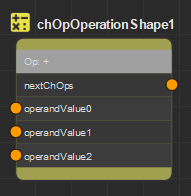
ChOp Operation
The Channel Operator Operation lets you do mathematics operations on
values from previous Channel Operators
(ChOps).
Creation
Configuration
A Channel Operator Operation defines the following specific attributes.
For common attributes see Channel Operator Common Attributes.
Channel Operator Attributes
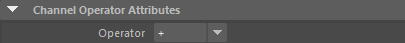
| Operator |
Operator to apply to the previous channel operator value. Note
that the number of previous channel operators that are taken into
account may differs depending on the Operator value.
Available values are:
- + will add all the previous channel operators
values:
previousChOp[0] + previousChOp[1] + previousChOp[2] + ...
- - will subtract all the previous channel operators
values from the first value:
previousChOp[0] - previousChOp[1] - previousChOp[2] - ...
- * will multiply all the previous channel operators
values
previousChOp[0] * previousChOp[1] * previousChOp[2] * ...
- / will divide the first value by all the previous
channel operators values, in the order of inputs indices:
previousChOp[0] / previousChOp[1] / previousChOp[2] / ...
- % will return the modulo value of the first
previous channel operator by the next ones:
previousChOp[0] % previousChOp[1] % previousChOp[2] % ...
- min will return the minimum value of all previous
channel operators. For channel operators that are vector3, the
comparison is done with the norm:
min(previousChOp[0], previousChOp[1], previousChOp[2],
...)
- max will return the maximum value of all previous
channel operators. For channel operators that are vector3, the
comparison is done with the norm:
max(previousChOp[0], previousChOp[1], previousChOp[2],
...)
- clamp will clamp previousChOp[0] between
previousChOp[1] and previousChOp[2] (takes
only 3 values into account)
- abs will return the absolue value of the first
previous channel operator (takes only 1 value into
account)
abs(previousChOp[0])
- sqrt will return the square root value of the first
previous channel operator (takes only 1 value into
account)
sqrt(previousChOp[0])
- pow will return the power of the first previous
channel operator by the second (takes only 2 values into
account)
pow(previousChOp[0], previousChOp[1])
- sin will return the sinus value of the first
previous channel operator (considered as degrees) (takes
only 1 value into account)
sin(previousChOp[0])
- cos will return the cosinus value of the first
previous channel operator (considered as degrees) (takes
only 1 value into account)
cos(previousChOp[0])
- tan will return the tangent value of the first
previous channel operator (considered as degrees) (takes
only 1 value into account)
tan(previousChOp[0])
- asin will return the arcsinus value of the first
previous channel operator (in degrees) (takes only 1 value
into account)
asin(previousChOp[0])
- acos will return the arccosinus value of the first
previous channel operator (in degrees) (takes only 1 value
into account)
acos(previousChOp[0])
- atan will return the arctangent value of the first
previous channel operator (in degrees) (takes only 1 value
into account)
atan(previousChOp[0])
- norm will return the norm (also called magnitude or
length) of the first previous channel operator (takes only 1
value into account). The first previous channel operator
must be a vector.
norm(previousChOp[0])
- dist will return the distance between the first and
the second previous channel operators (takes only 2 values
into account). The first and second previous channel
operators must be vectors.
dist(previousChOp[0], previousChOp[1])
- rand will return a random value between the first
and the second previous channel operators (takes only 2
values into account)
rand(previousChOp[0], previousChOp[1])
- round will return a rounded value of the first
previous channel operator (takes only 1 value into
account)
round(previousChOp[0])
- ceil will return a ceiled value of the first
previous channel operator (takes only 1 value into
account)
ceil(previousChOp[0])
- floor will return a floored value of the first
previous channel operator (takes only 1 value into
account)
floor(previousChOp[0])
- rotateVector will rotate the entry vector (second
previous channel operator) by a given euler angle (in °) (first previous
channel operator) (takes only 2 values into
account). The first and second previous channel operators
must be vectors.
- rotateEuler will rotate the entry euler angle (in
°) (second previous channel operator) by a given euler angle (in °)
(first previous channel operator) (takes only 2 values into
account). The first and second previous channel operators
must be vectors.
- dot will return the dot product (floating value)
between the first and the second previous channel operators
(takes only 2 values into account). The first
and second previous channel operators must be vectors.
- cross will return the cross product (vector value)
between the first and the second previous channel operators
(takes only 2 values into account). The first
and second previous channel operators must be vectors.
|