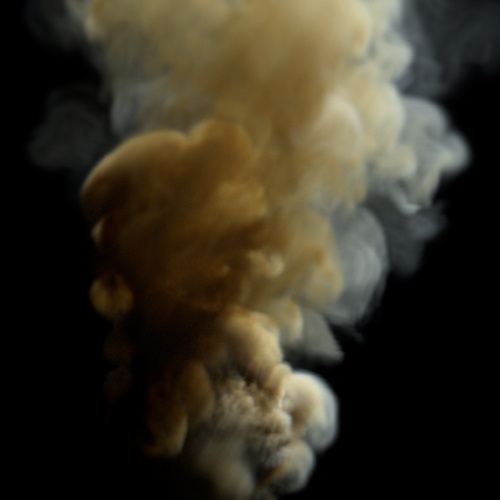
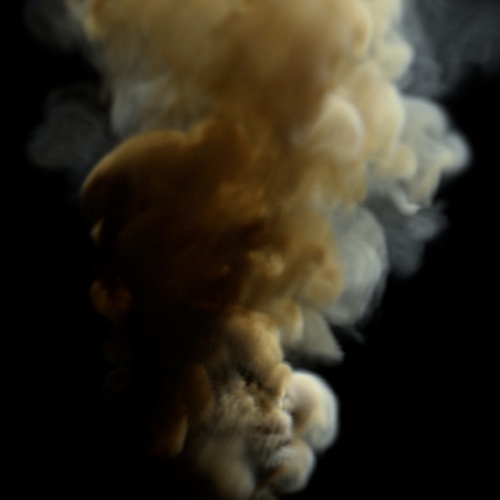
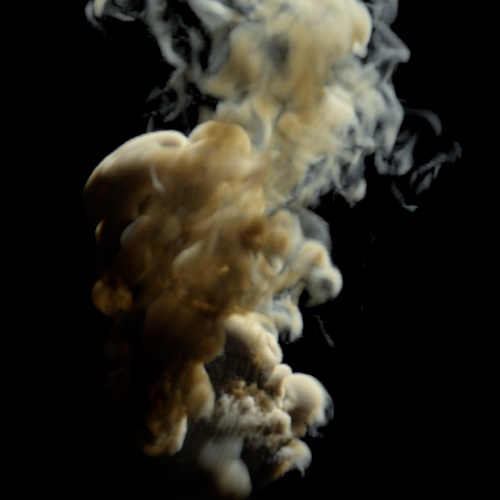
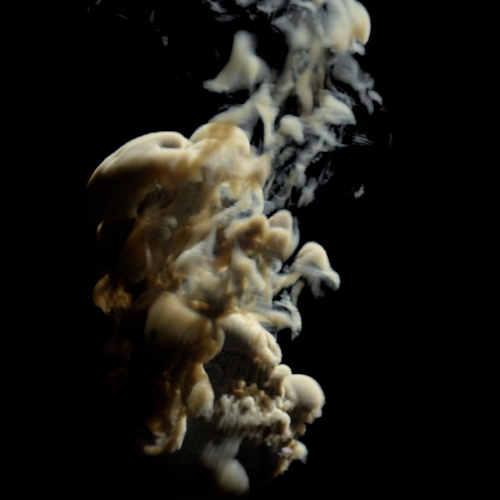
Contrast
Scale values around the Contrast Pivot.
