Description
The MAT12 entry defines the material properties for an orthotropic material for solid elements.
Format
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| MAT12 | MID | E1 | E2 | E3 | NU12 | NU23 | NU31 | RHO | |
| G12 | G23 | G31 | A1 | A2 | A3 | TREF | GE |
Example
| MAT12 | 105 | 2.+7 | 2.+7 | 1.+4 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.066 | |
| 4.5+5 | 2.5+5 | 2.5+5 | 1.1-6 | 1.1-6 | 0.0 | 70.0 |
| Field | Definition | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| MID | Material identification number. Referenced on a PSHELL or PCOMP entry only. | Integer > 0 | Required |
| E1 | Modulus of elasticity in longitudinal direction, also defined as the fiber direction or 1-direction. | Real > 0.0 | Required |
| E2 | Modulus of elasticity in lateral direction, also defined as the matrix direction or 2-direction. | Real > 0.0 | Required |
| E3 | Modulus of elasticity in thickness direction, also defined as the matrix direction or 3-direction. | Real > 0.0 | Required |
| NU12 | Poisson's ratio (-ε2/ε1 for uniaxial loading in 1-direction). Note that
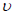 21 = -ε2/ε1 for uniaxial loading in 2-direction is related to 21 = -ε2/ε1 for uniaxial loading in 2-direction is related to
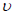 12, E1, and E2 by the relation 12, E1, and E2 by the relation
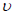 12 E2 = 12 E2 =
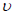 21 E1. See Remark 3. 21 E1. See Remark 3.
|
Real | Required |
| NU23 | (-ε3/ε2 for uniaxial loading in 2-direction). Note that
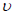 32 = -ε3/ε2 for uniaxial loading in 3-direction is related to 32 = -ε3/ε2 for uniaxial loading in 3-direction is related to
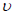 23, E2, and E3 by the relation 23, E2, and E3 by the relation
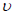 23 E3 = 23 E3 =
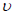 32 E2. See Remark 3. 32 E2. See Remark 3.
|
Real | Required |
| NU31 | (-ε1/ε3 for uniaxial loading in 3-direction). Note that
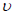 13 = ε3/ε1 for uniaxial loading in 1-direction is related to 13 = ε3/ε1 for uniaxial loading in 1-direction is related to
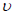 31, E1, and E3 by the relation 31, E1, and E3 by the relation
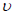 31 E1 = 31 E1 =
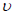 13 E3. See Remark 3. 13 E3. See Remark 3.
|
Real | Required |
| RHO | Mass density. | Real or blank | 0.0 |
| G12 | Shear modulus in plane 1-2. | Real > 0.0 | Required |
| G23 | Shear modulus in plane 2-3. | Real > 0.0 | Required |
| G31 | Shear modulus in plane 3-1. | Real > 0.0 | Required |
| Ai | Thermal expansion coefficient in i-direction. | Real or blank | 0.0 |
| TREF | Reference temperature for the calculation of thermal loads. | Real or blank | 0.0 |
| GE | Structural element damping coefficient. See Remarks 9, 10, and 12. | Real or blank | 0.0 |
Remarks
- The material identification number must be unique for all MATi entries.
- An approximate value for G23 and G31 is the in-plane shear modulus G12. If test data is not available to accurately determine G23 and G31, the value to G12 may be supplied for G23 and G31.
- Material stability requires that
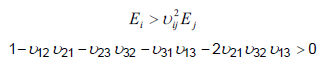
If either condition is not met a warning message will be issued.
- It may be difficult to find all nine orthotropic constants. In some practical problems, the material properties may be reduced to normal anisotropy in which the material is isotropic in a plane (that is, plane 1-2) and has different properties in the direction normal to this plane. In the plane of isotropy, the properties are reduced as follows:
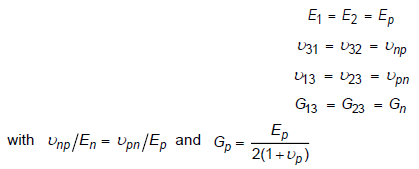
There are five independent material constants for normal anisotropy (that is, Ep, En,
 p,
p,
 np, and
Gn). In case the material has a planar anisotropy, in which the material is orthotropic only in a plane, the elastic constants are reduced to seven(E1,
E2, E3,
np, and
Gn). In case the material has a planar anisotropy, in which the material is orthotropic only in a plane, the elastic constants are reduced to seven(E1,
E2, E3,
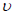 12,
G12,
G23, and
G31).
12,
G12,
G23, and
G31).
- The mass density, RHO, will be used to automatically compute mass for all structural elements.
- Weight density may be used in field 9 if the value 1/g is entered on the PARAM, WTMASS entry, where g is the acceleration of gravity.
- To obtain the damping coefficient GE, multiply the critical damping ratio C/C0, by 2.0.
- TREF and GE are ignored if the MAT12 entry is referenced by a PCOMP entry.
- TREF is used only as the reference temperature for the calculation of thermal loads in linear solutions. If TEMPERATURE(INITIAL) is specified, TREF will be ignored.
