Rigid Triangular Plate
Description: Defines a rigid triangular plate.
Format:
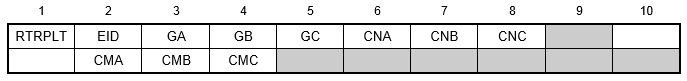
Example:

| Field | Definition | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| EID | Element identification number. | Integer > 0 | Required |
| GA, GB | Grid point identification number of connection points. | Integer > 0 | Required |
| CNA, CNB, CNC | Independent degrees of freedom in the global coordinate system for the element at grid points GA, GB, and GC. (Up to six unique digits may be placed in the field with no embedded blanks.) | 1 ≤ Integers ≤ 6 or blank | See Remark 1 |
| CMA, CMB, CMC | Component numbers of dependent degrees of freedom in the global coordinate system assigned by the element at grid points GA and GB. (Up to six unique digits may be placed in the field with no embedded blanks.) | 1 ≤ Integers ≤ 6 or blank |
Remarks:
- The total number of components in CNA, CNB, and CNC must equal six; for example, CNA = 1235, CNB = 3, and CNC = 3. Furthermore, they must jointly be capable of representing any general rigid body motion of the element.
- If CMA, CMB, and CMC are all zero blank or if the continuation entry is omitted, all of the degrees of freedom not in CNA, CNB, or CNC will be made dependent.
- A dependent degree of freedom assigned by one element cannot be assigned dependent by another rigid element or MPC entry and cannot be additionally constrained (e.g., single-point constraint).
- Rigid elements, unlike MPCs, are not selected through the Case Control Section.
- Forces of multipoint constraint may be recovered with the MPCFORCES Case Control command.