 |
 |
 |
| 0 | 1.5 | 3 |
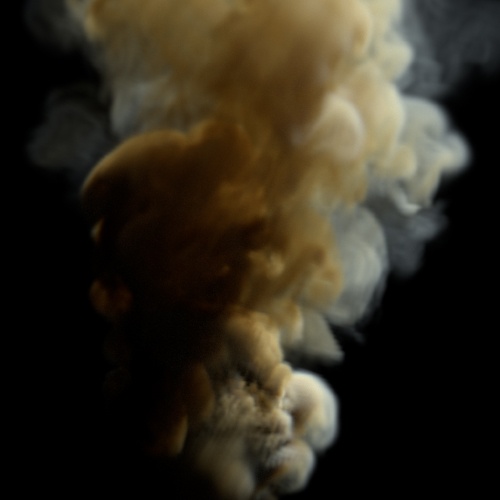
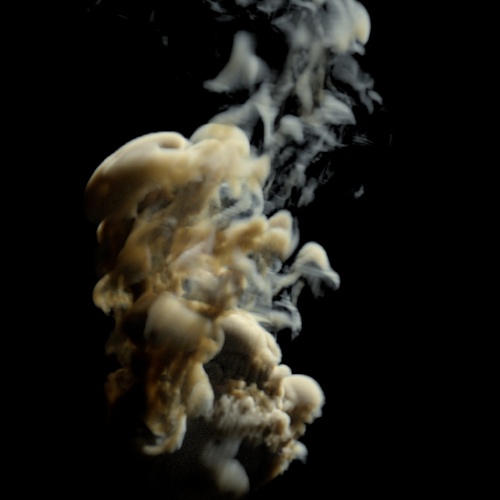
Contrast Pivot
The origin of the contrast scaling.
 |
 |
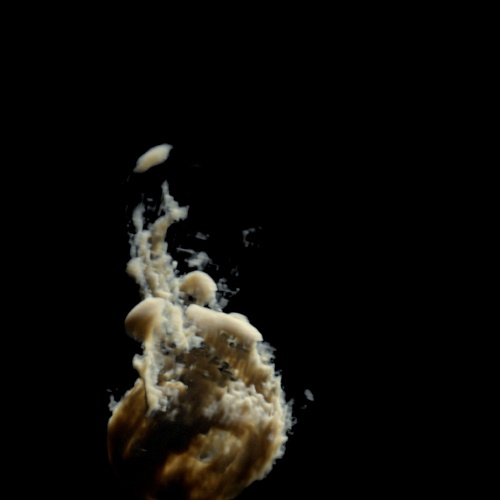 |
| 0.5 (default) | 1 | 5 |
Contrast: 1.5
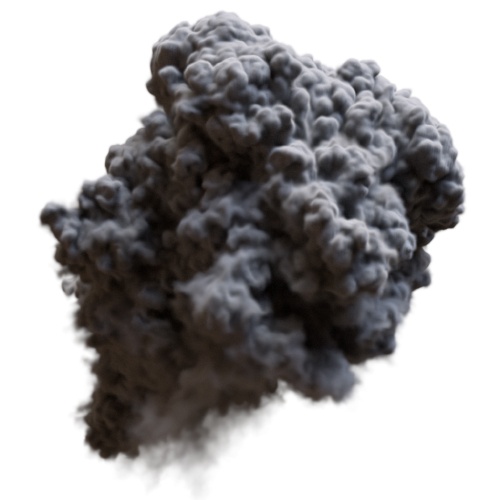
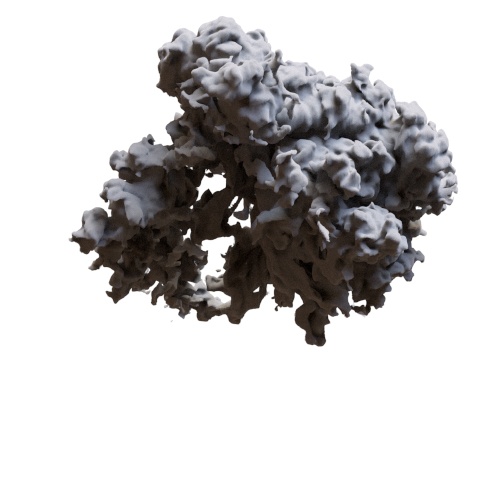
Bias
Push or pull values by altering the slope at the beginning of the range. bias values below 0.5 decreases the slope and lower values overall. Above 0.5, the slope is higher, and the value grows more quickly. A value of 0.5 has no effect.
