X-Ray
The X-Ray material was created as a material for hands in a VR environment, in particular, for Oculus users. However, use it whenever you want to assign a transparent or semi-transparent material to an object, like for a technical illustration.
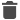
If an X-Ray material is in a layered material, the effect is not visible in OpenGL mode. It is visible, however, in Raytracing mode. In the images below, the first is an example in OpenGL mode. The second is in Raytracing mode.
In the Menu Bar, select Scene > Material Editor, then in the editor, select Create/Convert > Create Material > X-Ray.
X-Ray Material
Base Color - Defines the base color of the material. Click the color field on the right to access the Color Picker dialog and select a color.
Single-sided - Toggles the visibility of backfaces. By default, this attribute is enabled, so only one side of the object is rendered. When enabled, it is important for normals to be correctly oriented. Single-sided can also be switched off in the Material options.
Cast Shadows - Casts a shadow, when enabled. In OpenGL, the shadow is based on non-transparent object forms. In Raytracing, transparency is considered.
Fresnel Transparency
The three Fresnel Transparency attributes help define the transparency of the object. When Bias is increased, the surface of your object becomes opaquer. When Scale is increased, the edges of your object become opaquer, as it takes into account the normal falloff. When Power is increased, it defines the intensity of the outline created with Scale.
Fresnel Color
The Color attribute defines the color of opaque surfaces and outlines. It is added on top of any base color that was set separately. Use it to change the color or brighten the outline. The other Fresnel Color attributes are the same as the Fresnel Transparency attributes, since they customize the falloff, based on surface normals and viewing direction. They will influence the strength of the hue, applying more or less color to opaque surfaces and outlines.
Transparency
This is based on the viewing angle. The surface is rendered ore opaquely when viewed from a gazing view. The surface is rendered more transparent, when it is facing the view.
See Through - Renders the shader transparent.
Use Texture - Click the box to enable Use Texture and expose options for modifying the texture. Set how the texture will be mapped and the type of mapping it will use, whether to use the original texture size or not, how often the texture repeats and/or if it offset, whether it's rotated, and is there any anisotropy.
- Click
 to open the directory to locate a different texture or correct the location.
to open the directory to locate a different texture or correct the location. - Click
 to save the texture to a different location.
to save the texture to a different location. - Click the folder icon and select the texture you want; if at any point the texture is updated, click
 Reload to load the latest version.
Reload to load the latest version. - Click
 to delete the texture.
to delete the texture.
- Click
Use Image Sequence - Select when an image sequence is loaded in the Use Texture box. This uses an image sequence as a texture. The image name for the sequence will be generated based on the filename and the image number. Use the Curve Editor to animate the image number. Go to Animation > Timeline. Click play to view the animated image sequence on the material.
Note:For a group of images to be considered an image sequence, there must be at least two images with the same name with an increasing numeric value. The required naming format is name, number, and extension. For example, image000.png image01.png.
Invert Texture - Inverts the transparency, making opaque areas transparent and vice versa.
Mapping Type - Available only when Use Texture is enabled. Sets the mapping type of the texture. There are three modes which can be selected:
- UV - For radial and planar brush mapping. UV mapping is always used for Incandescence, Transparency, and Displacement textures.
- Planar - For decals. The first two values define the orientation of the plane in 3D, the third value defines the rotation in 2D around the plane normal.
- Triplanar - For triplanar brush mapping orientation. Use to apply textures to a geometry with no UVs. There is a blend zone where the projections overlap on the surface. If this does not give the desired result, actual UV coordinates need to be created, and UV must be used as the Mapping type for the texture in the material.
Repeat Mode UV - Available only when Use Texture is enabled. Sets how the texture is repeated. There are four modes:
- Repeat - Repeats the texture in all directions.
- Mirror - Repeats and mirrors the texture on the x- and y- axis with every repetition.
- Decal - The texture is not repeated.
- Clamp - Repeats only the last pixel of the texture
Texture Size - Defines the textures size along the X and Y-axis. Enter the width and height of the texture in millimeters. Only available with the mapping type - UV and Use Texture Size selected or with the mapping type - Triplanar.
Edge Blend - Sets the range for overlapping areas of the planar projection.
Uniform Repeat - Synchronizes the repetition value for all projection axes. If selected, the repeat factors of the x, y, and z axes of the triplanar texture projection are linked.
X Repeat UV - Sets the UV repeat factors for the x-axis of the triplanar texture projection.
X Offset UV - Sets the UV offset for the x-axis of the triplanar texture projection.
X Rotate - Sets the rotation value for the x-axis texture coordinates of the triplanar texture projection.
Y Repeat UV - Sets the UV repeat factors for the y-axis of the triplanar texture projection.
Y Offset UV - Sets the UV offset for the y-axis of the triplanar texture projection.
Y Rotate - Sets the rotation value for the y-axis texture coordinates of the triplanar texture projection.
Z Repeat UV - Sets the UV repeat factors for the z-axis of the triplanar texture projection.
Z Offset UV - Sets the UV offset for the z-axis of the triplanar texture projection.
Z Rotate - Sets the rotation value for the z-axis texture coordinates of the triplanar texture projection.
Manipulate - Displays the manipulator for manually changing the rotation, offset, or repeat of the texture.
Anisotropy - Sets the texture filter quality for the image texture in raytracing. Use the following as a guide:
- A value of 0.0 switches the filtering to normal bilinear filtering without mipmapping.
- A value of 1.0 uses normal trilinear filtering with mipmapping.
- Values between 1.0 and 16.0 will use anisotropic filtering.
- A value of 16.0 is the maximum and provides the highest filtering quality.
Use Infinite Tiling - Removes repetition artifacts from tiled, seamless textures.
Raytracing
Set the Material ID and Line Tube Radius when raytracing the texture.
- Material ID - Sets the ID of the material.
- Line Tube Radius - Sets the radius of tubes used to render lines in raytracing (given in object space).
For information regarding Rounded Edges, see Rounded Edges.
Common
- Occlusion Color - Sets the color of the pre-calculated ambient occlusion or environment shadows.
- Occlusion Intensity - Sets the shader’s pre-calculated ambient occlusion intensity for shadow areas.
- Sort Key - Only supported in OpenGL mode. Changes the order in which transparent materials are rendered in OpenGL. Transparent surfaces with the same sort key are sorted back to front.
- Environment - Use the context menu to set the HDR image used for reflections on this material. The HDR image of the assigned environment is used for diffuse, glossy, and specular reflections on this material in OpenGL rendering. Different materials can have different environments assigned to get different lighting effects. In Raytracing, the handling of the environment depends on the active illumination mode.