Using Model Property Filters in Takeoff
Use model property filters in the Model Browser in Takeoff to include only the elements relevant to your current work.
Applying Basic Filters
A few basic filters are shown by default. Click Show more to view all basic filters, which include:
- Levels
- Categories
- Disciplines
- Rooms
- Assembly
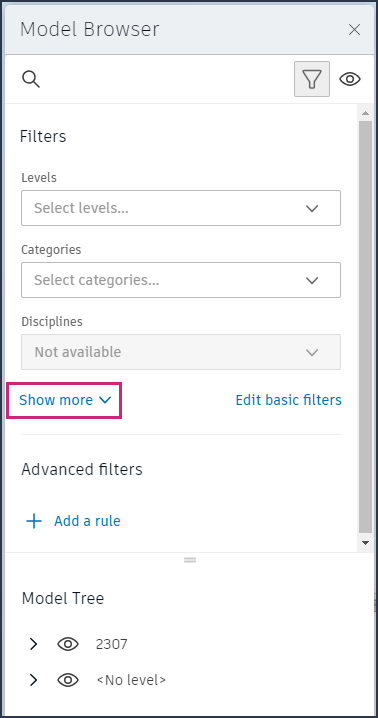
The basic filters available depend on the file types that you have open and the properties that were defined in the model. Some filters will only apply to certain models.
To apply basic filters
Select filters and choose the elements you want to include in the view.
Tip:Select the Empty or undefined filter option to include all model elements that don't apply to the selected filters, or that have no value defined for the property.
To edit basic filters
If the default basic filters don't meet your needs, click Edit basic filters in the Model Browser. This will open the Add and reorder filters dialog where you can add, reorder, and remove filters, as well as create custom filters based on model properties.
In the Add and reorder filters dialog, use the search field to search for the required model property.
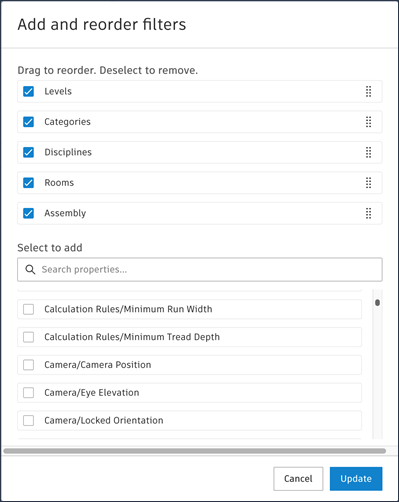
Select the property to add it to the list of filters at the top of the dialog box.
Drag the selected filters to control the order in which they appear in the Model Browser. You can also deselect the default filters so they no longer appear.
Click Update to save your selection to the Model Browser.
By default, only three filters are displayed on the Model Browser. Click Show more to expand the filter list.
Creating and Applying Advanced Filters
You can create custom rule-based filters where each consists of a property and an operator.
Property: Choose from the properties in your models. Supported types currently include text, numbers, and boolean properties.
Operator: The operators you can choose will depend on the selected property's type.
Property Operator Description Text Is / is not Is is used to match a property to a specific value and is not where it doesn't match. Select values from the Value drop-down list. Selecting multiple values will filter for objects that meet any one of those values. Contains / does not contain
The entered value is checked against the parameter value Starts with:
Determines whether a property starts with a specific text string. This operator is useful for filtering large sets of data where members want to focus on a specific subset of records Is empty / is not empty: Check whether a property has a value or not. The is empty operator returns true if the property doesn't have a value, and the is not empty operator returns true if the property has a value. Sometimes, "space values" (for example, blank or null values) are considered values for these operators, so they would still be considered not empty. Numeric Equals / not equals (= or ≠) Compare two values and determine if they are the same (equals) or different (not equals). Greater than / less than (< or >) Compare two values and determine if the first value is larger (greater than) or smaller (less than) than the second value. Greater than or equal to / less than or equal to (≤ or ≥) Determine if the first value is larger than or equal to (greater than or equal to) or smaller than or equal to (less than or equal to) the second value. Is empty / is not empty Check whether a property has a value or not. Is empty returns true if the property does not have a value, and is not empty returns true if the property has a value. Sometimes, "space values" (for example, blank or null values) are considered values for these operators, so they would still be considered not empty. Boolean Is true
The Is true boolean filter operator is used to retrieve objects that have a true value in a boolean field. When this filter is applied, only records where the boolean field is set to true will be included. Is false
The Is false boolean filter operator is used to retrieve objects that have a false value in a boolean field. When this filter is applied, only records where the boolean field is set to false will be included. Is null The Is null boolean filter operator is used to retrieve objects where a particular field does not have any value or is empty (null). This filter is helpful when you want to find objects that lack a value in a specific field. Value: The value field is the part of the rule that specifies the criteria or parameter against which the filter will be applied. This field can contain various types of values, depending on the specific property being filtered. For numeric values, use the same units as the selected property units. Only 256 characters are allowed for fields without drop-down values.
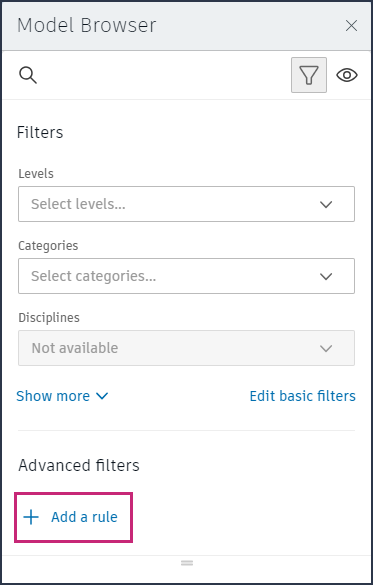
To create an advanced filter
Click Add a rule under Advanced filters.
Create your first rule part defining a property, operator, and value.
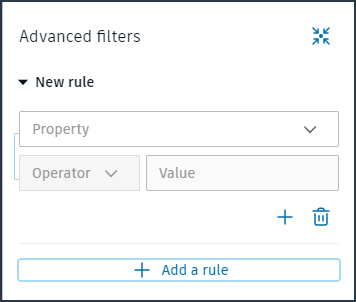
You can extend the first rule part by clicking + and adding another rule part as required. Two or more rule parts added together create a filter rule.
Add more rule parts as required to the filter rule by clicking +.
Multiple filter rules can be built and joined by a logical operator (and/or). The logical operator will determine whether a model object must pass all rule part conditions or one set of filter conditions to be displayed.
Click Add a rule to join your filter rule to another.
Choose between and/or. This selection will be applied to all filter rules in this view.
Once a logical operator is selected between the first and second filter rule, the same operator will be applied by default to subsequent filter rules. Keep this in mind as you build out your filter rules.
Note: You can create a maximum of 100 rule parts and filter rules for a single view.
Removing Filters
To clear all filters, click the X icon beside the Filters or funnel icon at the top of the Model Browser, or use the reset option in the viewer.
Delete any rule from the advanced filters by using the trash icon. If it is the only rule part in the filter rule, the rule part and its filter rule will both be removed.