 |
 |
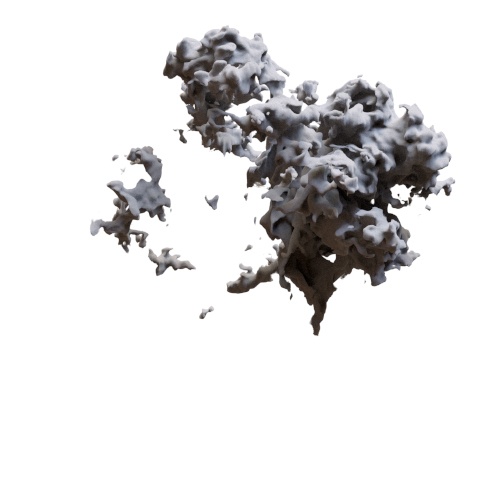 |
| 0.5 (default) | 1.5 | 5 |
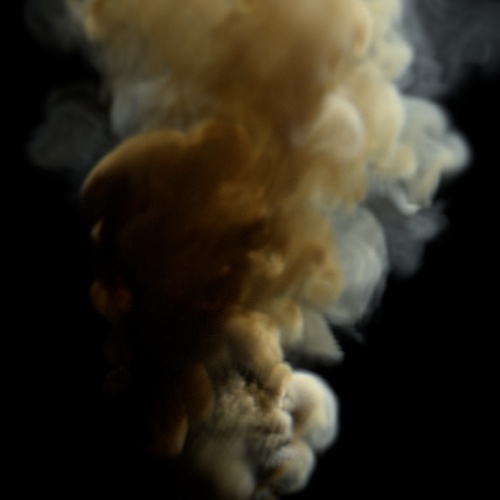
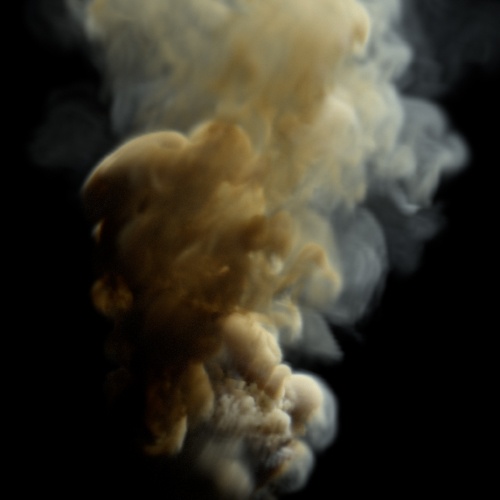
Gain
Increase or decrease the slope of the mid-range values. gain values below 0.5 increase the contrast whereas values above 0.5 flatten the mid-range values. A value of 0.5 has no effect.
 |
 |
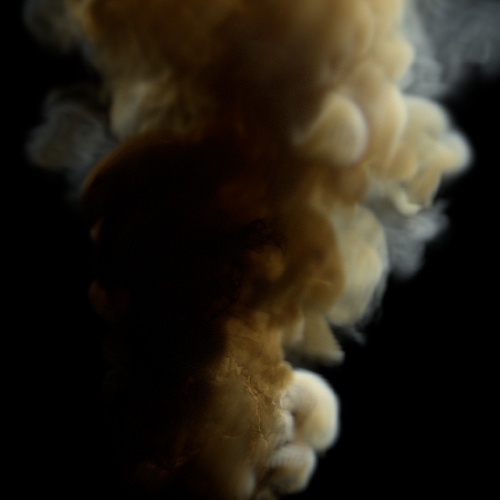 |
| 0 | 0.25 | 0.75 |
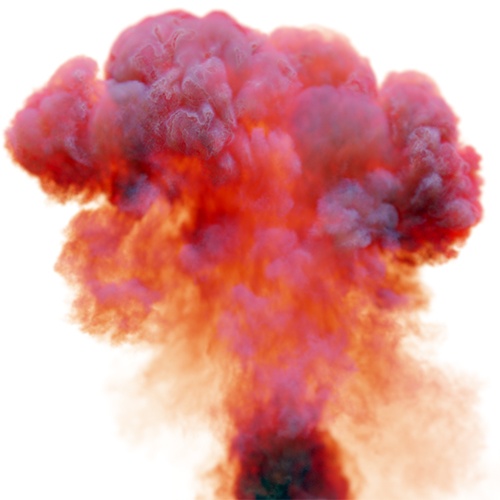
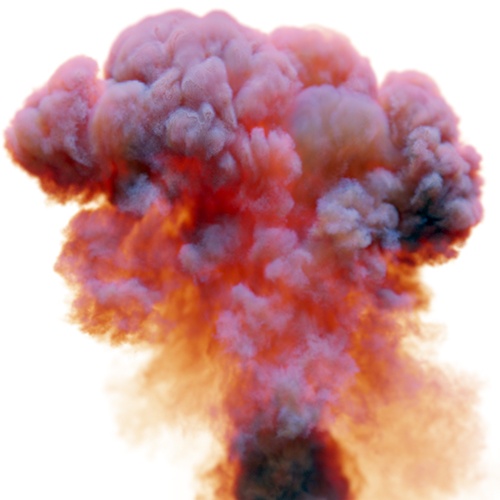
Output Min/Max
The range to remap the internal values to on output. No clamping is done by default, see clamp_min/max.
