Relighting: Image-Based Lighting IBL
Image-based lighting (IBL) is the process of illuminating scenes and objects (real or synthetic) using images of light from the real world. This is in contrast to using only direct light sources such as point lights or spotlights, which are more localized. A typical use of IBL is taking high-dynamic photos of a chrome ball placed in the original environment of a live-action shoot, then using the photos as an IBL map to simulate the lighting conditions of the shoot. In Action, you can use the IBL node in Reflection mode or Ambient mode (which more closely simulates a global illumination effect).
IBL maps can affect standard shading objects and physically based shading objects at the same time, depending on each object's rendering mode. In physically based mode, the IBL behaviour is controlled by the individual object material parameters, either from the Shader node, or the corresponding PBS Map. When an object is not physically based shaded, then the Standard Shading section of the IBL menu dictates how it affects the object (Ambient or Reflection mode).

Light Probe Images courtesy of Paul Debevec, www.debevec.org
Tips for working with IBL Maps:
You can colour blend images onto the backplate (the IBL map must be a shot of the environment that the backplate was taken from). This technique is useful for green screen work.
IBL maps can be useful for lighting 3D geometry or text objects from every direction using the colours in the environment.
You can use IBL maps to make surfaces perfectly reflective or perfectly diffuse. You can also make an IBL map act as a virtual spherical background plate.
Action supports angular, cubic, and lat-long (cylindrical) IBL mapping types. You can use the Map Convert tool to convert images to one of these types.
IBL maps work well with PBS shading in Action. One IBL map can be used for both PBS and standard shading in the same scene:
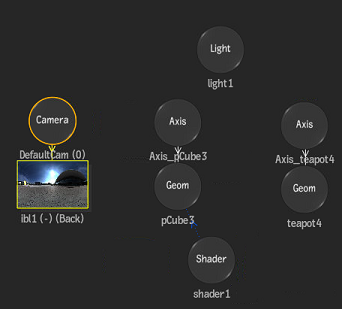
The cube has a Physically Based Shader attached, so its settings override the IBL shading settings. 
The teapot uses the IBL menu's Standard Shading.