 |
 |
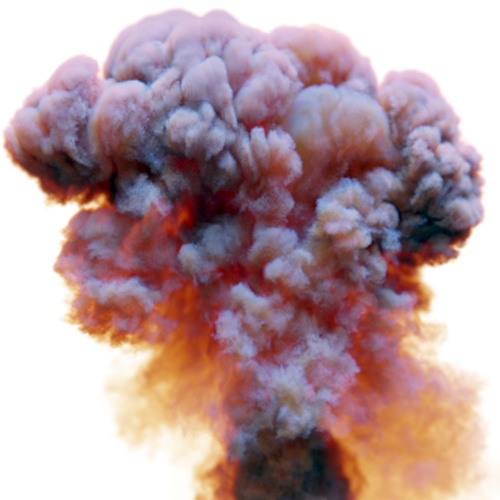 |
| 0.5 | 1 | 2 |
output_min
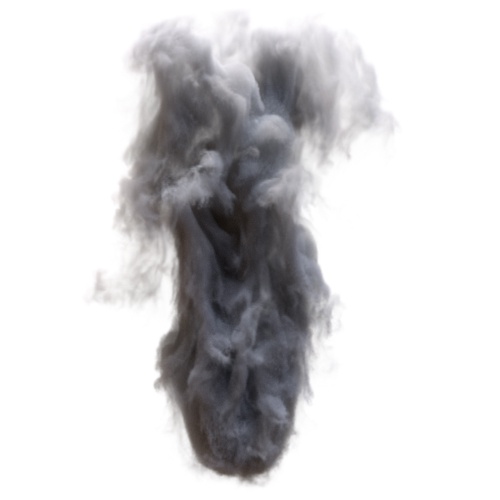 |
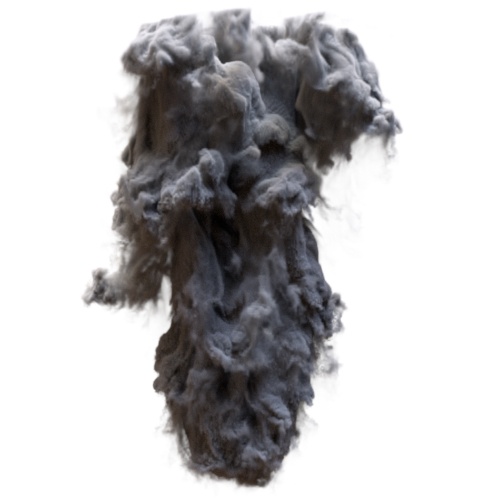 |
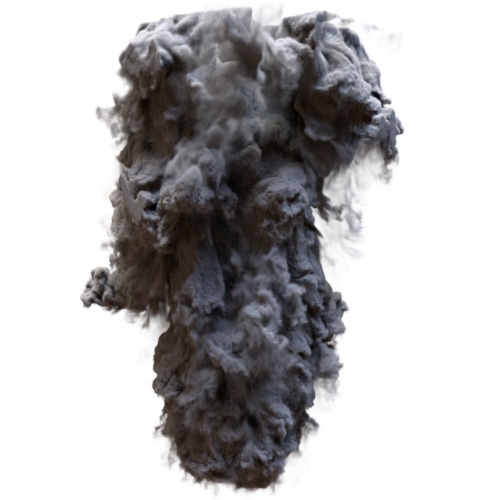 |
| 800 | 8000 | 80000 |
output_max
Clamp Min/Max
When enabled, the output values will be clamped at output_min and/or output_max.
